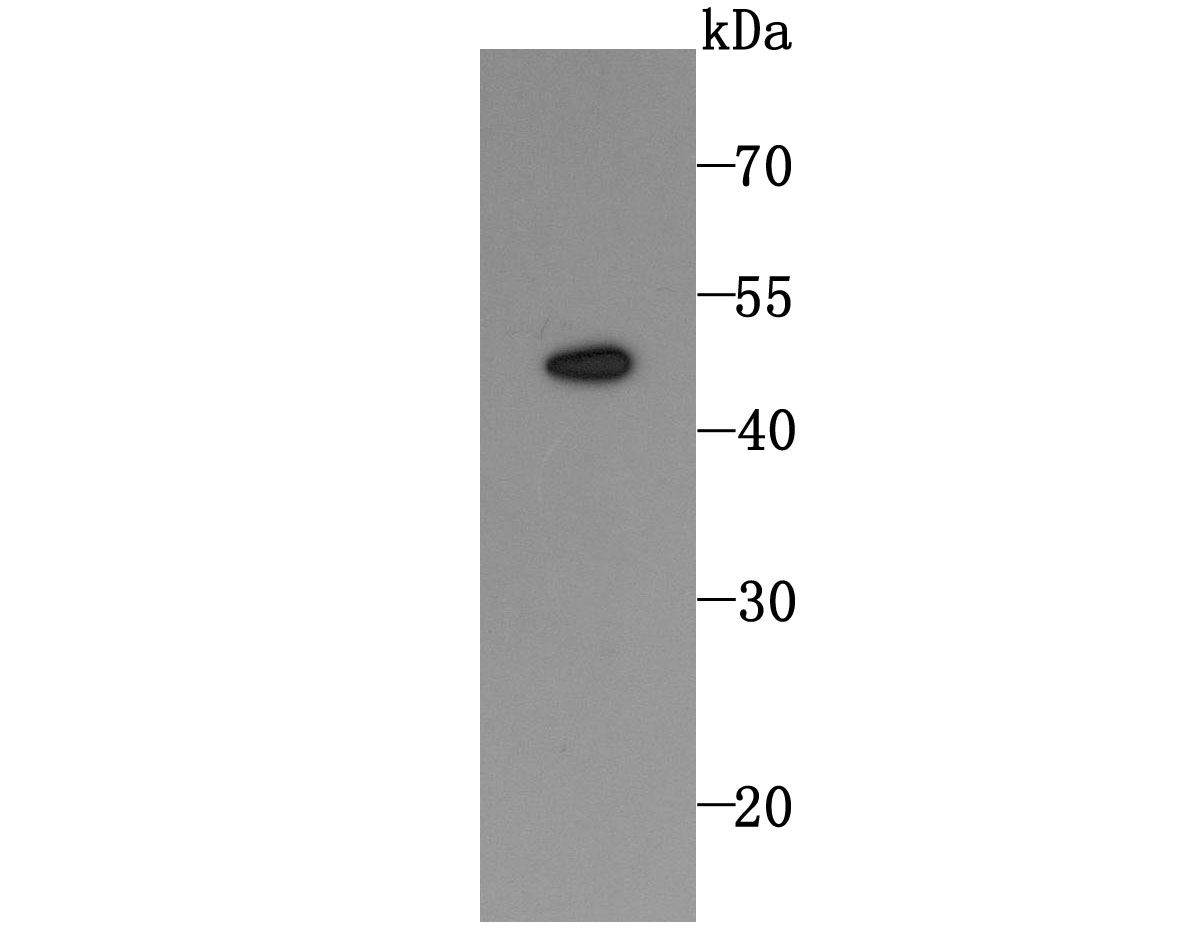
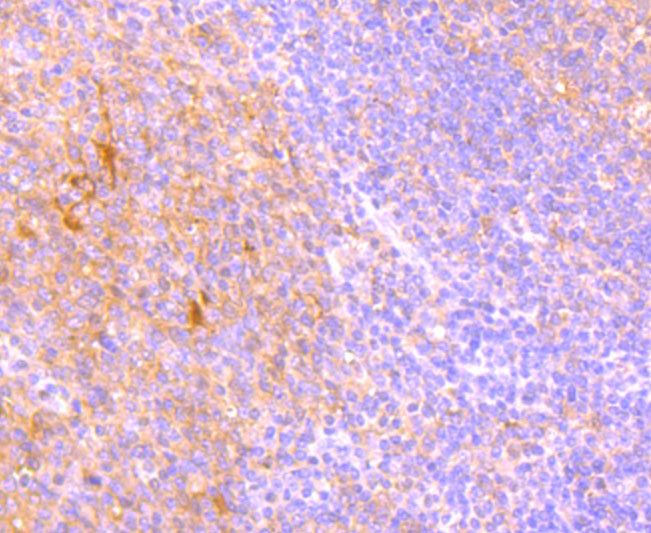
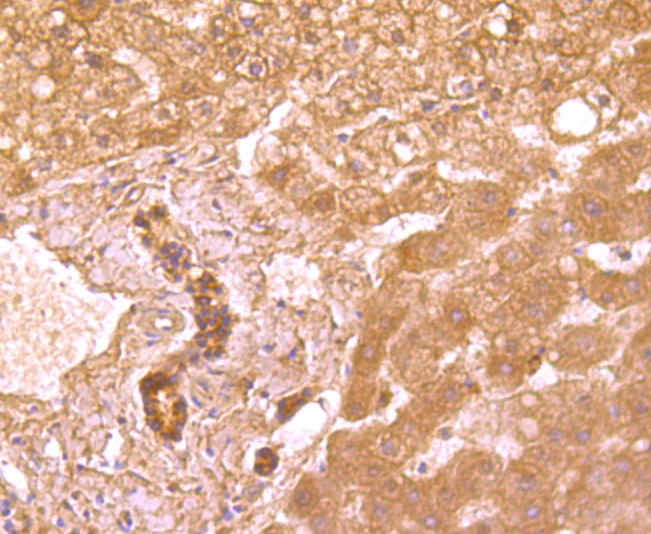
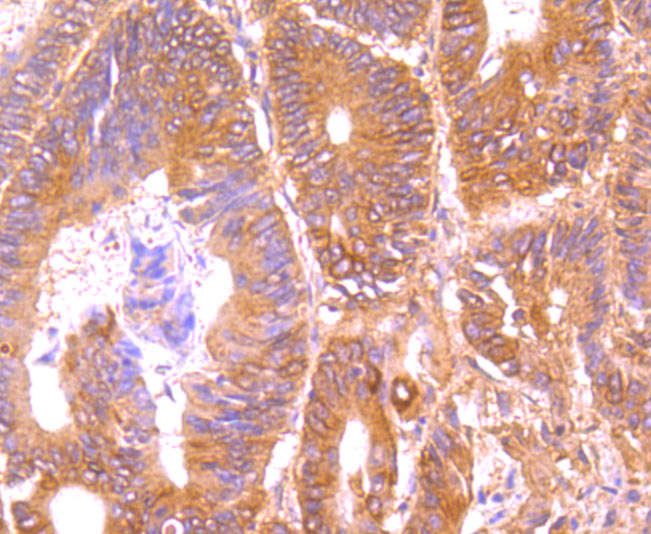
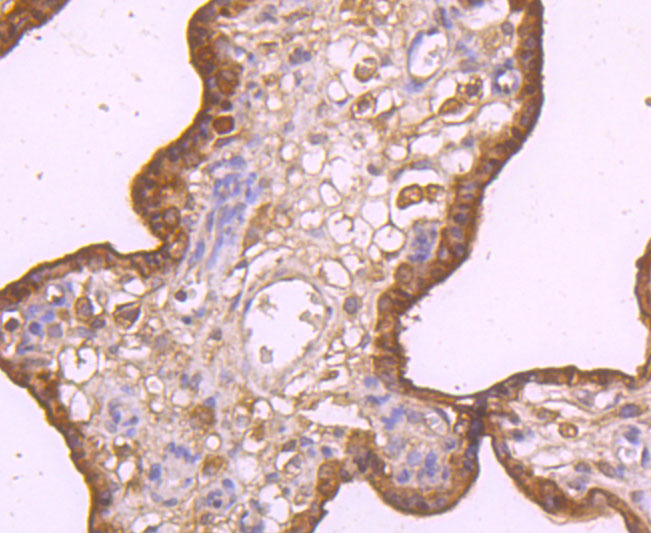
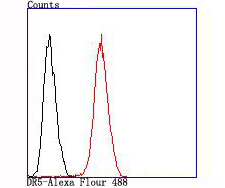
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a pleiotropic cytokine whose function is mediated by two distinct cell surface receptors, designated TNF-R1 and TNF-R2, which are expressed on most cell types. TNF function is primarily mediated through TNF-R1 signaling. Both receptors belong to the growing TNF receptor superfamily which includes FAS antigen and CD40. TNF-R1 contains a cytoplasmic motif, termed the "death domain," that has been found to be necessary for the transduction of the apoptotic signal. The death domain is also found in several other receptors, including FAS, DR2 (or TRUNDD), DR3 (Death Receptor 3), DR4 and DR5. TRUNDD, DR4 and DR5 are receptors for the apoptosis-inducing cytokine TRAIL. A non-death domain-containing receptor, designated decoy receptor (DcR1 or TRID), also specifically associates with TRAIL and may play a role in cellular resistance to apoptotic stimuli.