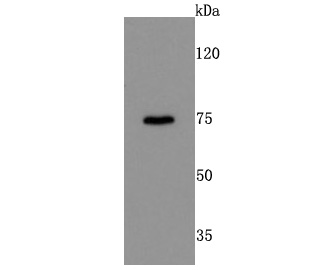
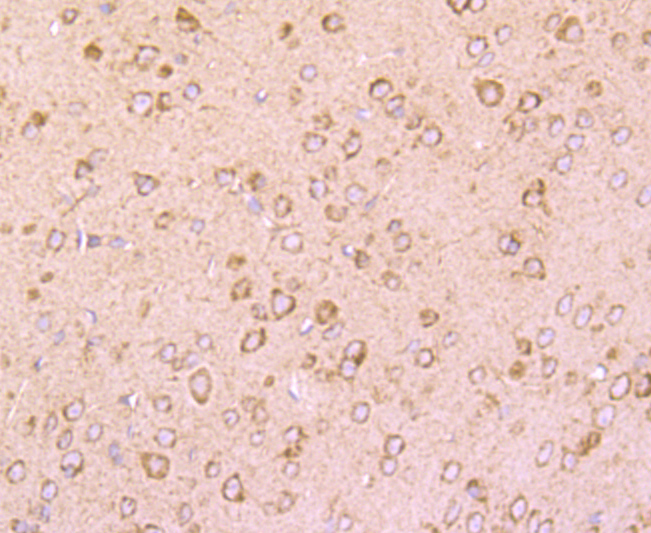
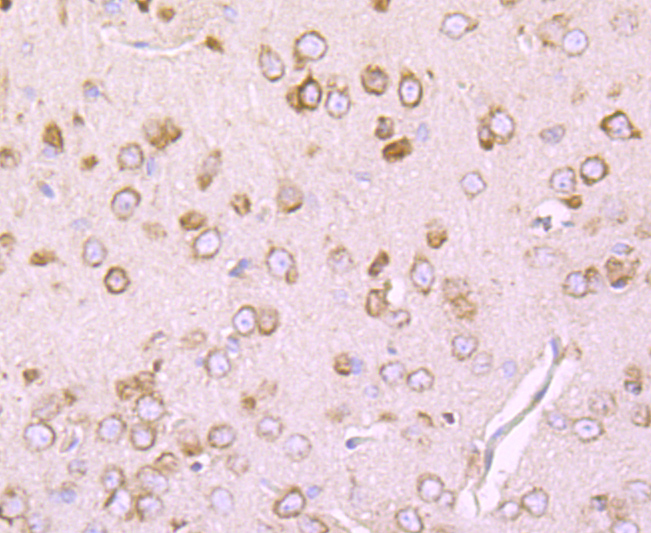
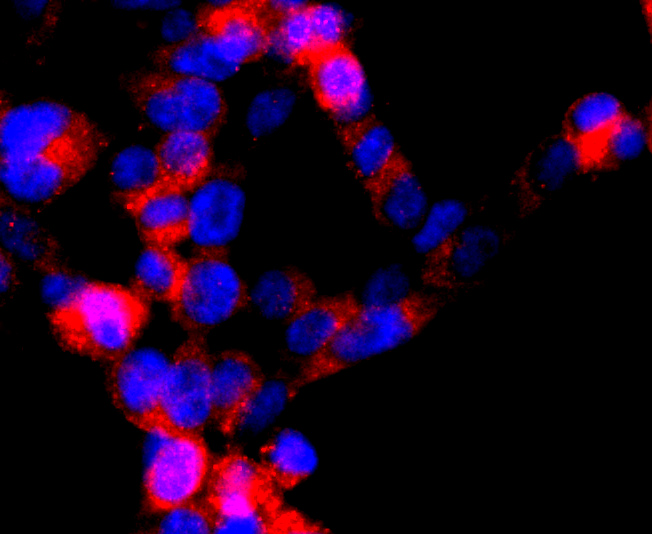
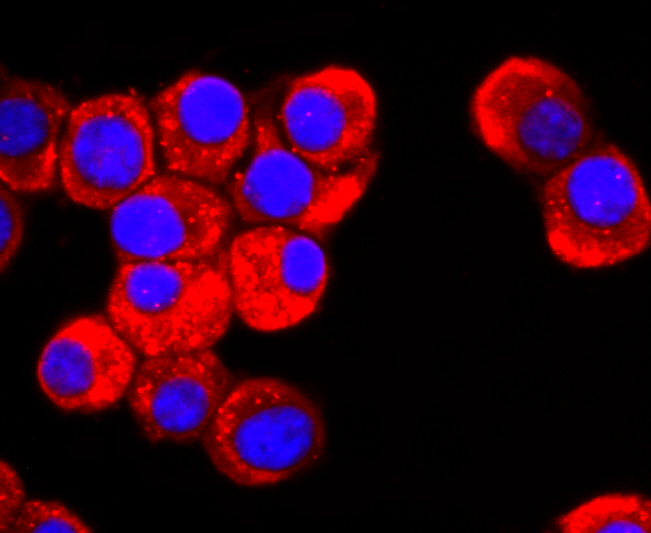
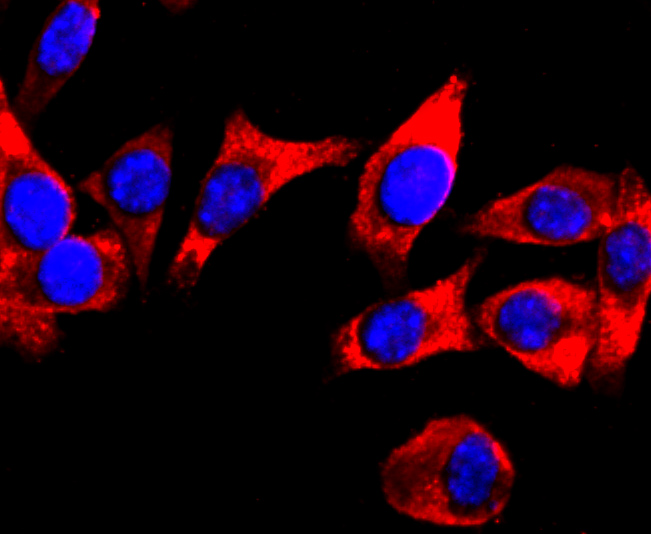
The members of the G protein coupled receptor family are distinguished by their slow transmitting response to ligand binding. These transmembrane proteins include the adrenergic, serotonin and dopamine receptors. The effect of the signaling molecule can be excitatory or inhibitory depending on the type of receptor to which it binds. β-adrenergic receptor binds to adrenaline activates adenylyl cyclase, while α2-adrenergic receptor binds to adrenaline inhibits adenylyl cyclase. The dopamine receptors are divided into two classes, D1 and D2, which differ in their functional characteristics in that D1 receptors stimulate adenylyl cyclase while D2 receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase activity. Five different subtypes of dopamine receptor have been described to date. D1DR and D5DR belong to the D1 subclass, while D2DR, D3DR and D4DR belong to the D2 subclass.