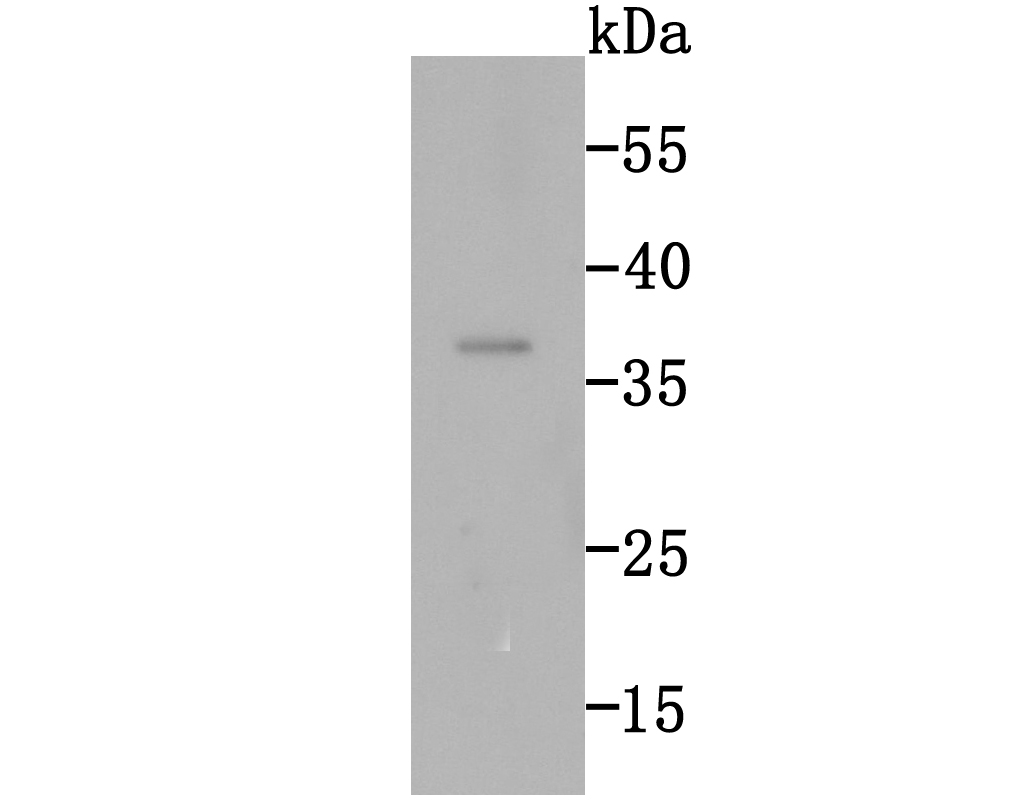
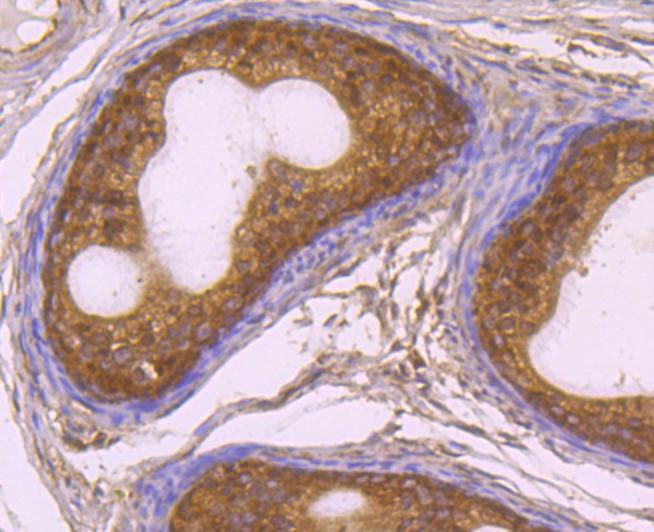
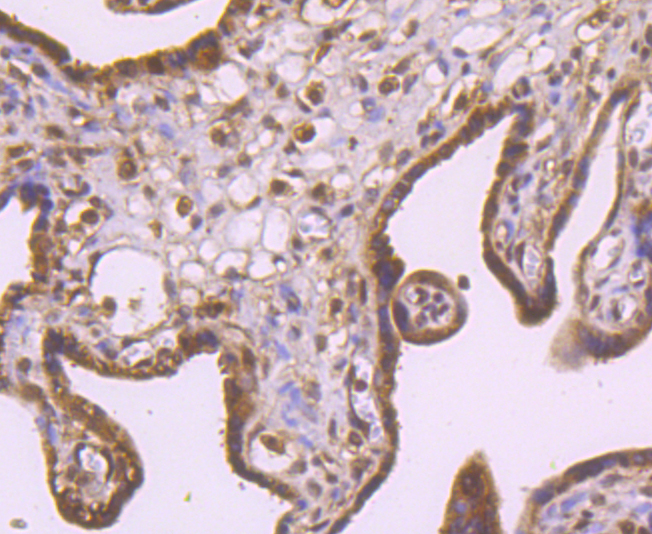
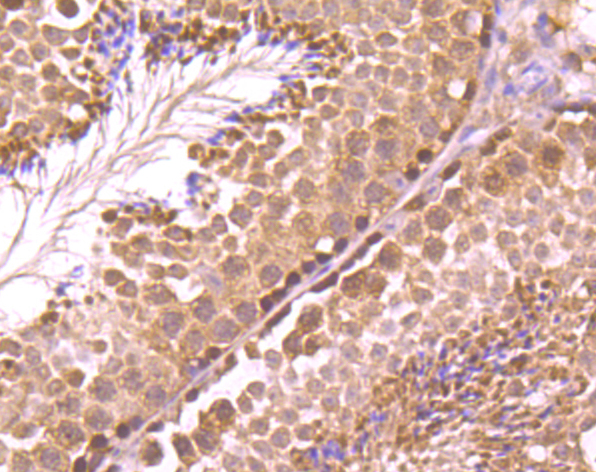
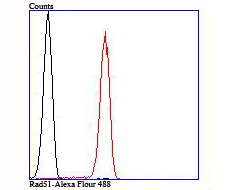
Rad51 (RECA, BRCC5) interacts with BRCA1 and BRCA2 to influence subcellular localization and cellular response to DNA damage. BRCA2 inactivation may be a key event leading to genomic instability and tumorigenesis from deregulation of Rad51. Rad52 forms a heptameric ring that binds single-stranded DNA ends and catalyzes DNA-DNA interaction necessary for the annealing of complementary strands. Rad52 can interact with Rad51. Rad54A of the DEAD-like helicase superfamily binds to double-strand DNA and induces a DNA topological change, which is thought to facilitate homologous DNA pairing and stimulate DNA recombination. Rad54B of the DEAD-like helicase superfamily binds to double-stranded DNA and displays ATPase activity in the presence of DNA. Rad54B is abundant in testis and spleen, and mutations of this gene occur in primary lymphoma and colon cancer. MRE11 (meiotic recombination 11, ATLD, HNGS1) is a nuclear 3-5 exonuclease/endonuclease that associates with Rad50 and influences homologous recombination, telomere length maintenance, and DNA double-strand break repair. MRE11 is most abundant in proliferating tissues.