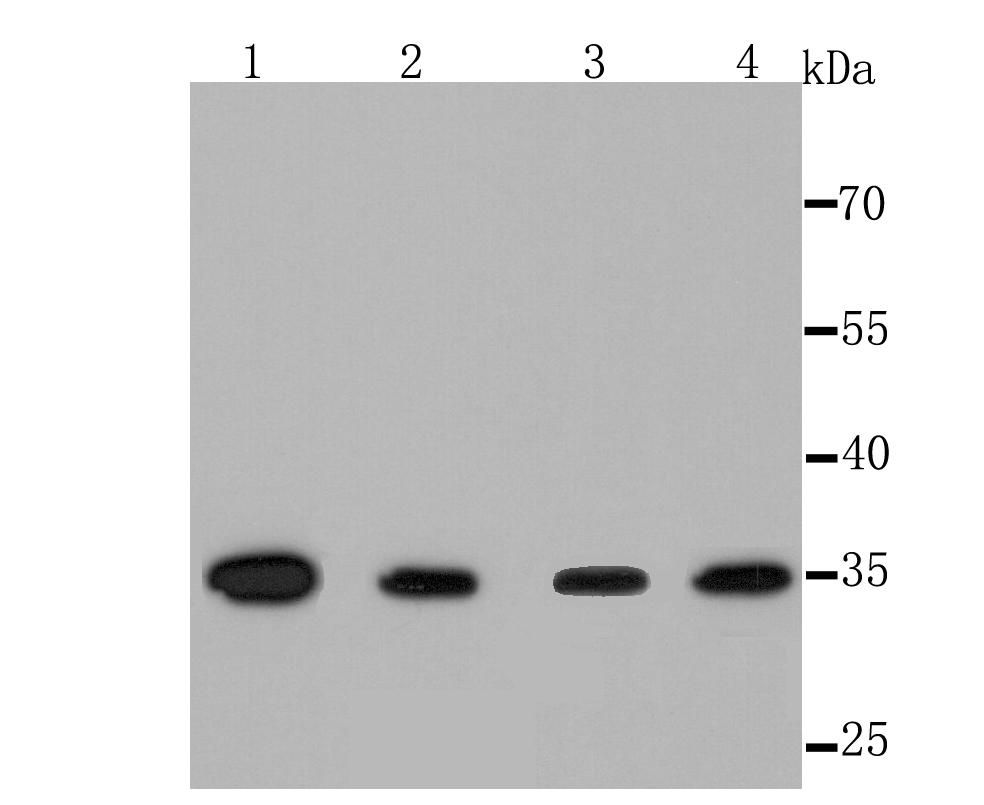
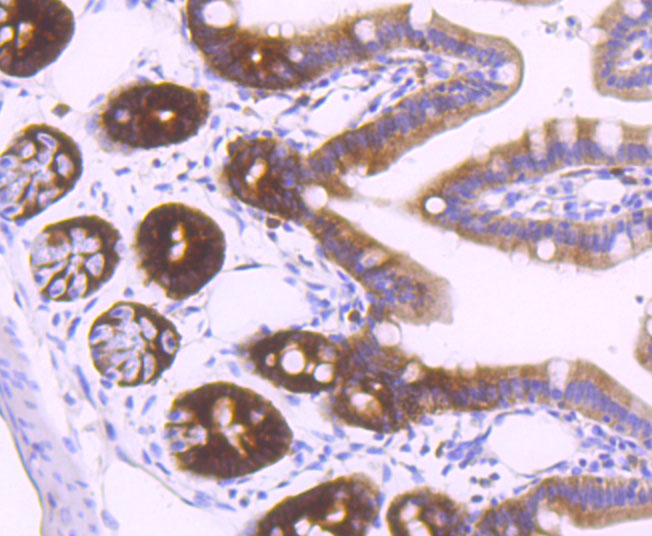
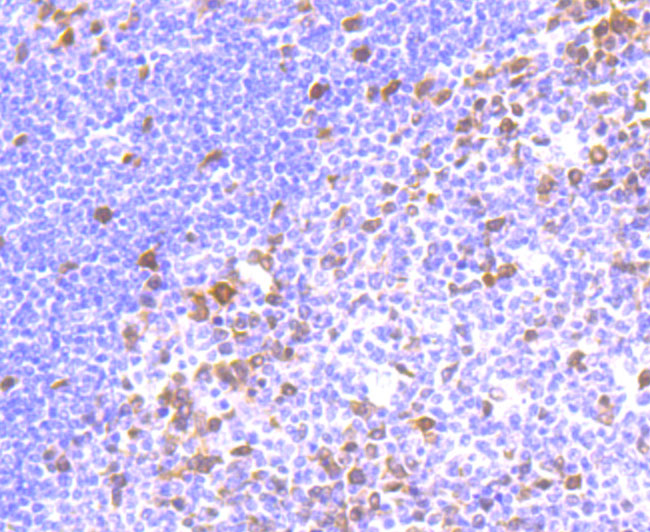
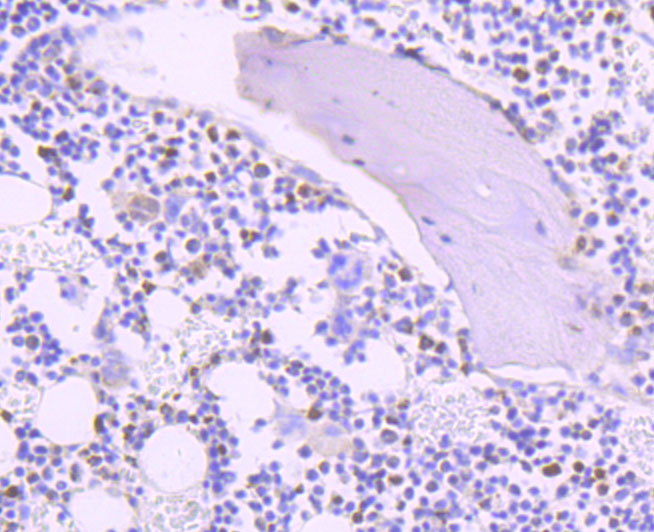
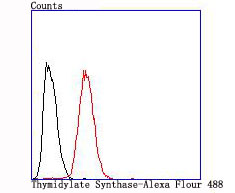
Thymidylate synthase (TS), also designated TYMS, TMS, TSase and HsT422, uses 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (methylene-THF) as a cofactor in the synthesis of 2'-deoxythymidine-5'-monophosphate (dTMP), an essential precursor for DNA biosynthesis. TS is an RNA-binding protein that can interact with its own mRNA. The TS/mRNA ribonucleoprotein complex can also associate with a number of other cellular mRNAs, including those corresponding to the p53 tumor suppressor gene and the Myc family of transcription factors. Inhibition of DNA replication and cell death resulting from thymidine depletion occurs when TS enzyme activity is inhibited with substrate or cofactor analogs, making the TS enzyme an important target for chemotherapy. Cancer cells are sensitive to thymidine depletion, as they multiply rapidly.