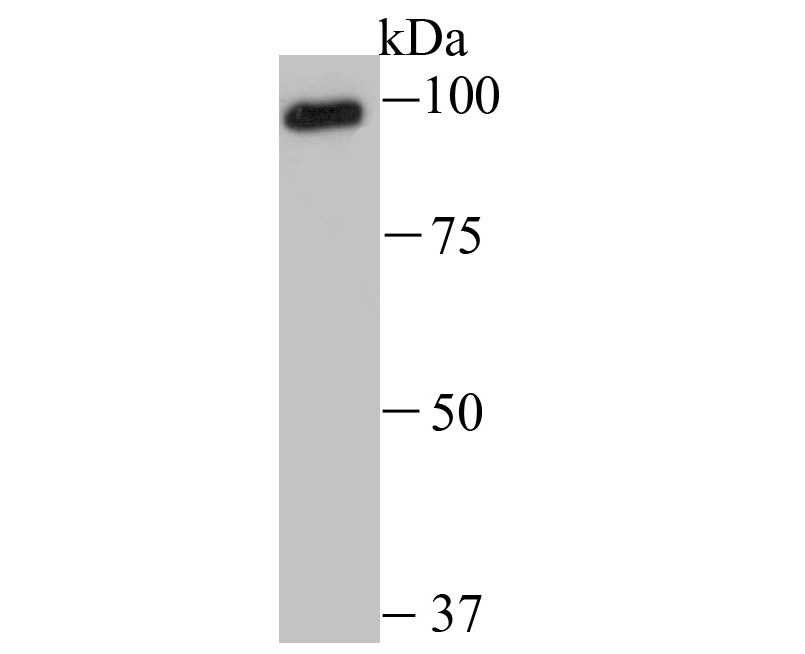
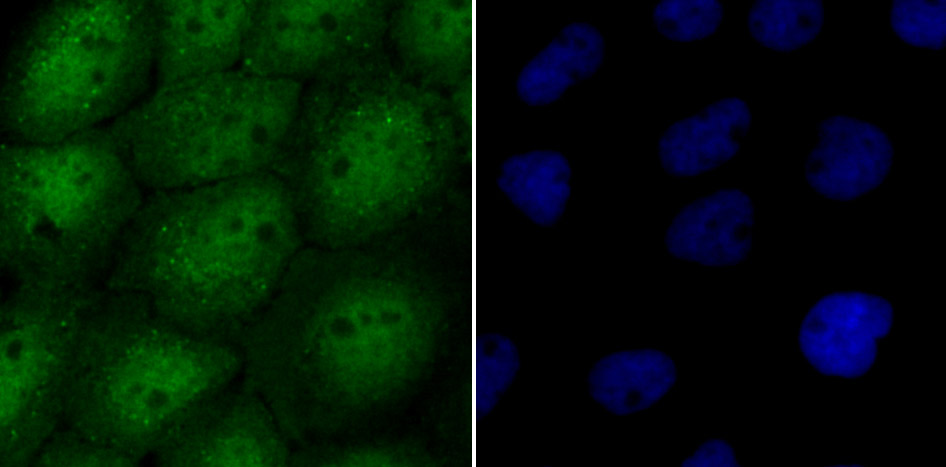
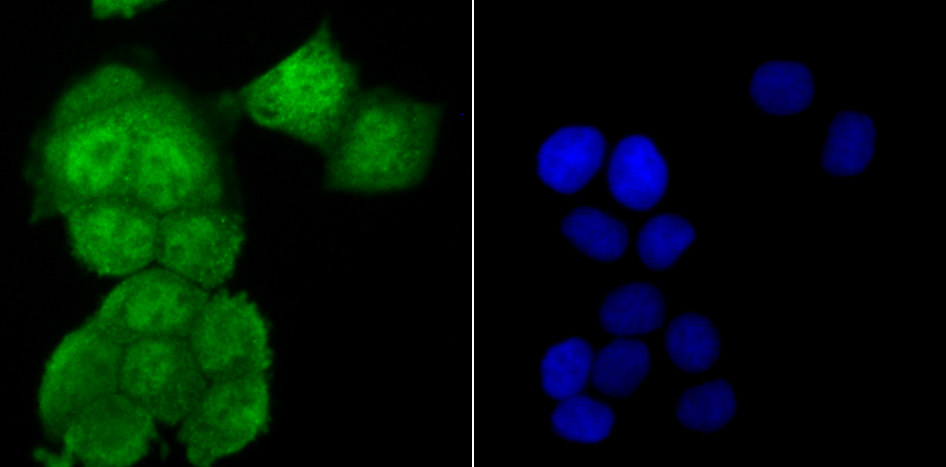
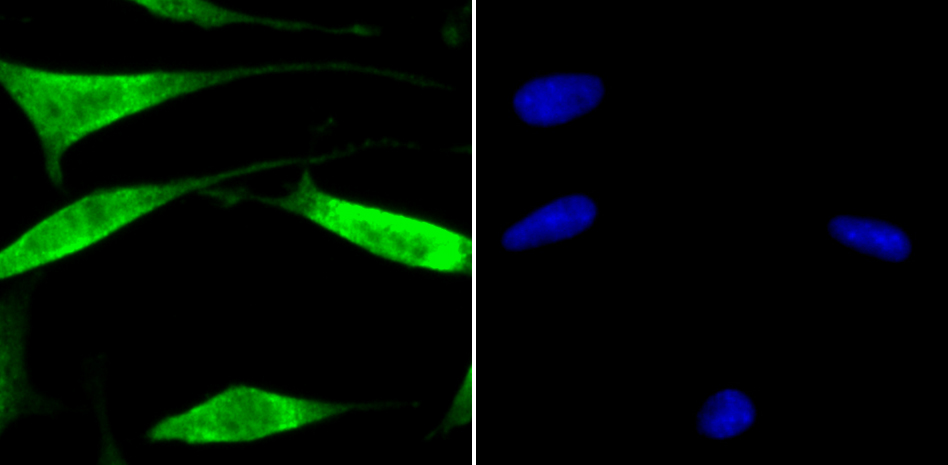
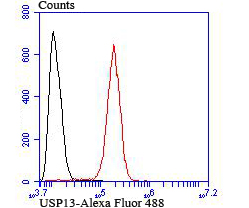
The ubiquitin (Ub) pathway involves three sequential enzymatic steps that facilitate the conjugation of Ub and Ub-like molecules to specific protein substrates. Through the use of a wide range of enzymes that can add or remove ubiquitin, the Ub pathway controls many intracellular processes such as signal transduction, transcriptional activation and cell cycle progression. USP13 (ubiquitin specific peptidase 13), also known as ISOT3 (Isopeptidase T-3), is an 863 amino acid protein that belongs to the peptidase C19 family and contains one UBP-type zinc finger and two UBA domains. Highly expressed in testicular and ovarian tissue, USP13 functions to catalyze the water-dependent conversion of a ubiquitin C-terminal thioester to a thiol and a free ubiquitin.