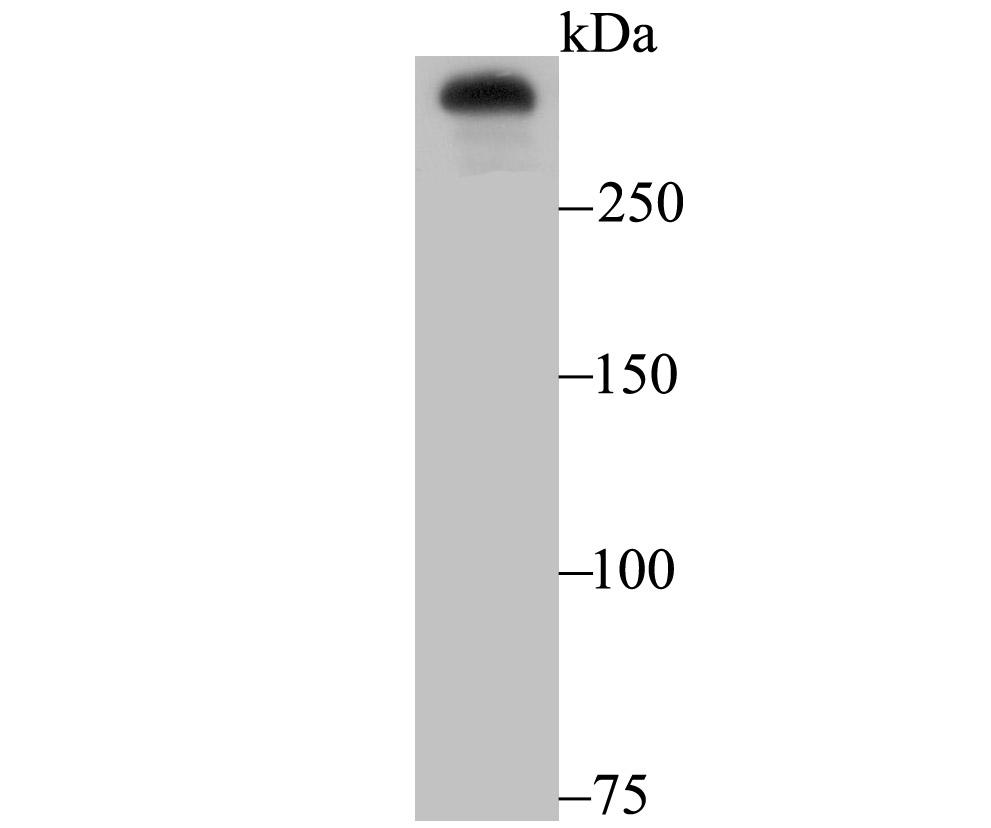
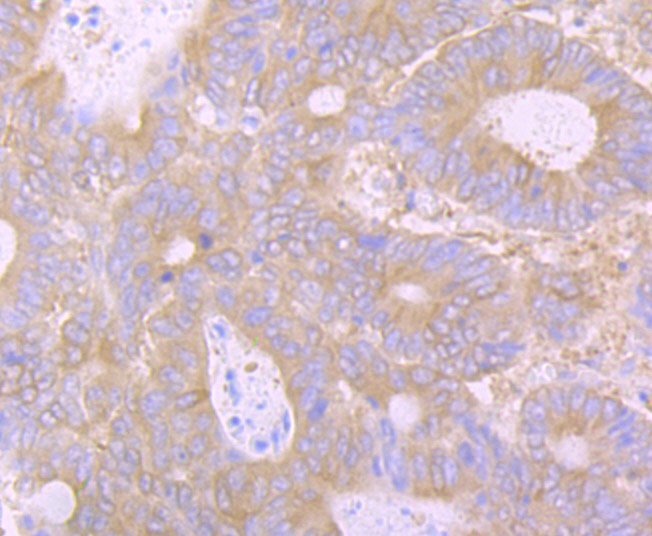
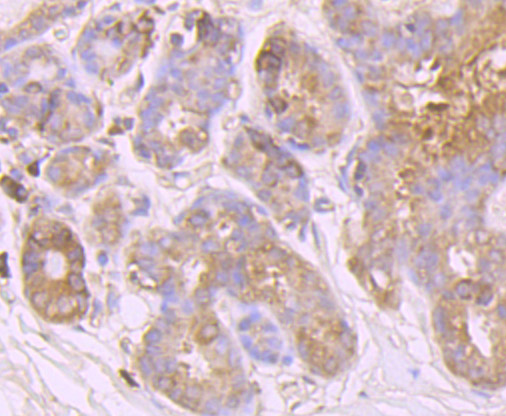
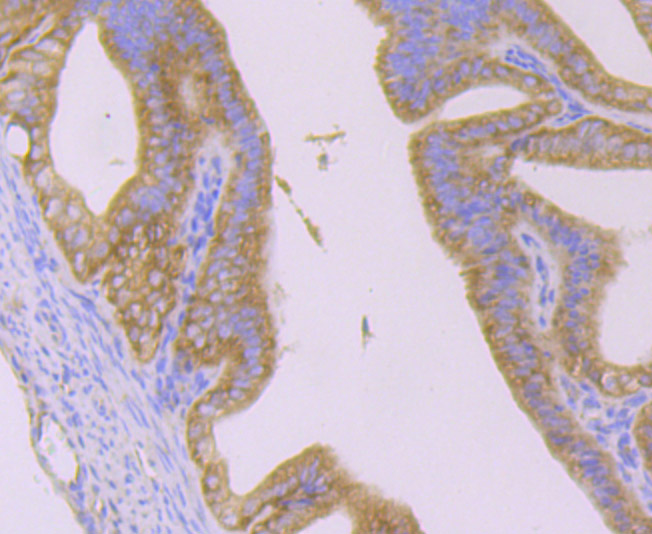
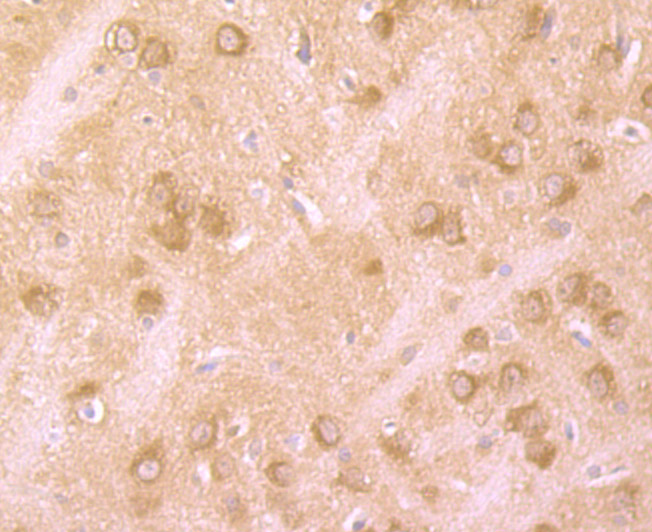
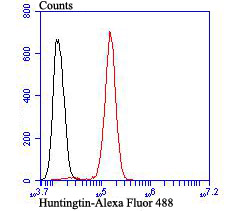
The huntingtin gene, also called the HTT or HD (Huntington disease) gene, is the IT15 ("interesting transcript 15") gene, which codes for a protein called the huntingtin protein. It is variable in its structure, as the many polymorphisms of the gene can lead to variable numbers of glutamine residues present in the protein. The mass of huntingtin protein is dependent largely on the number of glutamine residues it has, the predicted mass is around 350 kDa. Normal huntingtin is generally accepted to be 3144 amino acids in size. The exact function of this protein is not known, but it plays an important role in nerve cells. Within cells, huntingtin may be involved in signaling, transporting materials, binding proteins and other structures, and protecting against programmed cell death (apoptosis). The huntingtin protein is required for normal development before birth. It is expressed in many tissues in the body, with the highest levels of expression seen in the brain.