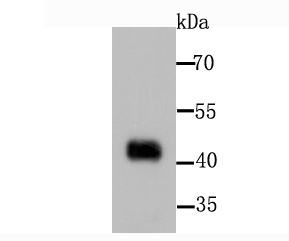
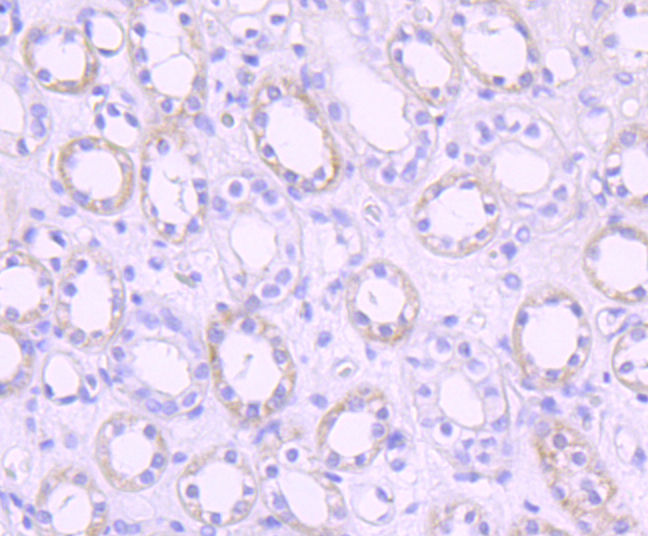
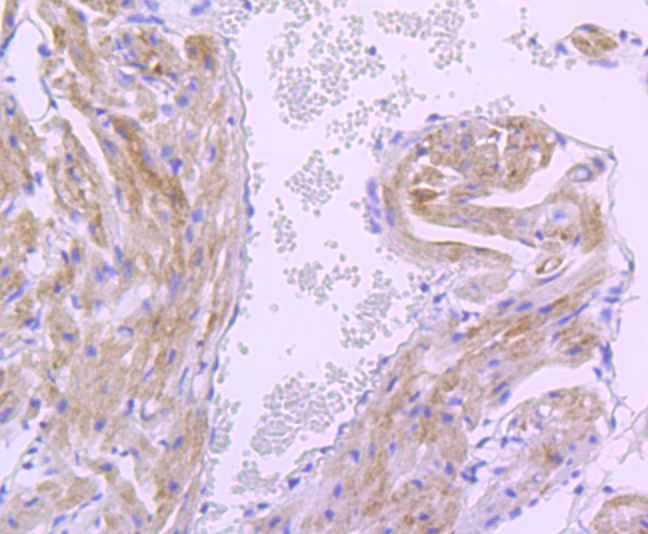
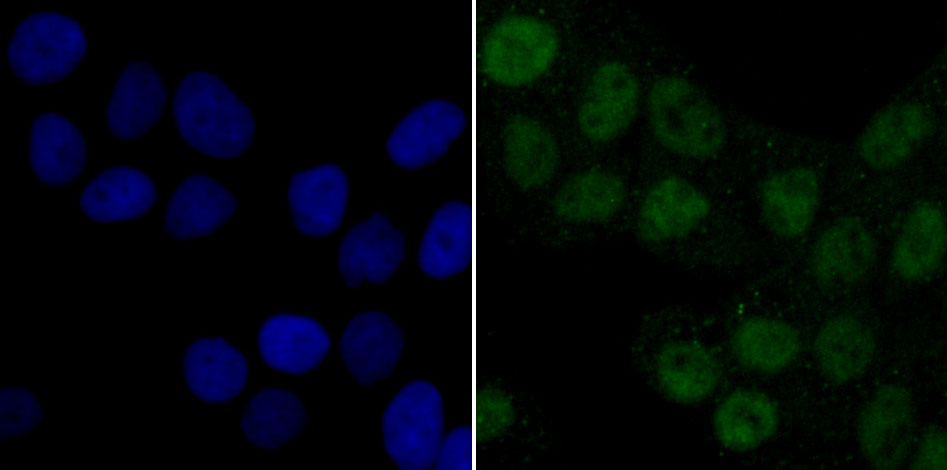
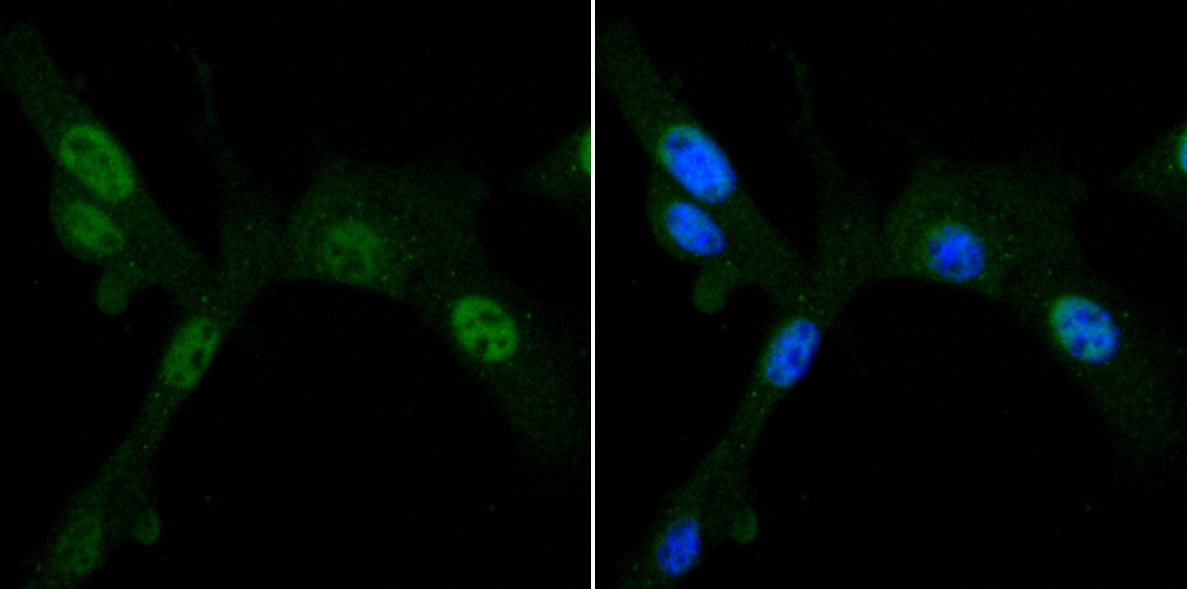
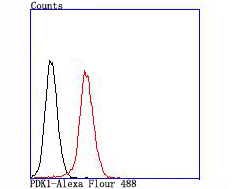
Mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate and plays a central role in the regulation of homeostasis of carbohydrate fuels in mammals. PDH activity is controlled by a phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cycle, phosphorylation leading to inactivation and dephosphorylation leading to reactivation of PDH. The phosphorylation of PDH is catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK), the activity of which is stimulated by the products of PDH catalysis. PDK1 consists of alpha and beta subunits; the kinase activity resides in the alpha subunit. Three PDK isoenzymes have been identified in humans (PDK1, 2 and 3) and two have been identified in rodent (PDK1 and 2).