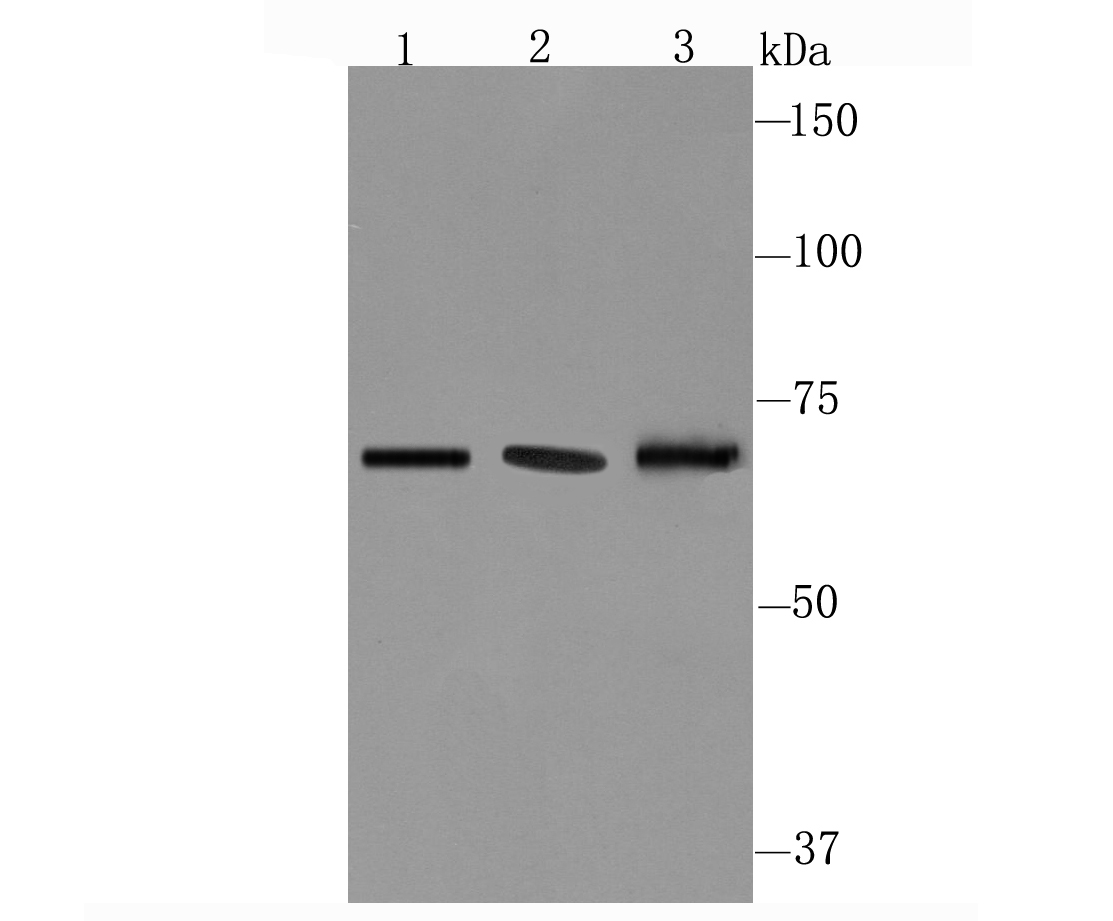
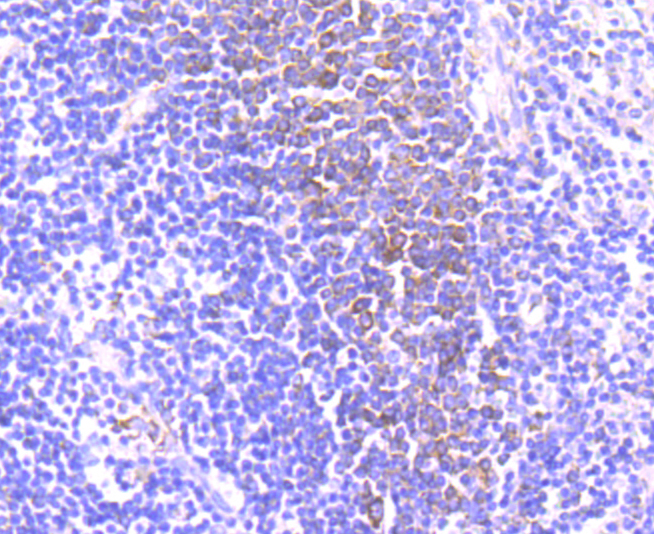
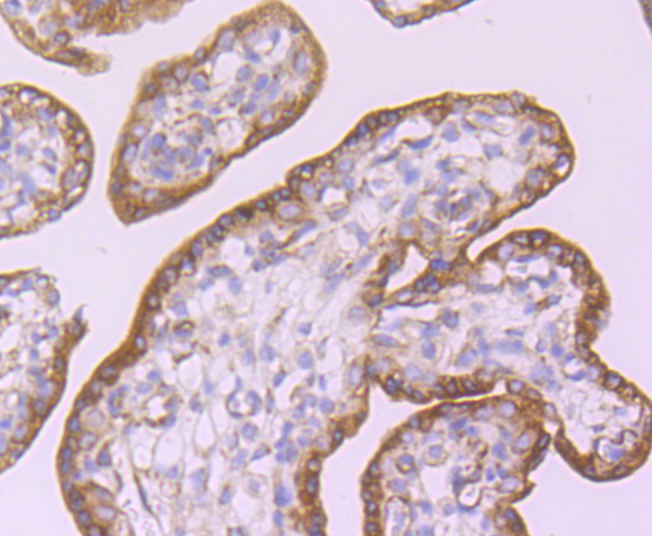
CD39, also known as ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 (ENP1), is an integral membrane glycoprotein that acts as an extracellular nucleotide-hydrolyzing enzyme. CD39 inhibits ADP-induced platelet aggregation by hydrolyzing ADP to AMP and ultimately generating adenosine. Intracellular CD39 undergoes glycosylation at 6 N-glycosylation sites and translocates to the membrane in order to be an active enzyme. Alternative splicing gives rise to three CD39 isoforms, vascular, placenta I and placenta II. The placenta I isoform differs at the amino terminus whereas the placenta II isoform is missing amino acids 300-510 at the C-terminus. CD39 is expressed in vascular tissues including placenta, lung, skeletal muscle and kidney, as well as endothelium, smooth muscle, cardiac cells, lymphocytes (such as activated B cells) activated NK cells, macrophages, dendridic cells and platelets. CD39 may be used as an anti-thrombic agent for pre-treating patients at risk for coronary artery occlusion and thrombic stroke.