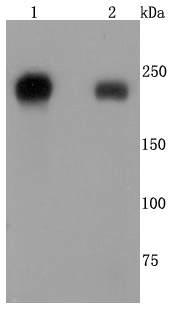
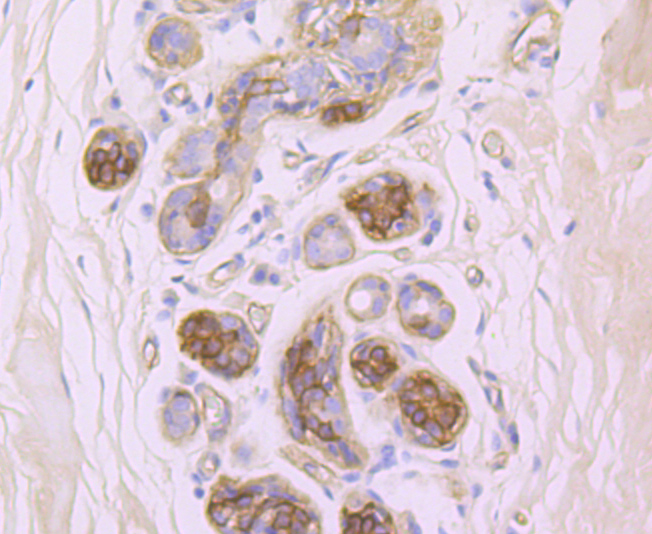
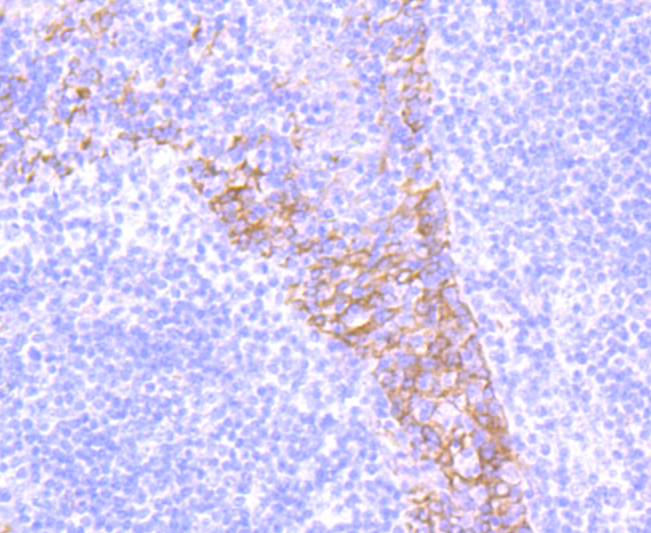
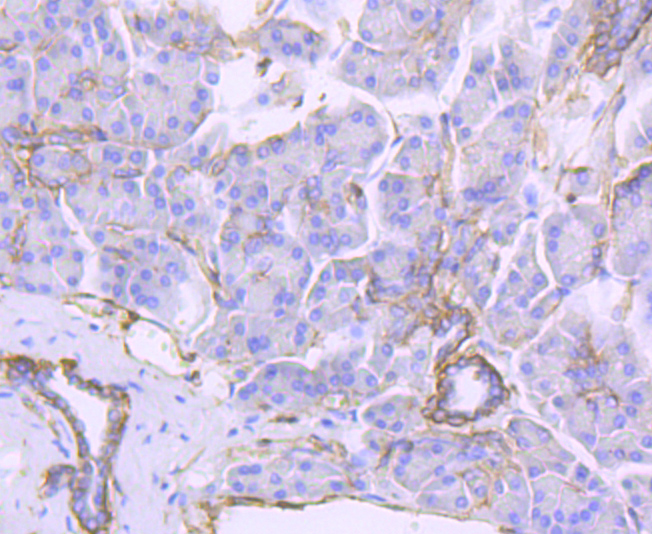
Integrins are heterodimers composed of noncovalently associated transmembrane a and b subunits. The 16 a and 8 b subunits heterodimerize to produce more than 20 different receptors. Most integrin receptors bind ligands that are components of the extracellular matrix, including Fibronectin, collagen and vitronectin. Certain integrins can also bind to soluble ligands, such as fibrinogen, or to counterreceptors on adjacent cells such as the intracellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs), leading to aggregation of cells. Integrin β4 (ITGB4), also known as CD104, is a 1,822 amino acid single-pass type I membrane protein belonging to the Integrin β chain family. Known to associate with Integrin α6, Integrin β4 functions as a receptor for Laminin and is predominantly expressed by epithelia. Integrin β4 exists as five alternatively spliced isoforms that are encoded by a gene located on human chromosome 17q25.1.