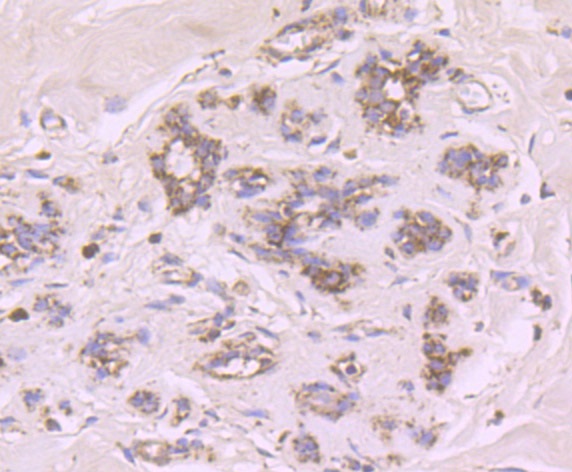
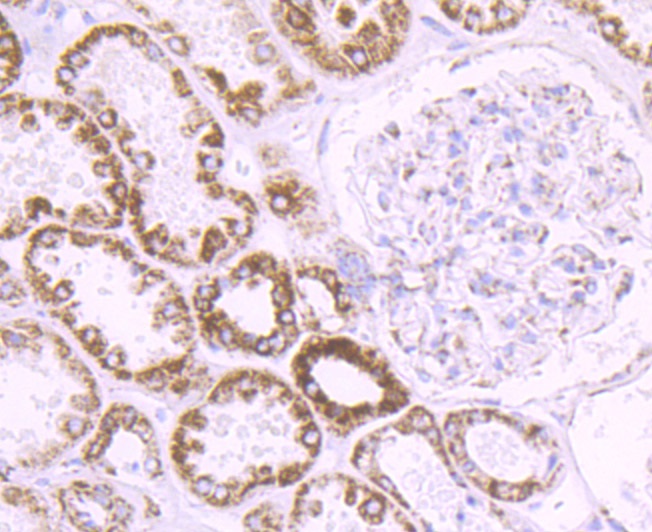
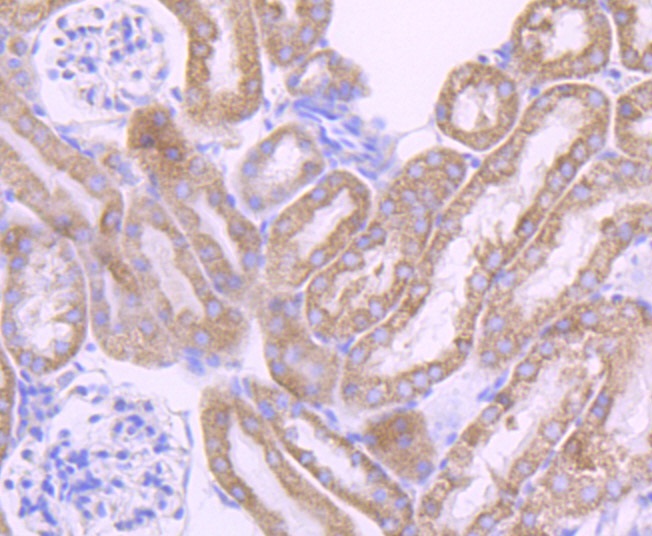
The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. P450 enzymes are classified into subfamilies, such as CYP1A, CYP2A, CYP2C, CYP2D, CYP4A14, CYP7A, CYP7B, CYP8B, CYP11A, CYP17A1, CYPI9 and CYP27A, based on sequence similarities. CYP17A (17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase) is important for the conversion of pregnenolone and progesterone to dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and androstenedione. In this process, it catalyzes both the 17-alpha-hydroxylation and the 17,20-lyase reaction. CYP17A1 is crucial during sexual development, both during fetal development and during puberty, and is intracellularly regulated by cAMP levels. Defects in the CYP17A1 gene, which encodes for the protein, may cause adrenal hyperplasia type V (AH-V) which is characterized by hypokalemia and hypertension. Male patients affected by AH-V do not undergo normal sexual differentiation and develop female external genitalia and do not undergo pubertal develoment.