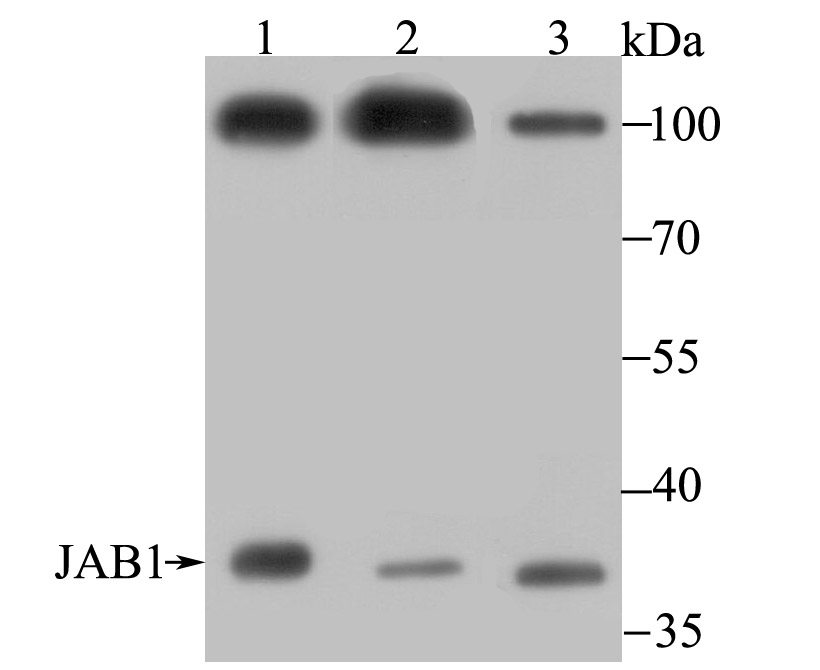
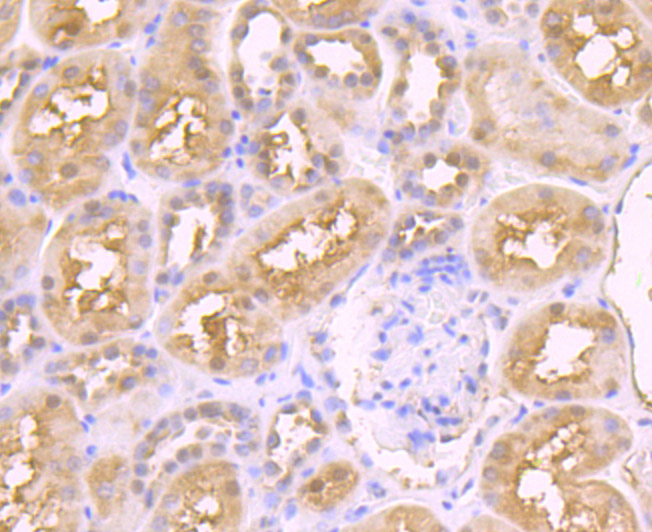
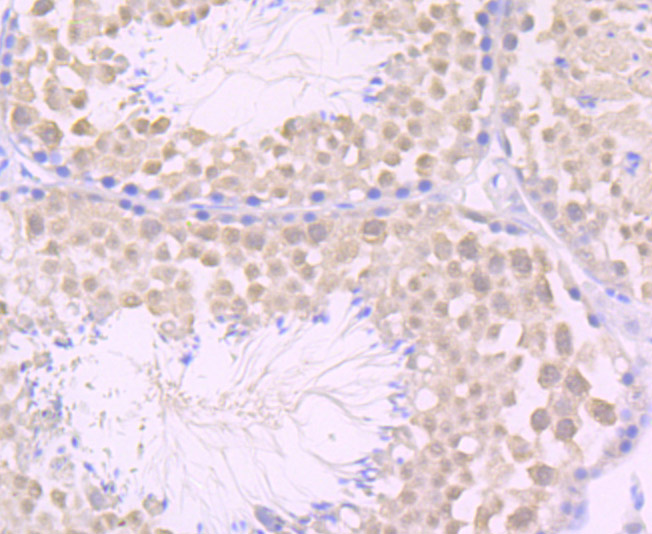
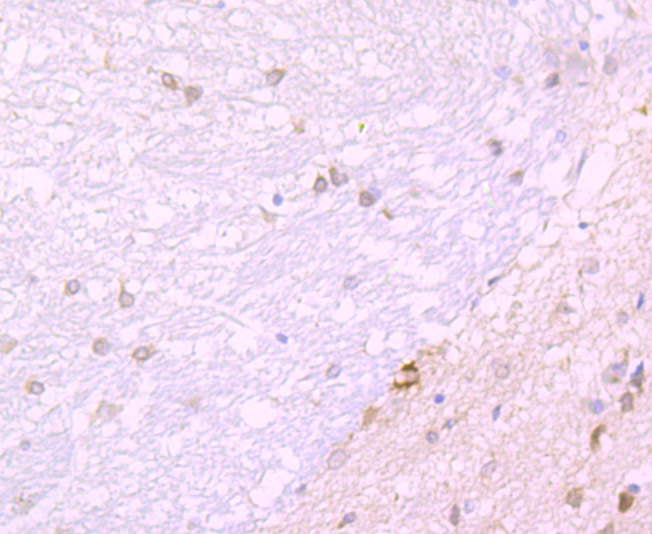
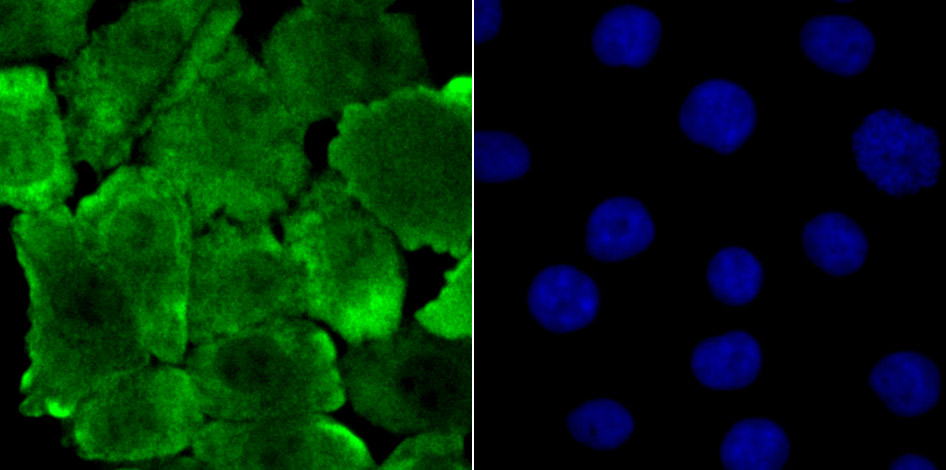
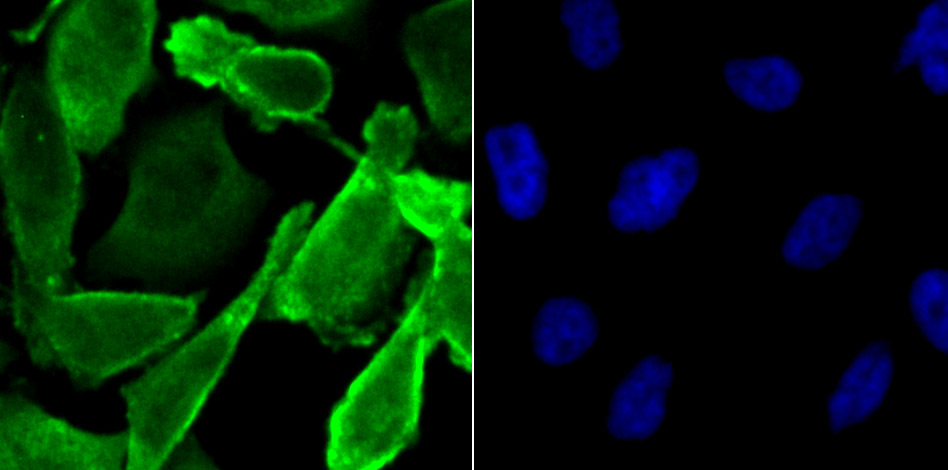
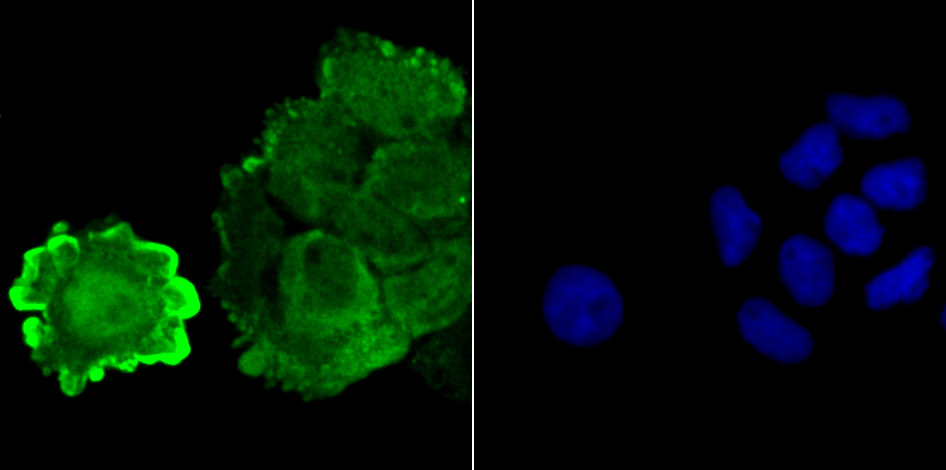
Genes belonging to the Jun and Fos oncogene families encode nuclear proteins that are found to be associated with a number of transcriptional complexes. The c-Jun protein is a major component of the transcription factor AP-1, originally shown to mediate phorbol ester tumor promoter (TPA)-induced expression of responsive genes through the TPA-response element (TRE). The Jun proteins form homo- and heterodimers which bind the TRE, but the Fos proteins are active only as heterodimers with any of the Jun proteins. Fos/Jun heterodimers have a much higher affinity for the TRE than Jun homodimers. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. The coactivator of Jun, designated JAB1 (for Jun-activation domain-binding protein), interacts with c-Jun and Jun D, but not with Jun B or v-Jun. This interaction enhances the transactivating ability of Jun proteins by stabilizing their binding to the TRE. The gene encoding JAB1 maps to human chromosome 8q12.3.