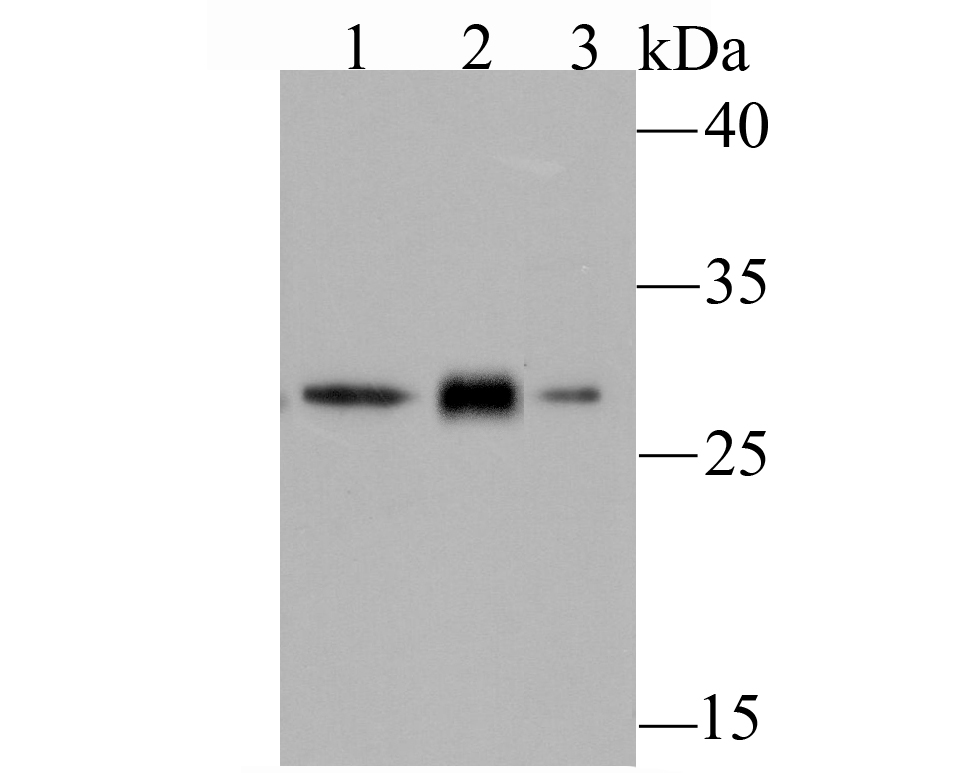
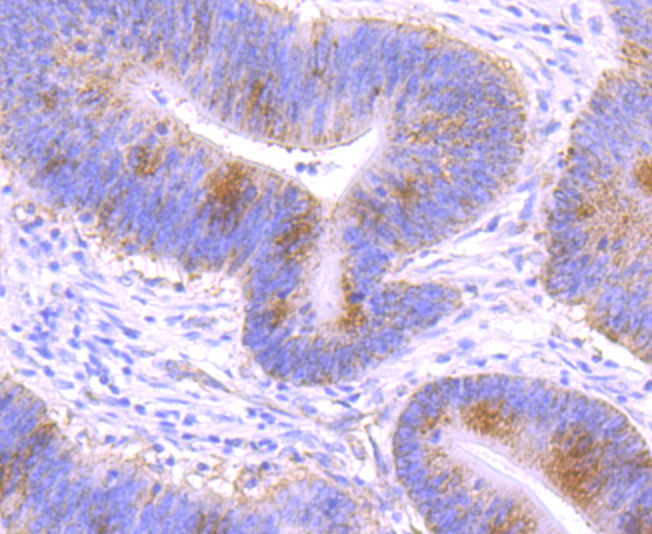
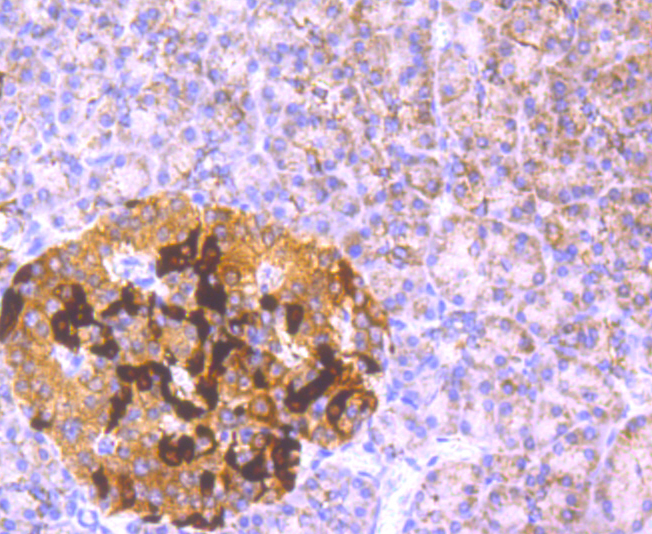
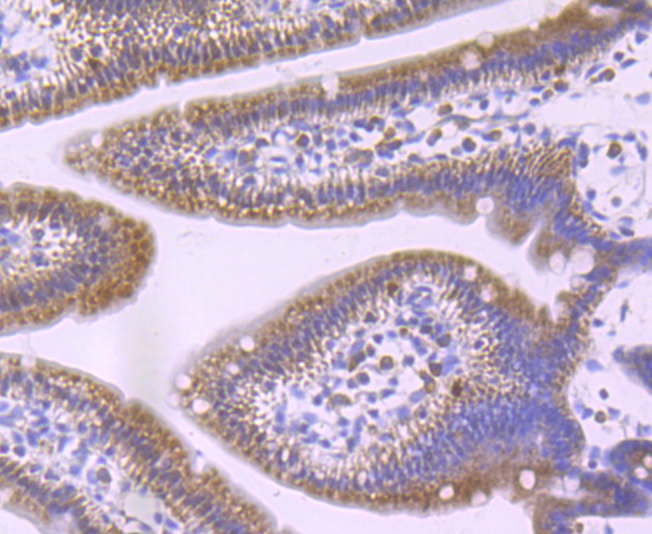
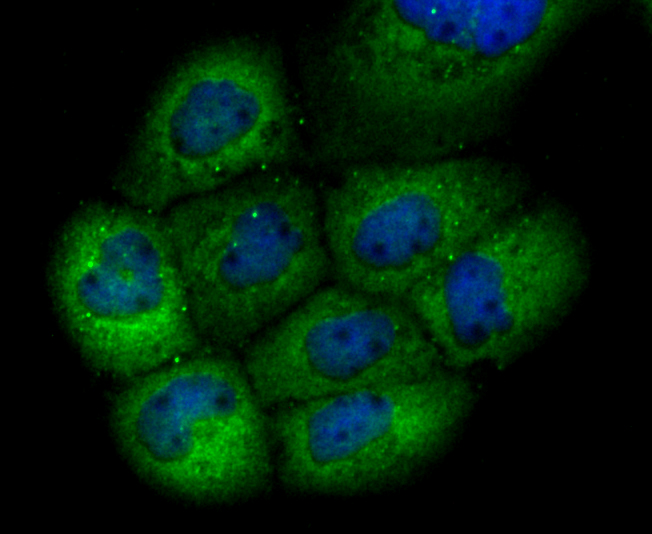
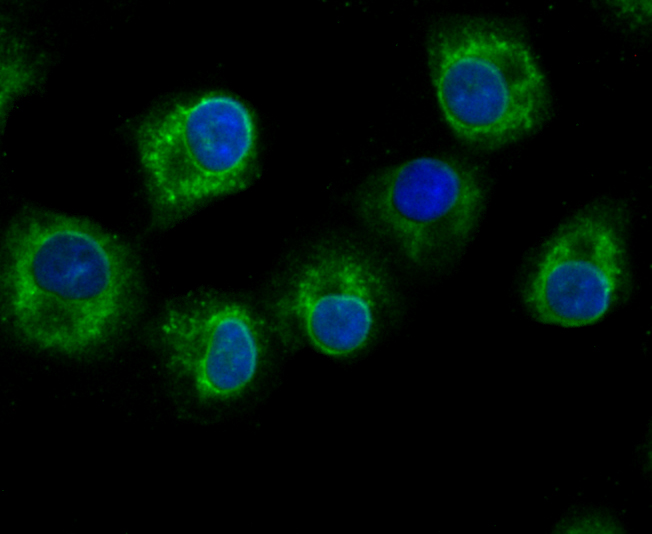
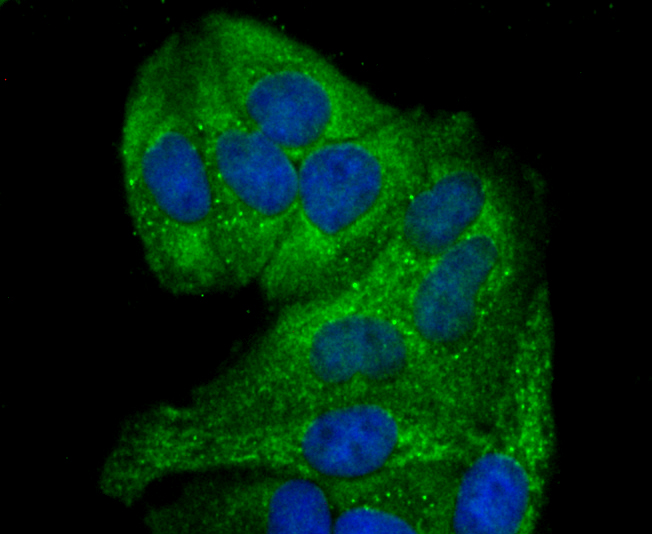
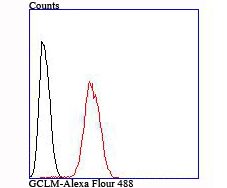
Gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (γ-GCS) is the rate limiting enzyme for glutathione (L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine, GSH) synthesis. GSH is ubiquitous in mammalian cells as a vital intra- and extracellular protective antioxidant. γ-GCS is a heterodimer of a heavy catalytic subunit and a light regulatory subunit that is responsive to inflammation, phenolic antioxidants, heat shock, oxidants and cytokines. The human gamma-GCS gene encoding the 367 amino acid catalytic subunit maps to chromosome 6p12. The human γ-GCS gene encoding the regulatory subunit maps to chromosome 1p22-p21. The two subunits of γ-GCS form a heterodimeric zinc metalloprotein that gains activity through formation of a reversible disulfide bond.