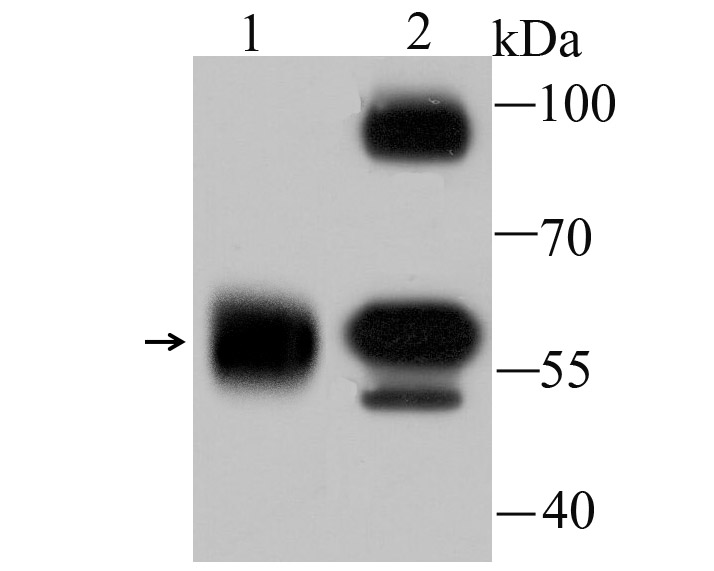
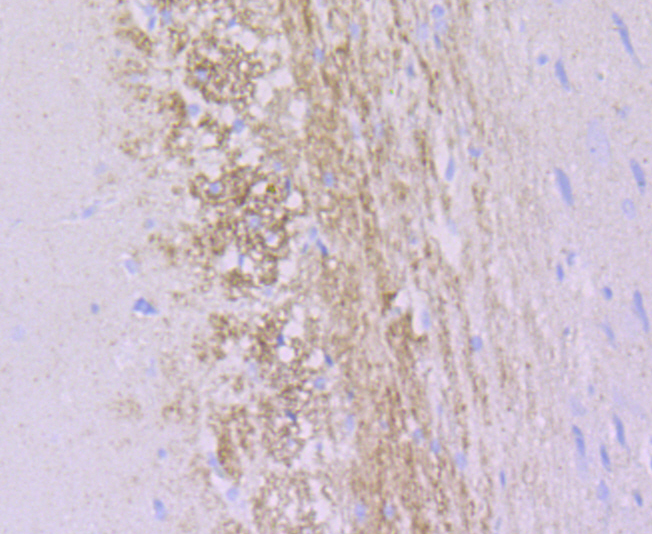
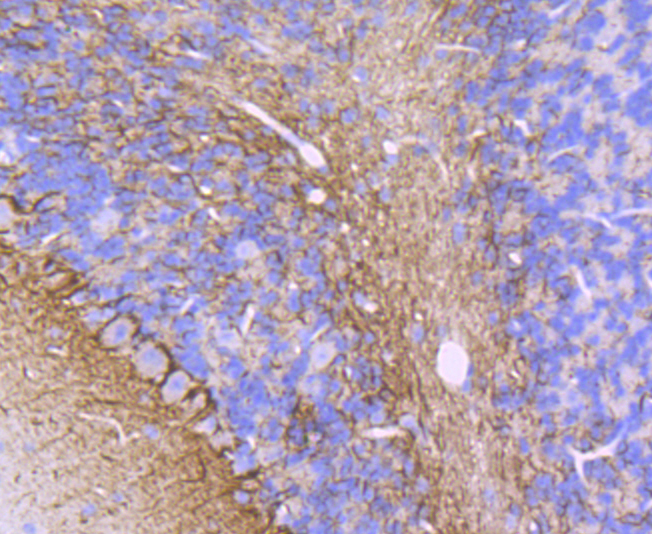
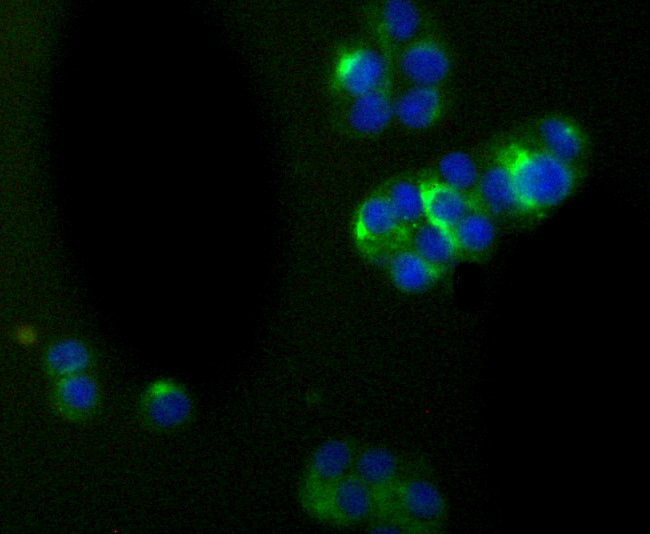
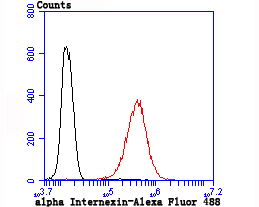
Alpha-internexin is a brain specific type IV intermediate filament protein. This axonal protein is found in most, if not all, neurons of the CNS. The head domain of alpha-internexin is essential for self-assembly into a filament network. Expression levels of alpha-internexin have been shown to be maximal during late embryogenesis and to decline into adulthood, suggesting that this protein plays a role in regulatory processes during the development of the brain. The alpha-internexin promoter has been shown to be activated by Brn-3a or Brn-3c transcription factor binding, while Brn-3b binding to the promoter results in alpha-internexin repression.