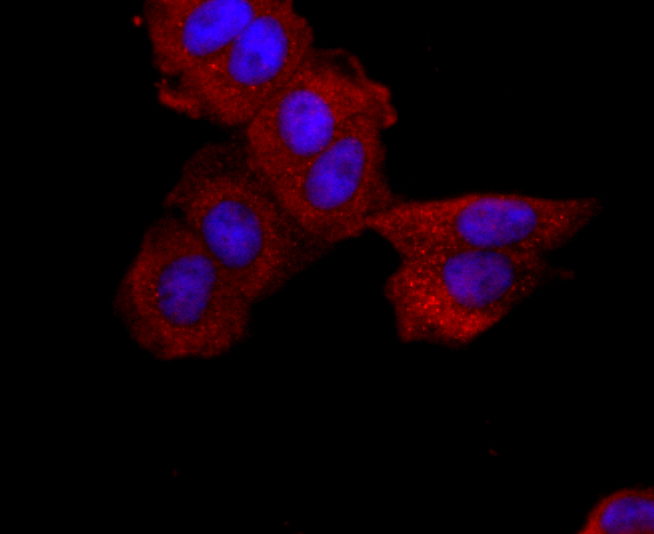
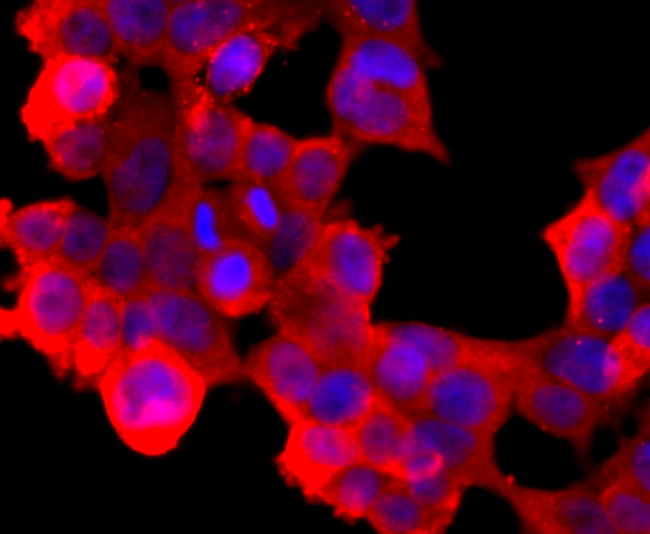
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are an evolutionarily conserved family of proteins that catalyze the transport of molecules across extracellular and intracellular membranes through the energy of ATP hydrolysis. The ABC half-transporter, ABCG2, is also known as placenta-specific ABC transporter and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP1). ABCG2 confers resistance for a variety of chemotherapeutic agents, including anthracyclines, mitoxantrone, bisantrene and topotecan. Under normal conditions, ABCG2 may serve a protective function by removing toxins from the cell, and plays an important role in regulating stem cell differentiation. ABCG2 is responsible for the side population (SP) phenotype and is widely expressed in a large variety of stem cells, making it an important stem cell marker. ABCG2 may have N-linked glycosylation and may dimerize in vivo. ABCG2 is abundantly expressed in placenta, liver, intestine and stem cells.