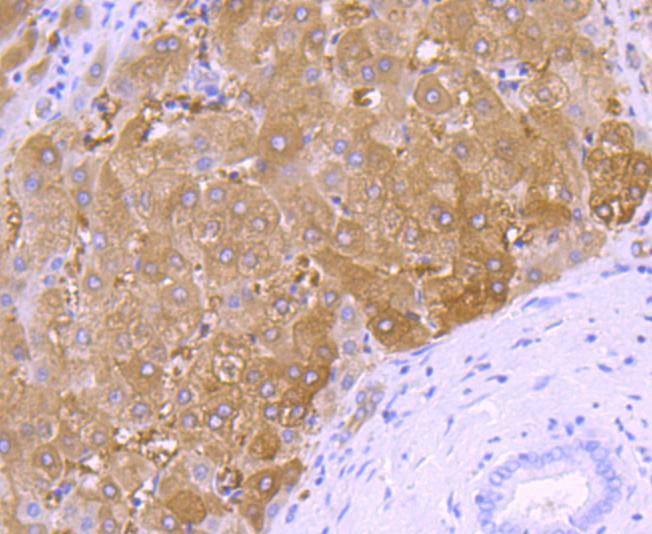
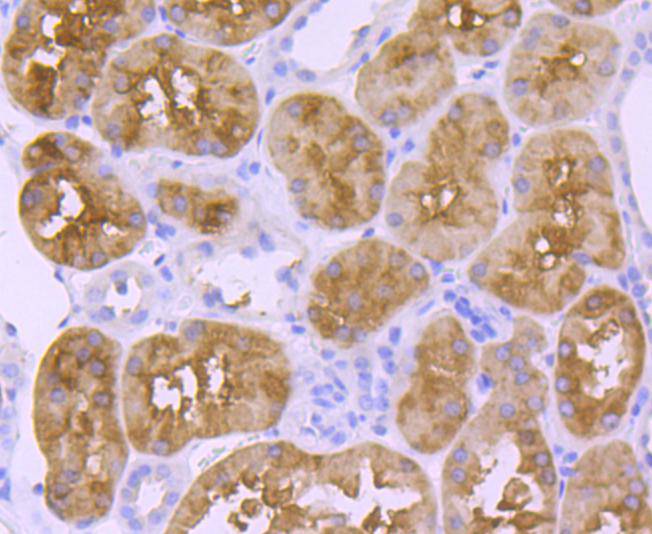
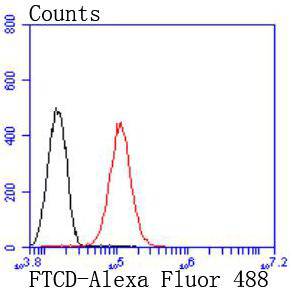
58K protein antibodies are excellent for use as markers for the Golgi complex. The 58K protein has been identified as being FTCD, a bifunctional enzyme that channels 1-carbon units from formiminoglutamate, a metabolite of the histidine degradation pathway, to the folate pool. Defects in FTCD are the cause of glutamate formiminotransferase deficiency [also known as formiminoglutamicaciduria (FIGLU-uria)], an autosomal recessive disorder. Features of a severe phenotype include elevated levels of formiminoglutamate (FIGLU) in the urine in response to histidine administration, megaloblastic anemia and mental retardation. Features of a mild phenotype include high urinary excretion of FIGLU in the absence of histidine administration, mild developmental delay and no hematological abnormalities.