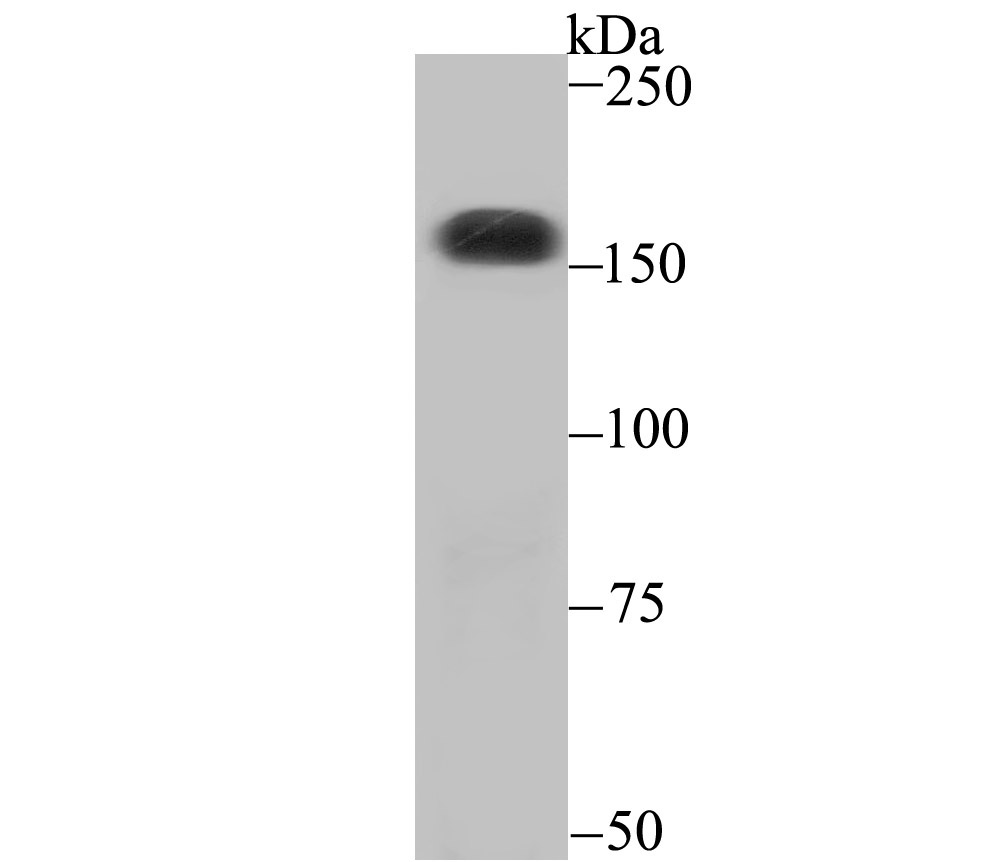
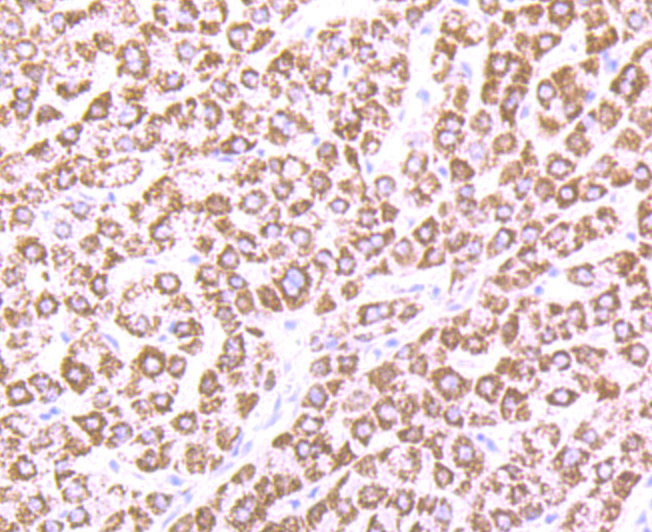
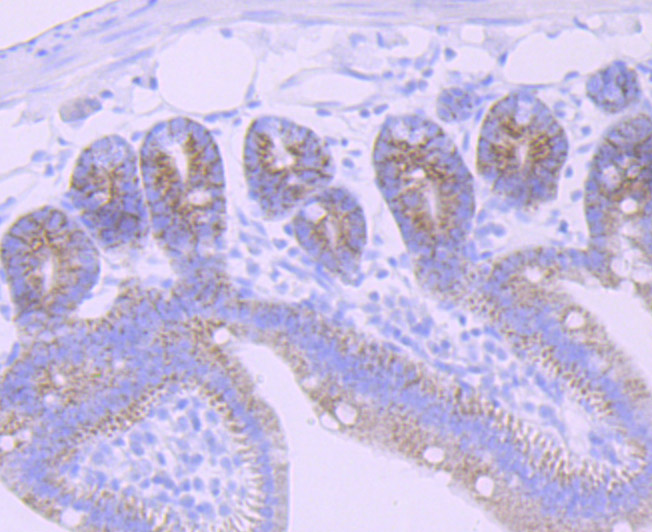
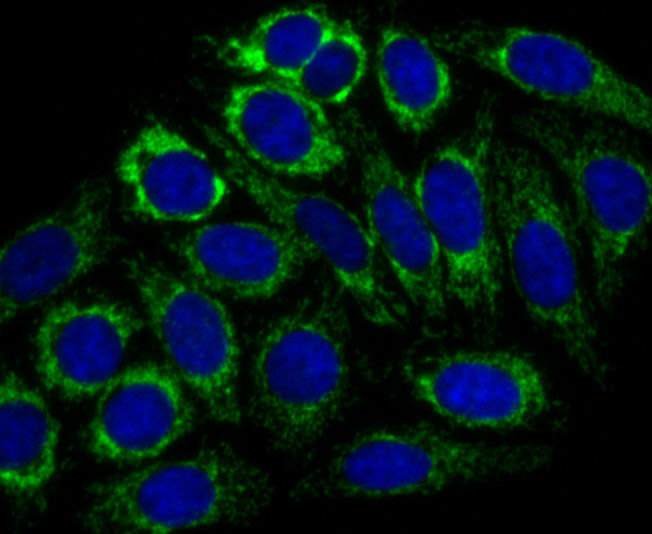
The multicomplex protein, carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase-aspartate carbamoyl transferase-dihydro-orotase (CAD), consists of three distinct proteins, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 2 (CPS2), aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydro-orotase, which catalyze the second and third steps of pyrimidine biosynthesis. CAD is allosterically regulated by the phosphorylation of CPS2 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, and this activation enables CPS2 to catalyze the rate-limiting step of pyrimidine synthesis. CAD is expressed in brain and skeletal muscle. A related protein, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) is expressed in liver. CPS1 catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the urea cycle, and deficiency of CPS1 is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes hyperammonemia.