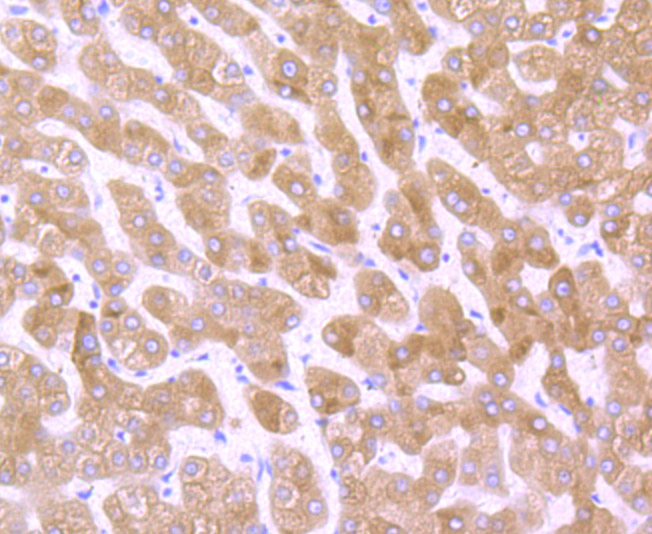
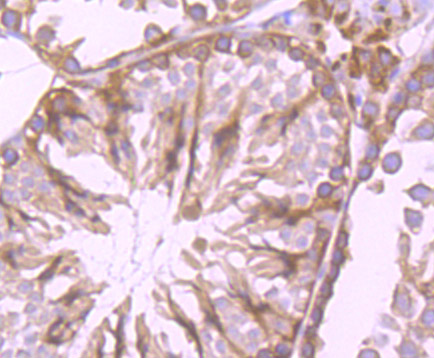
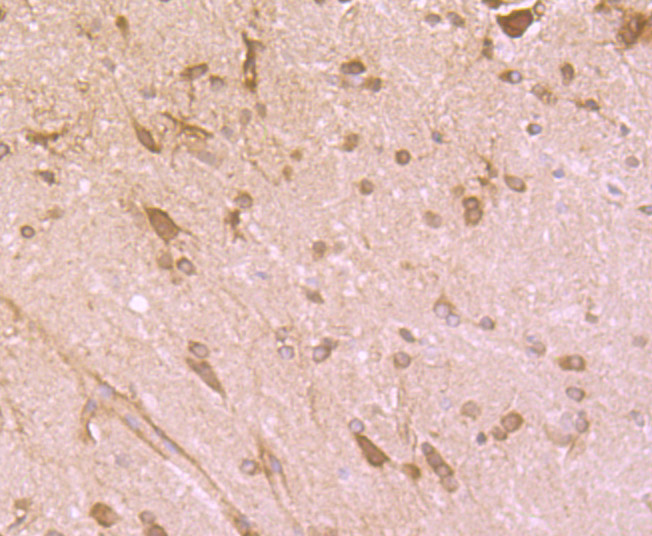
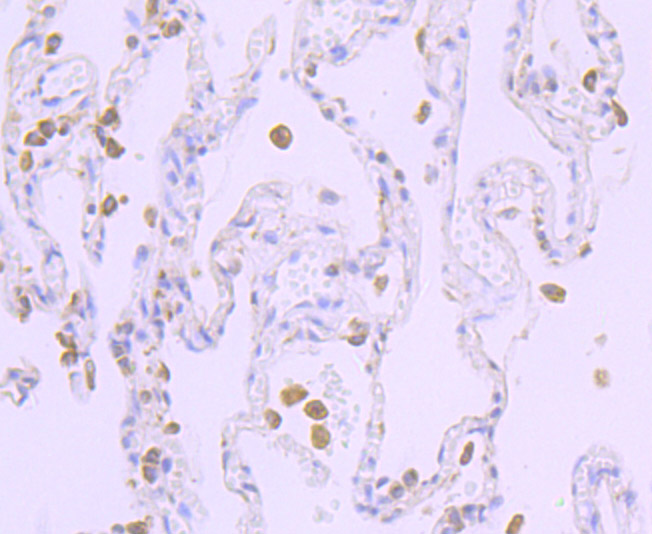
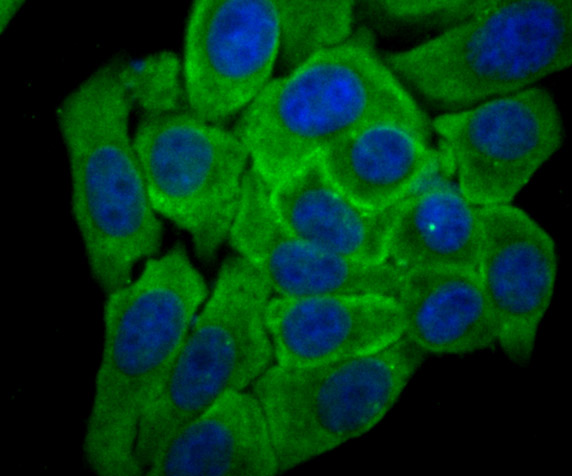
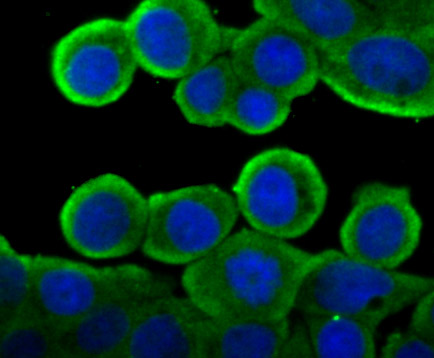
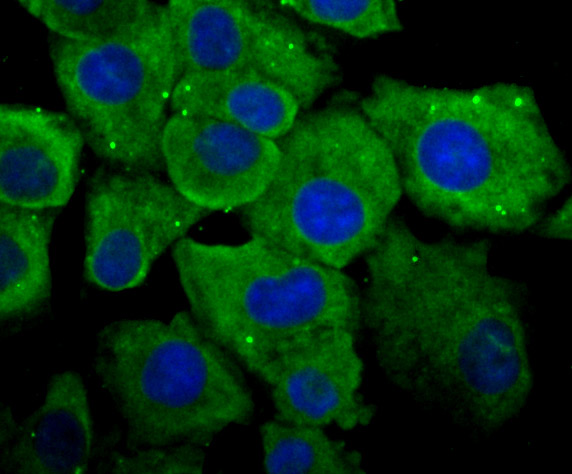
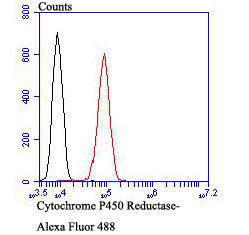
P450 enzymes constitute a family of monooxygenase enzymes that are involved in the metabolism of a wide array of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Several P450 enzymes have been classified by sequence similarities as members of the CYP1A and CYP2A subfamilies. CYPOR, also known as cytochrome P450 reductase and NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase, is a microsomal enzyme responsible for the transfer of electrons from NADPH to cytochrome P450 enzymes during the P450 catalytic cycle. CYPOR is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is also able to transfer electrons to heme oxygenase and cytochrome b5. CYPOR is structurally related to two separate flavoprotein families, ferredoxin nucleotide reductase (FNR) and flavodoxin. Electron transfer of CYPOR requires the binding of two flavin cofactors, FAD and FMN, to the FNR and flavodoxin domains, respectively.