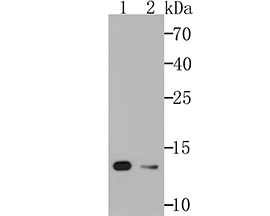
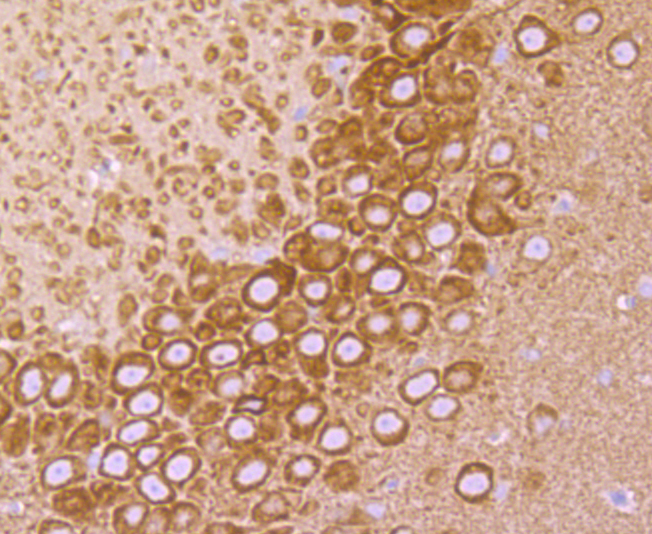
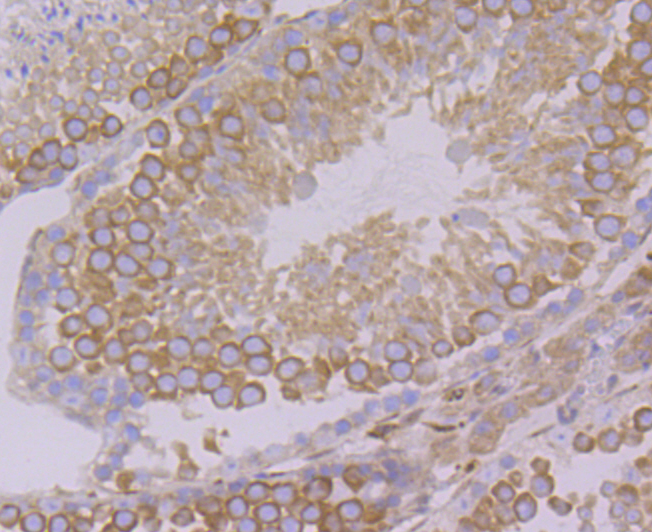
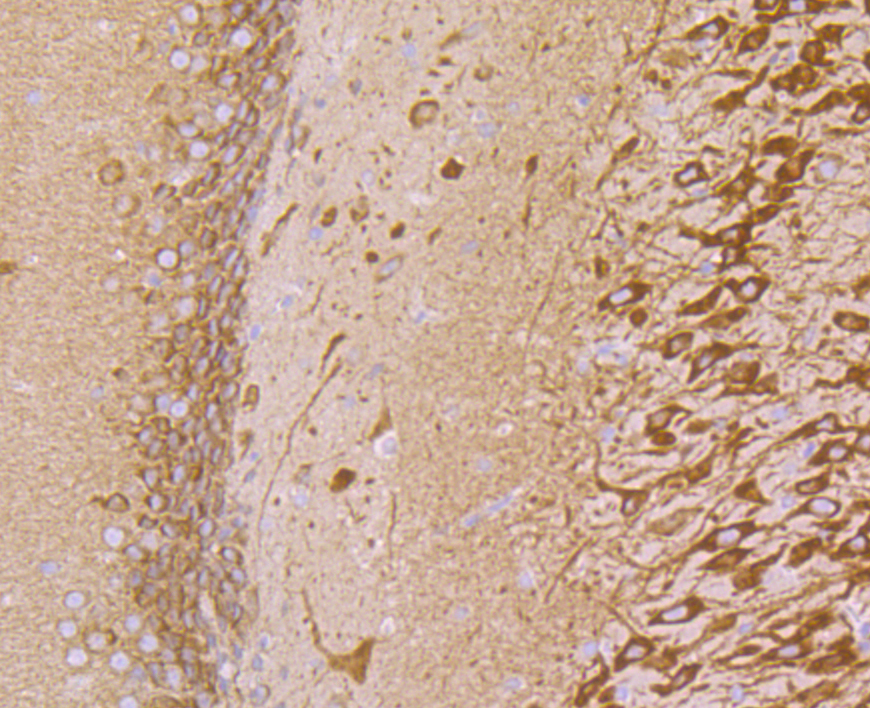
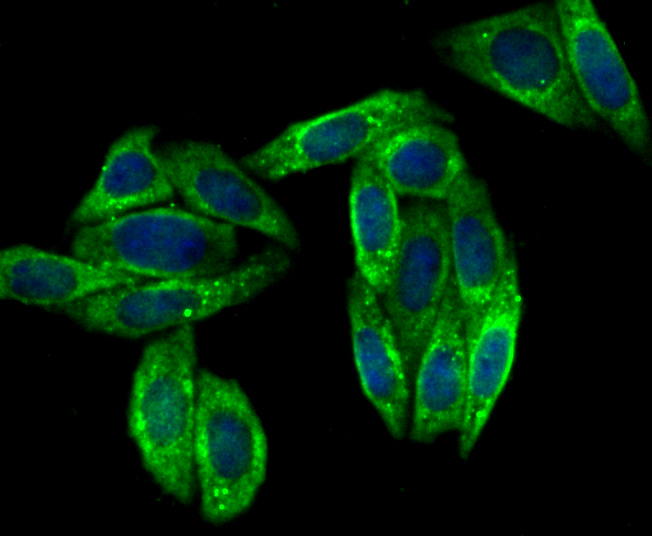
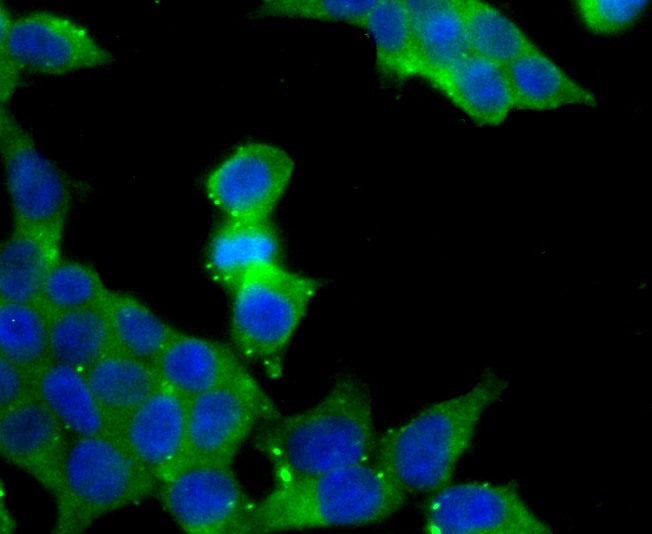
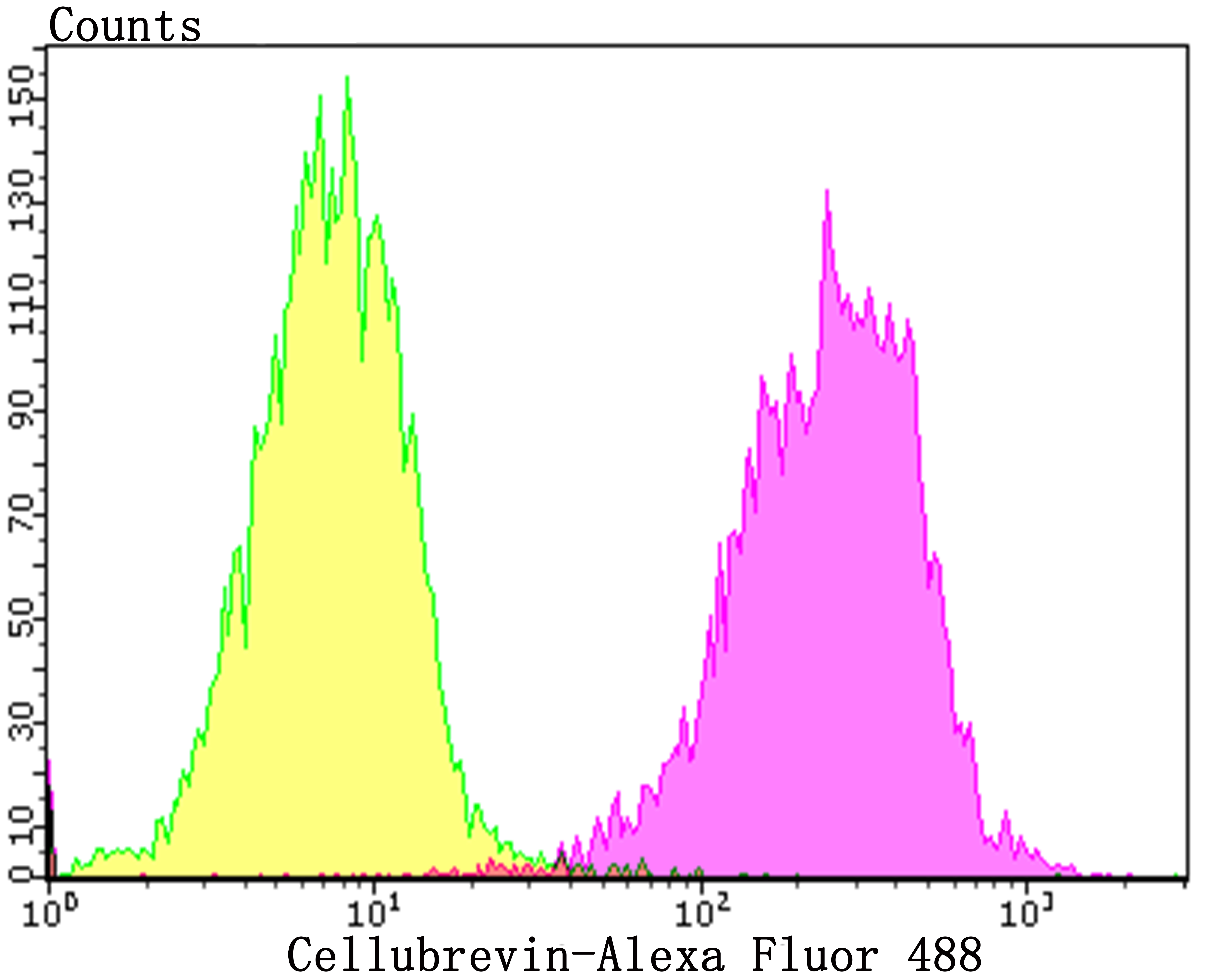
Vesicle-associated membrane proteins, known as VAMPs, also designated synaptobrevins, include VAMP-1, VAMP-2, VAMP-3 (cellubrevin), and synaptotagmin, a protein that may function as an inhibitor of exocytosis. VAMP proteins are vesicular factors that are important components of the machinery controlling docking and/or fusion of secretory vesicles with their target membrane. Synaptosomal-associated proteins, known as SNAPs, including alpha- and gamma-SNAP, are cytoplasmic proteins that bind to a membrane receptor complex composed of VAMP, SNAP 25 and syntaxin. Pancreatic beta-cells express VAMP-2 and VAMP-3, and either one or both of these proteins selectively control Ca2+-mediated insulin secretion. In addition, VAMP-2 and VAMP-3 are expressed on GLUT4-containing vesicle membranes isolated from 3T3-Ll adipocytes and are important components of the insulin-dependent translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface in adipocytes.