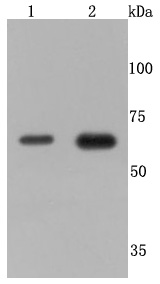
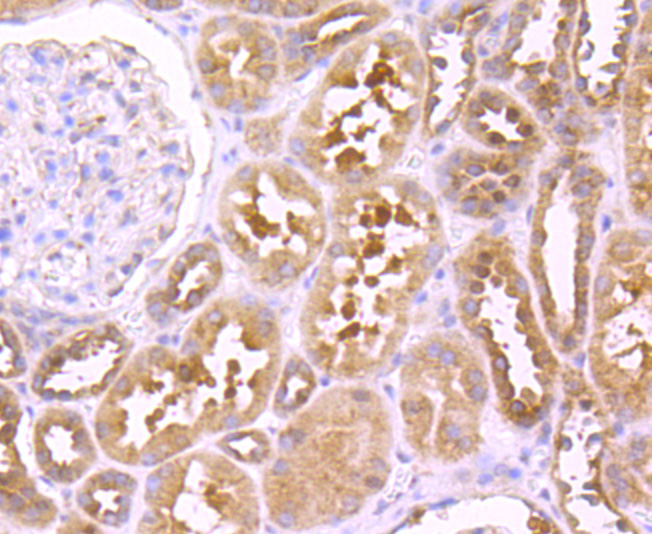
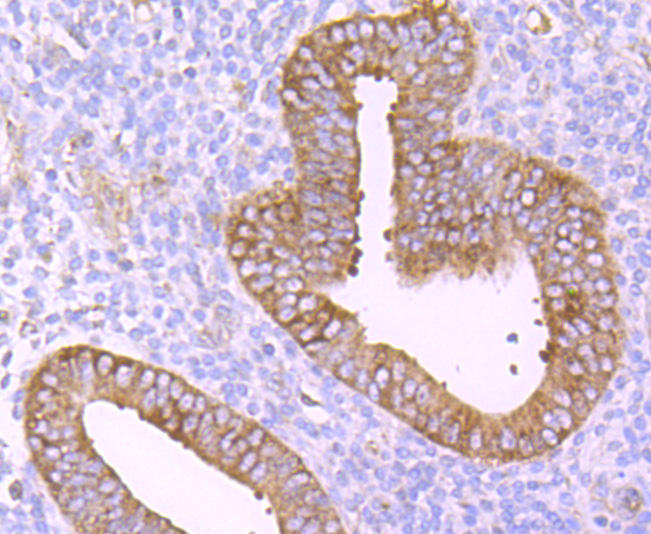
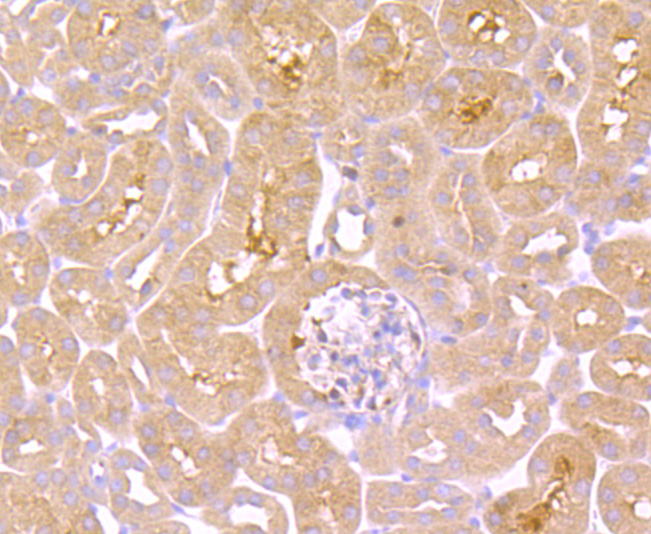
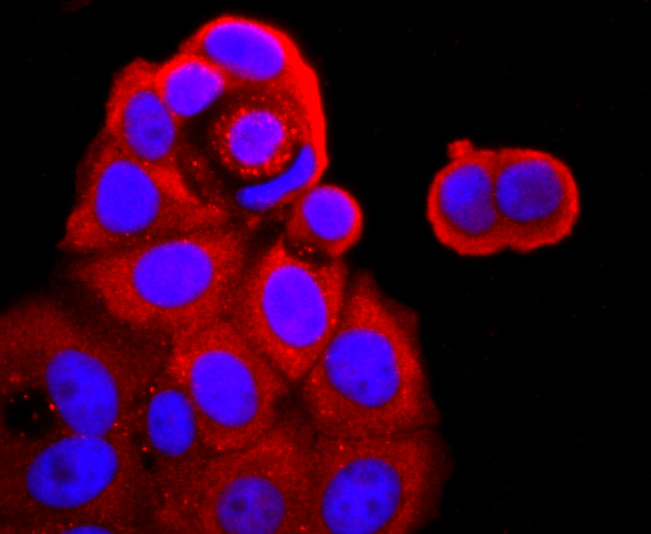
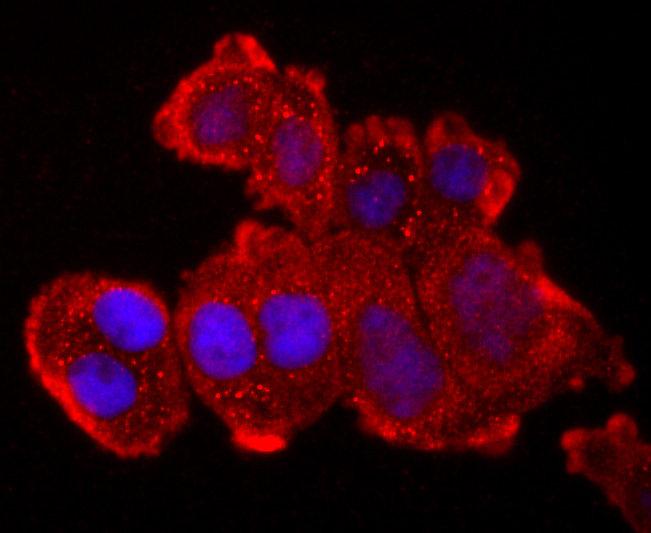
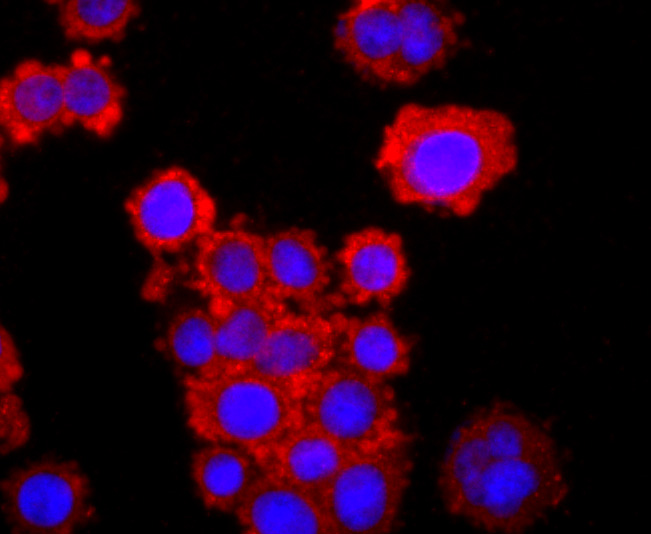
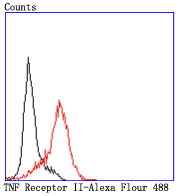
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a pleiotropic cytokine whose function is mediated through two distinct cell surface receptors. These receptors, designated TNF-R1 and TNF-R2, are expressed on most cell types. The majority of TNF functions are primarily mediated through TNF-R1, while signaling through TNF-R2 occurs less extensively and is confined to cells of the immune system. Both of these proteins belong to the growing TNF and nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor superfamily, which includes FAS, CD30, CD27 and CD40. The members of this superfamily are type I membrane proteins that share sequence homology confined to the extracellular region. TNF-R1 shares a motif termed the "death domain" with FAS and three structurally unrelated signaling proteins, TRADD, FADD and RIP (1,3-8). This death domain is required for transduction of the apoptotic signal.