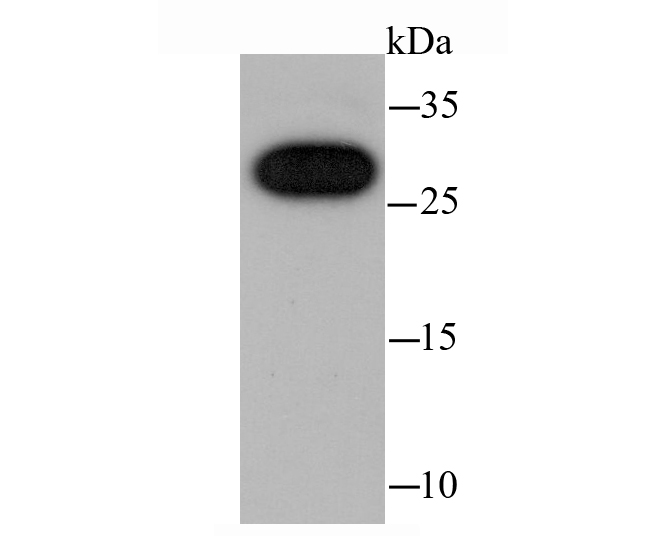
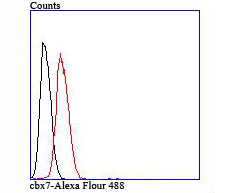
CBX7 (Chromobox protein homolog 7) is a 251 amino acid nuclear protein that contains one N-terminal chromo domain and one C-terminal Pc box. Highly expressed in kidney, brain, heart and skeletal muscle, with weaker expression in peripheral blood leukocytes, CBX7 functions as a component of the chromatin-associated polycomb complex (PcG) and is involved in maintaining the transcriptionally repressed state of target genes. Additionally, CBX7 modifies chromatin and is thought to extend the cellular life span of epithelial cells by repressing p14 ARF expression, while simultaneously repressing telomerase activity. Due to its ability to repress the transcription of cell-cycle related proteins, CBX7 is thought to play a role in tumorigenesis, specifically in the development of follicular lymphoma and thyroid cancer.