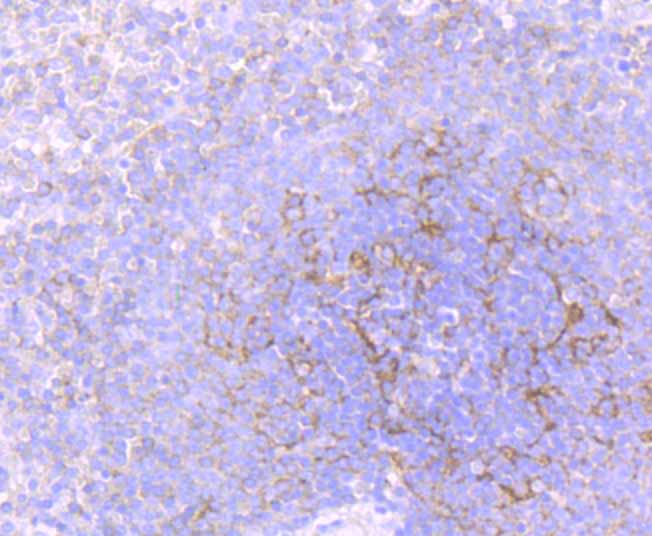
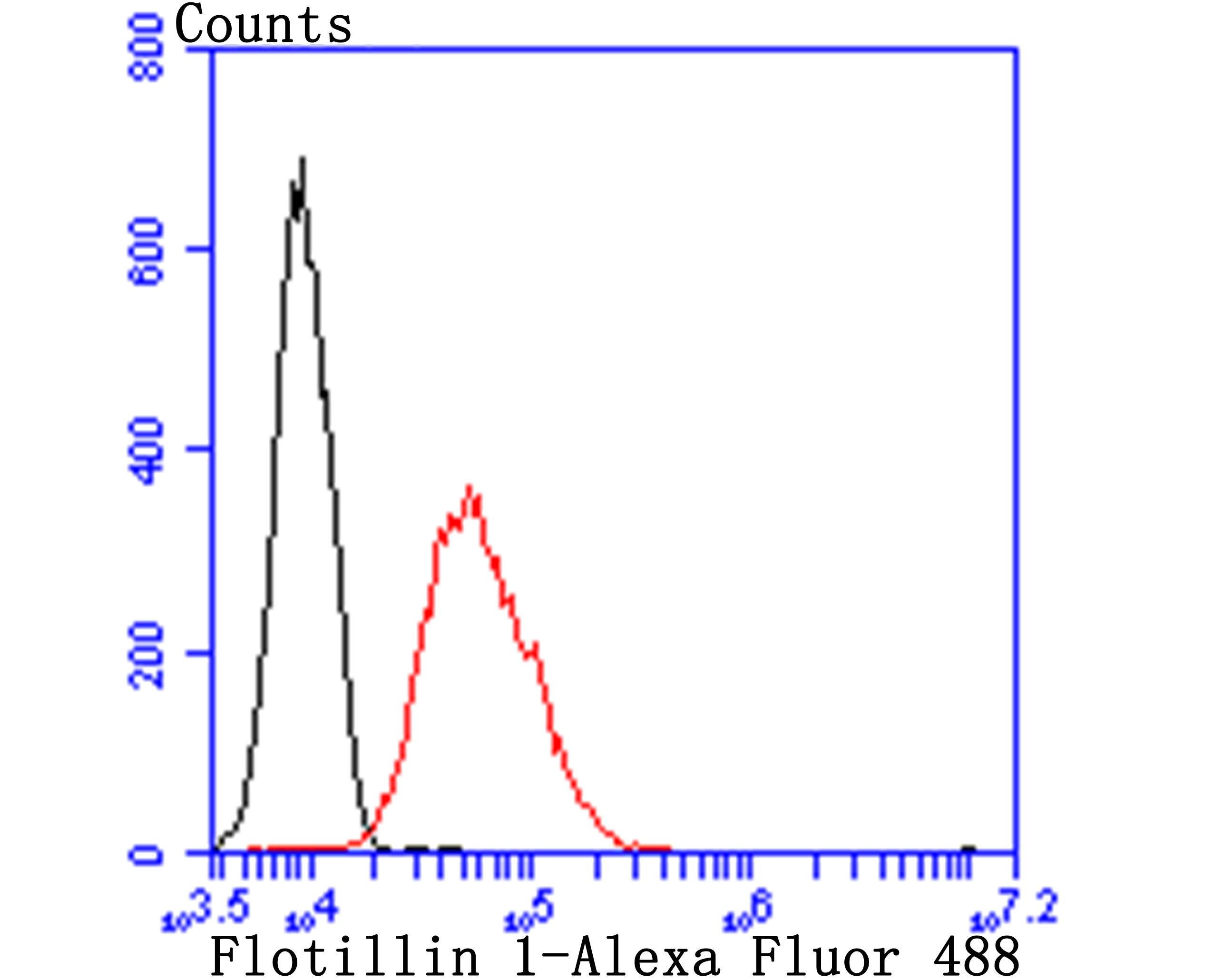
Lipid rafts are sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains that are insoluble in nonionic detergents. Lipid rafts are important for numerous cellular processes, including signal transduction, membrane trafficking and molecular sorting. Flotillins are lipid raft components in neurons and caveloae-associated proteins in A498 kidney cells. Flotillin-1 belongs to the band 7.2/stomatin protein family, whose members are characterized by the presence of a hydrophobic N-terminal region that is predicted to form a single, outside to inside, transmembrane domain. Flotillin-1 and -2 have complementary tissue distributions and their expression levels are independently regulated. At the cellular level, Flotillin-2 is ubiquitously expressed, whereas Flotillin-1 is expressed in A498 kidney cells, muscle cell lines and fibroblasts. Flotillins form a ternary complex with CAP and Cbl, directing the localization of the CAP-Cbl complex to a lipid raft subdomain of the plasma membrane. Association of ER-X with Flotillin localizes ER-X within plasma membrane caveloae and mediates rapid oestrogen activation of the MAP kinase cascade. The expression of the flotillins is also correlated to the progression of Alzhemier pathology.