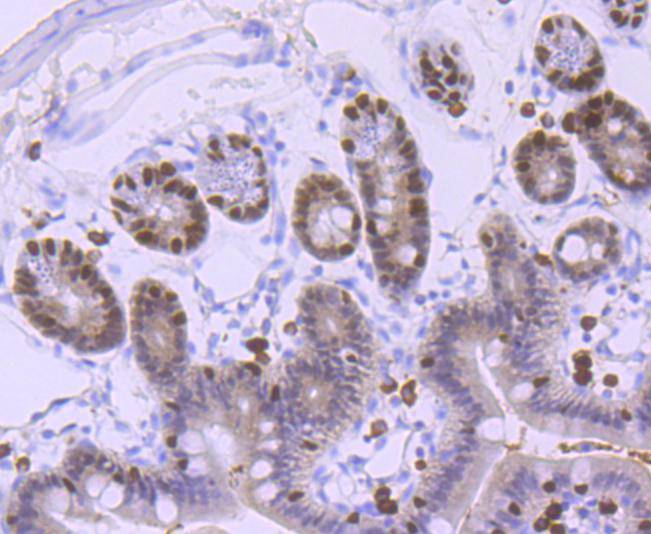
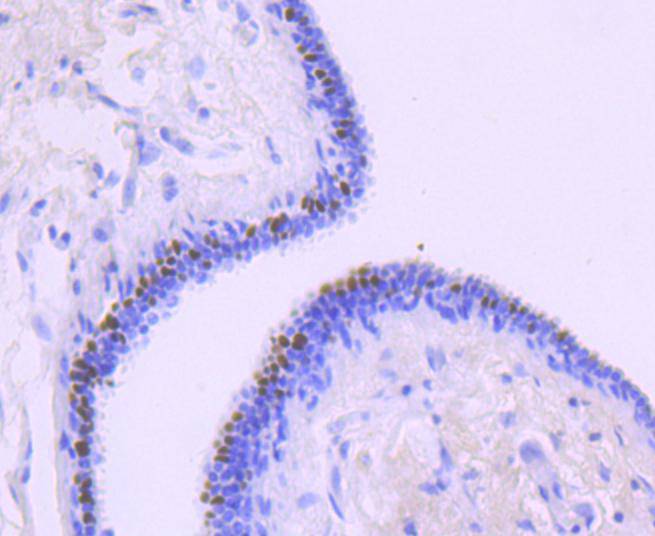
HNF-1 (α and β), HNF-3 (α, β and γ), HNF-4 (α and γ), and HNF-6 compose, in part, a homoeprotein family designated the hepatocyte nuclear factor family. The various HNF-1 isoforms regulate transcription of genes in the liver as well as in other tissues such as kidney, small intestine and thymus. HNF-3α, HNF-3β and HNF-3γ regulate the transcription of numerous hepatocyte genes in adult liver. HNF-3α and HNF-3β have also been shown to be involved in gastrulation events such as body axis formation. HNF-4α and HNF-4γ have been shown to be important for early embryo development. HNF-4α is expressed in liver, kidney, pancreas, small intestine, testis and colon; HNF-4γ is expressed in each of these tissues except liver. HNF-6 has been shown to bind to the promoter of HNF-3β, which indicates a potential role of HNF-6 in gut endoderm epithelial cell differentiation. Evidence suggests that HNF-6 may also be a transriptional activator for at least 22 other hepatocyte-enriched genes, including cytochrome P450 2C13 and α-1 antitrypsin.