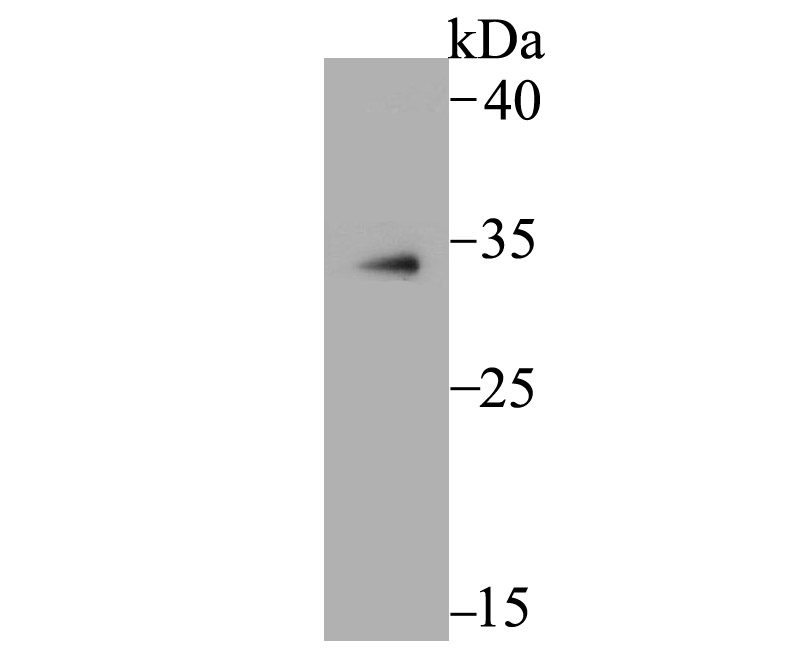
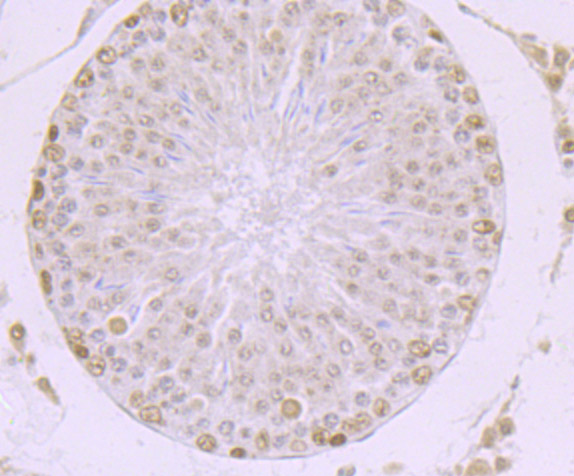
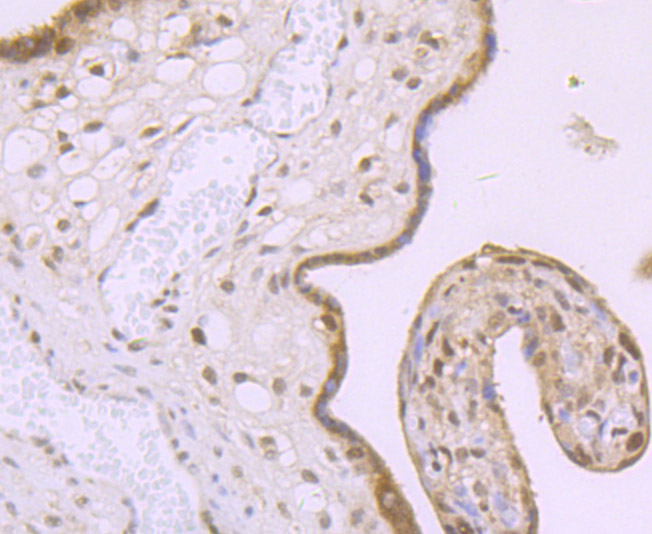
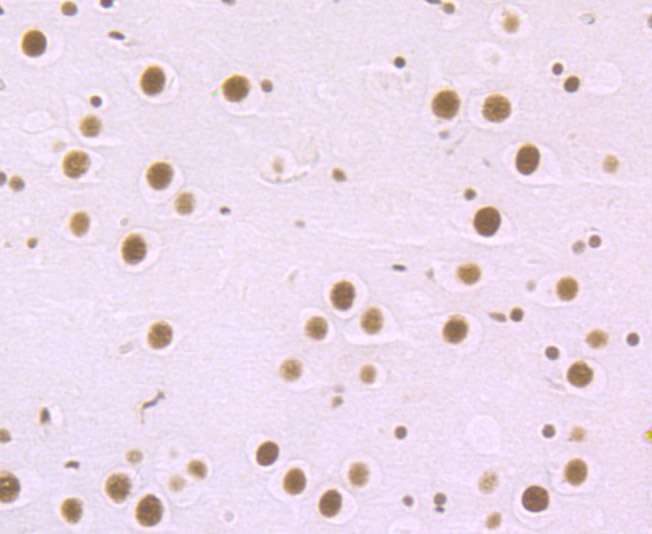
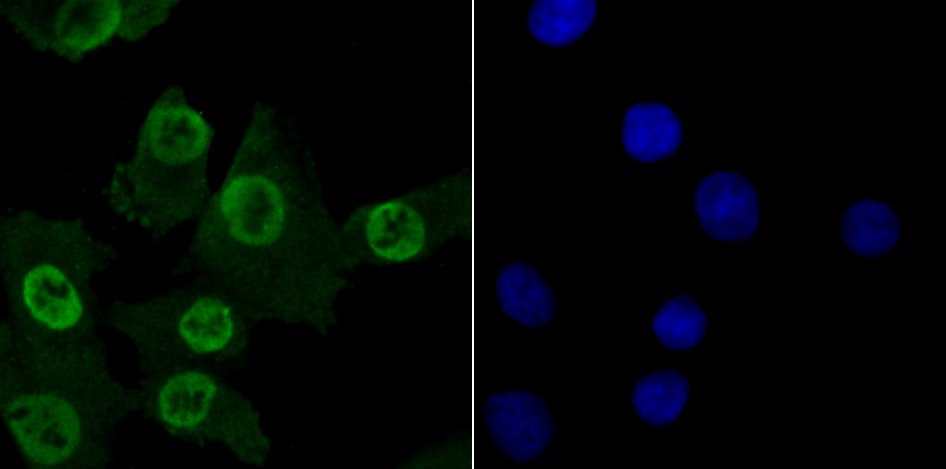
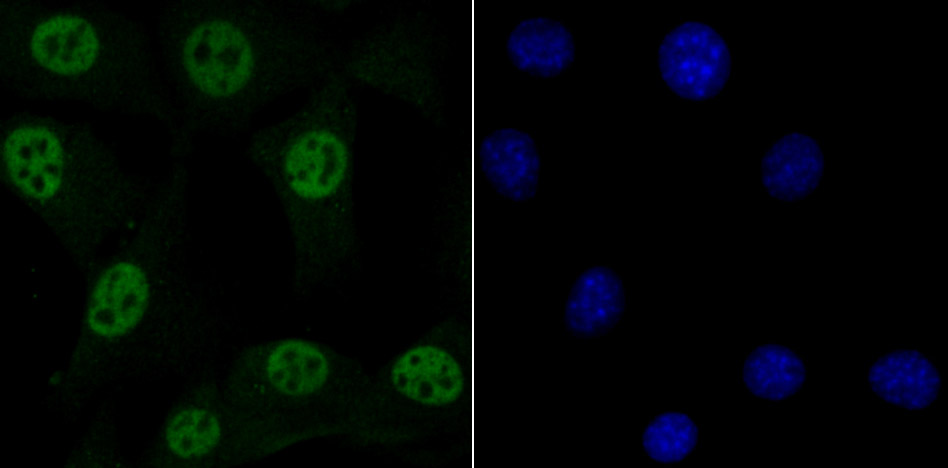
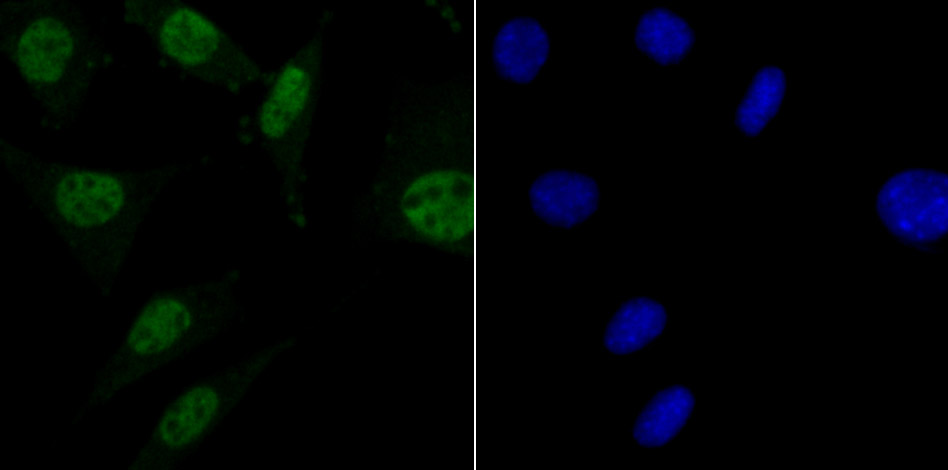
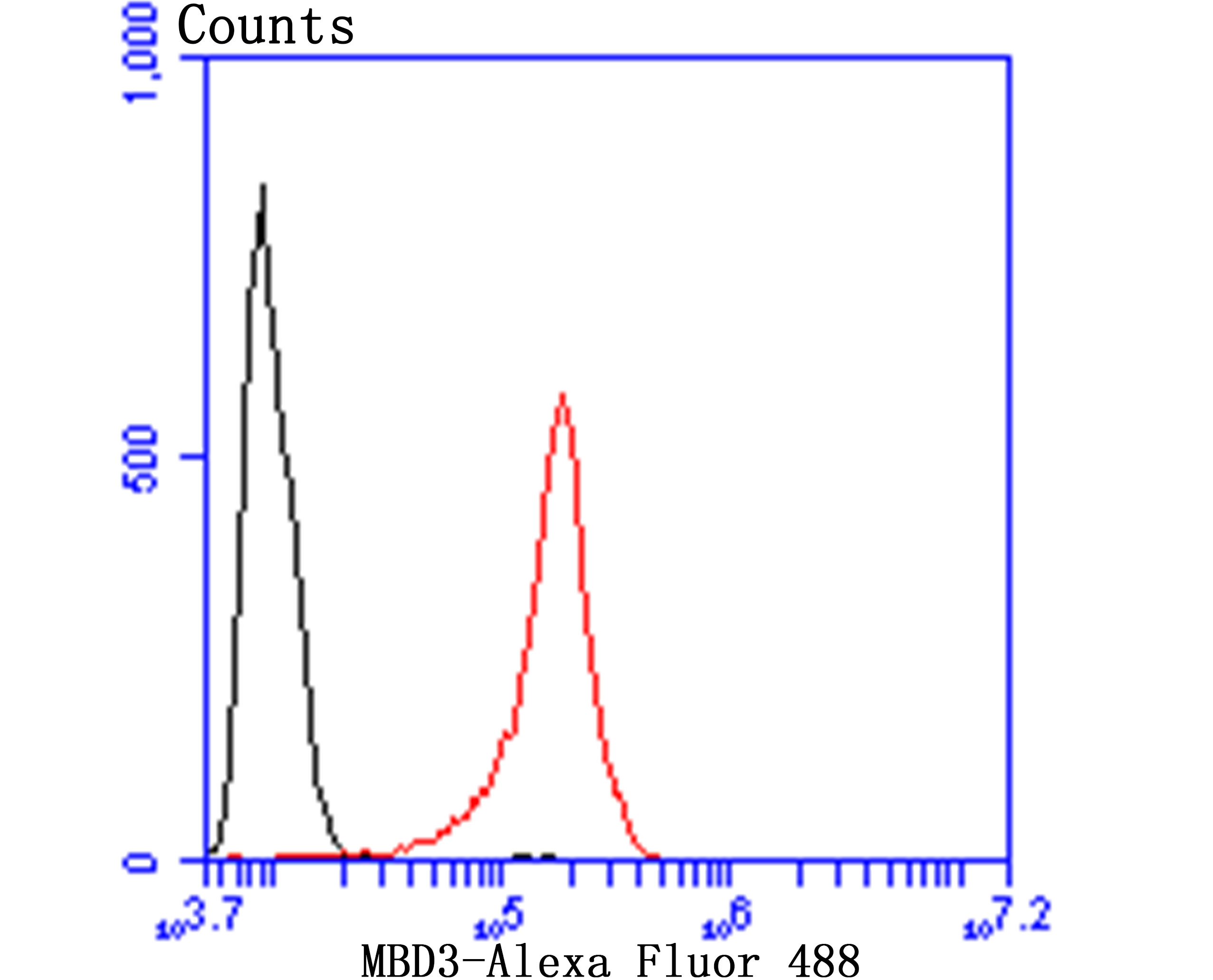
Methylation of DNA contributes to the regulation of gene transcription in both mammalian and invertebrate systems. DNA methylation predominates on cytosine residues that are present in dinucleotide motifs consisting of a 5 cytosine followed by guanosine (CpG), and it requires the enzymatic activity of DNA methyltransferase, which results in transcriptional repression of the methylated gene. Several proteins have been identified that associate with the methyl-CpG sites, and they include methyl-CpG binding protein-1 (MBD1), MBD2, MBD3, MBD4 and MeCP2. Expression of the MBD proteins is highest in somatic tissues.