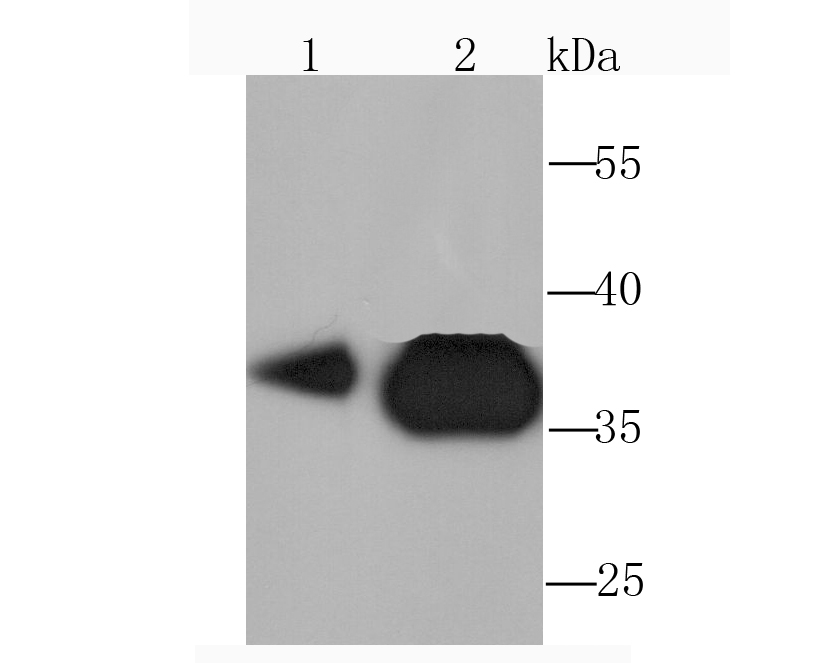
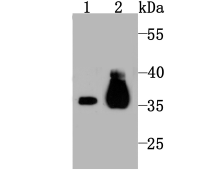
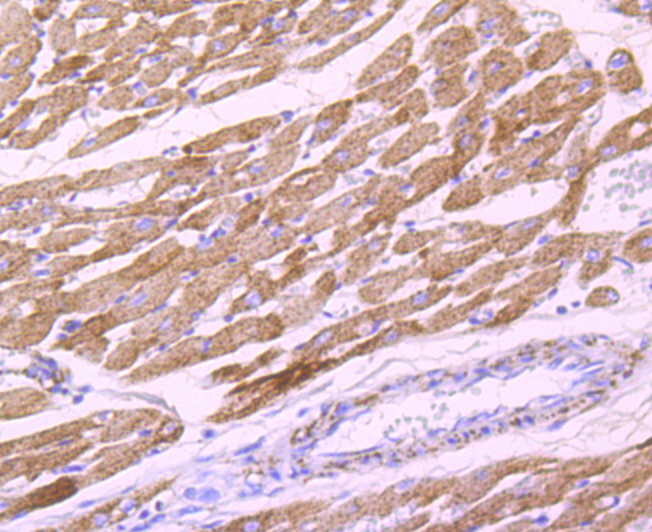
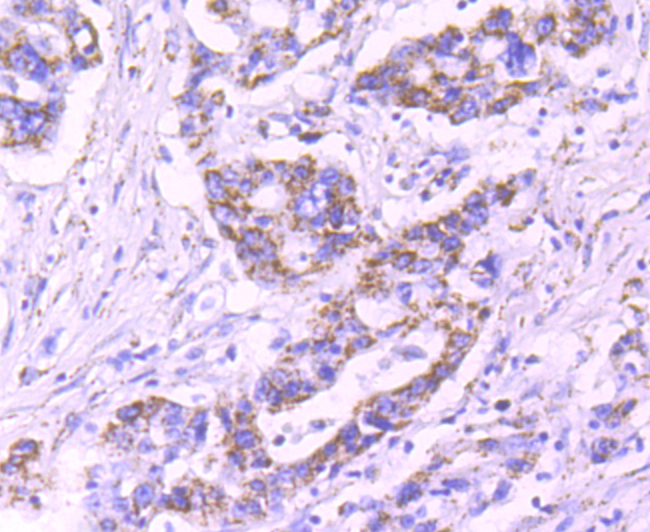
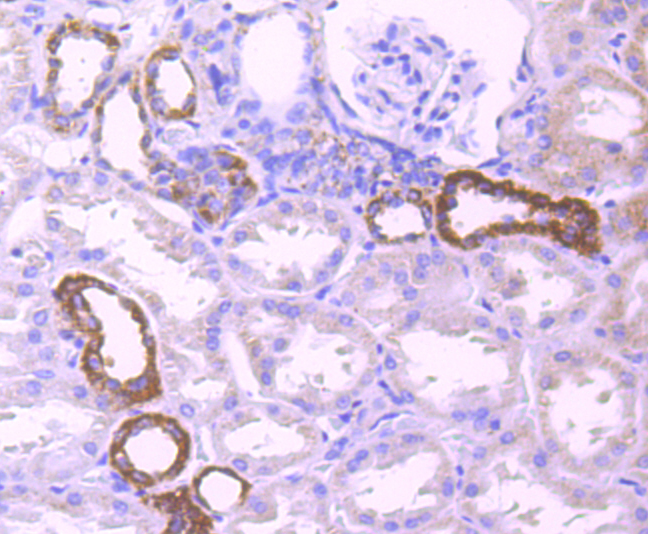
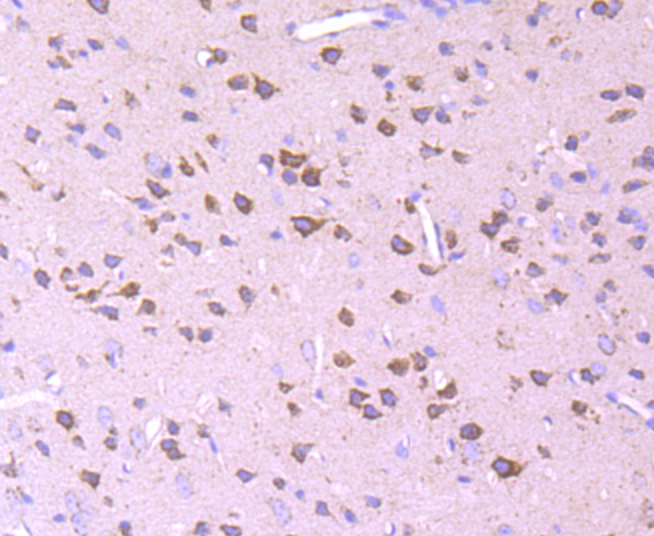
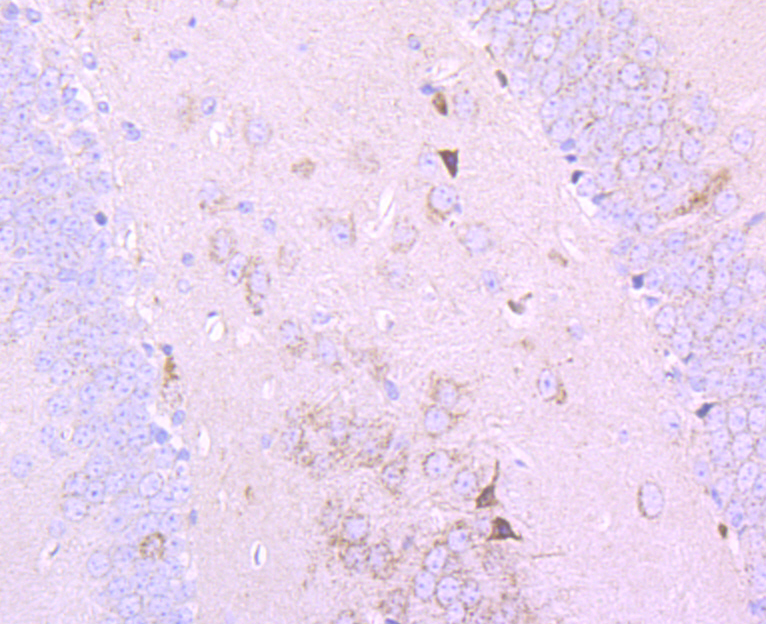
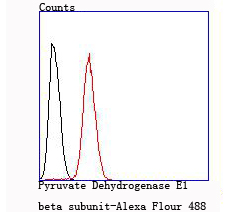
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO. It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components: pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3). Defects in PDHB are a cause of pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component deficiency (PDHE1 deficiency). PDHE1 deficiency is the most common enzyme defect in patients with primary lactic acidosis. It is associated with variable clinical phenotypes ranging from neonatal death to prolonged survival complicated by developmental delay, seizures, ataxia, apnea, and in some cases to an X-linked form of Leigh syndrome (LS) (Leigh encephalomyelopathy).