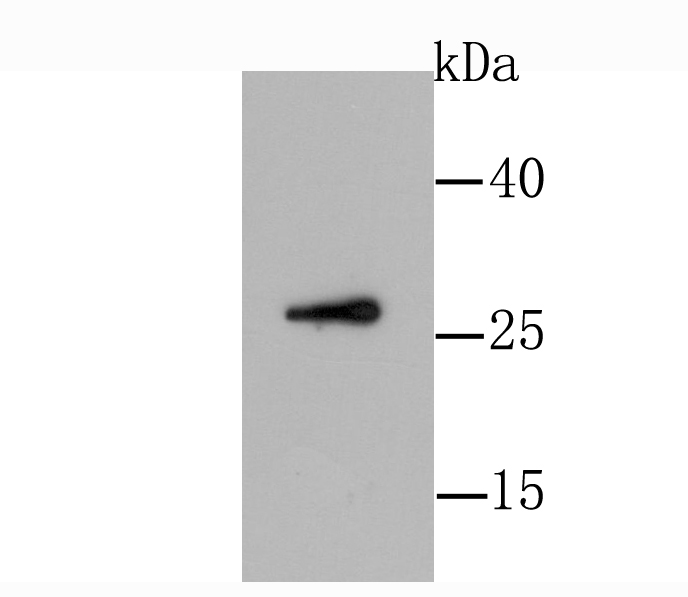
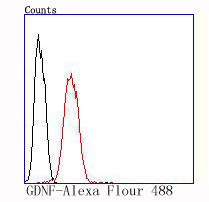
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) has been identified as a potent neurotrophic factor that enhances survival of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. GDNF is a glycosylated, disulfide-bonded homodimer and is a distantly related member of the TGFβ superfamily of growth regulatory ligands. GDNF contains the seven conserved cysteine residues in the same relative spacing characteristic of all members of the TGFβ superfamily. In embryonic midbrain cultures, GDNF promotes the survival and morphological differentiation of dopaminergic neurons and increases their high-affinity dopamine uptake. On the basis of these findings, it has been suggested that GDNF may have utility in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, which is marked by progressive degeneration of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.