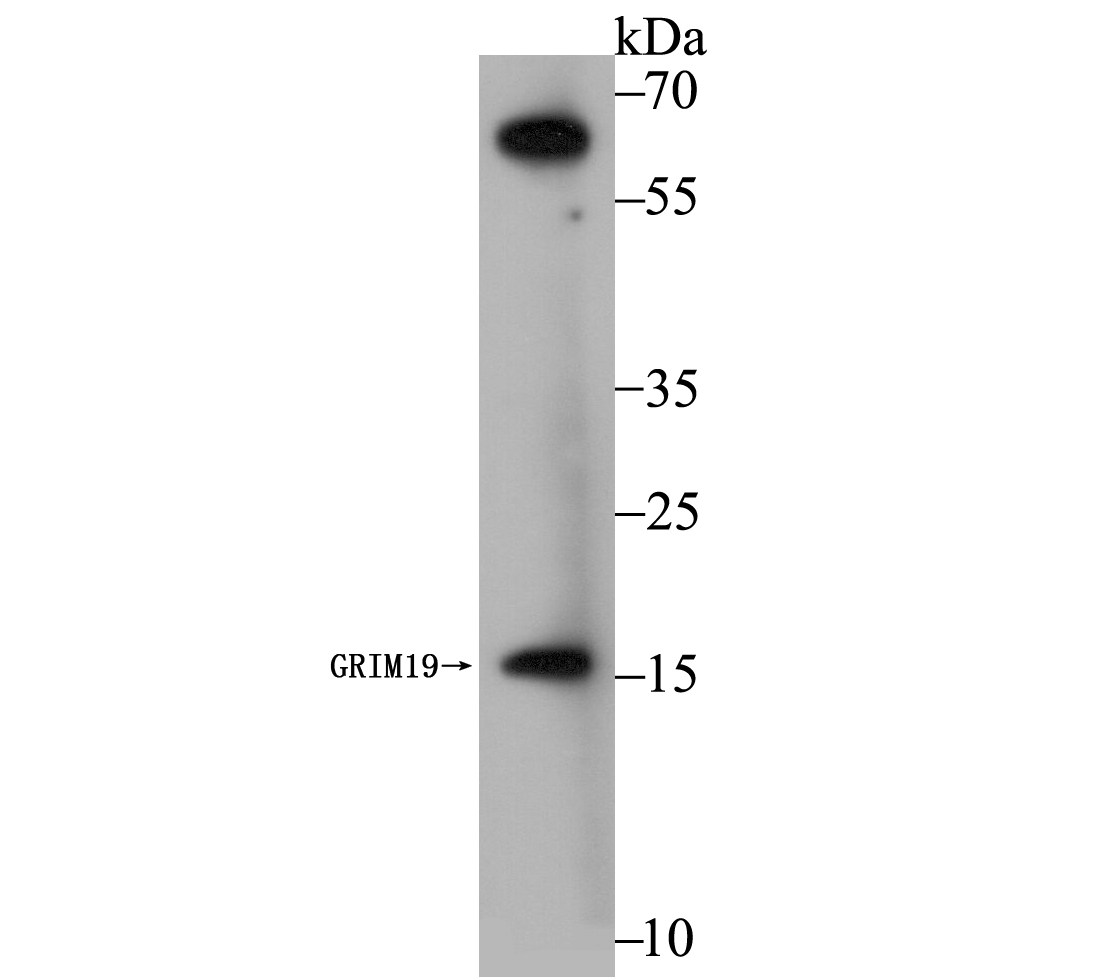
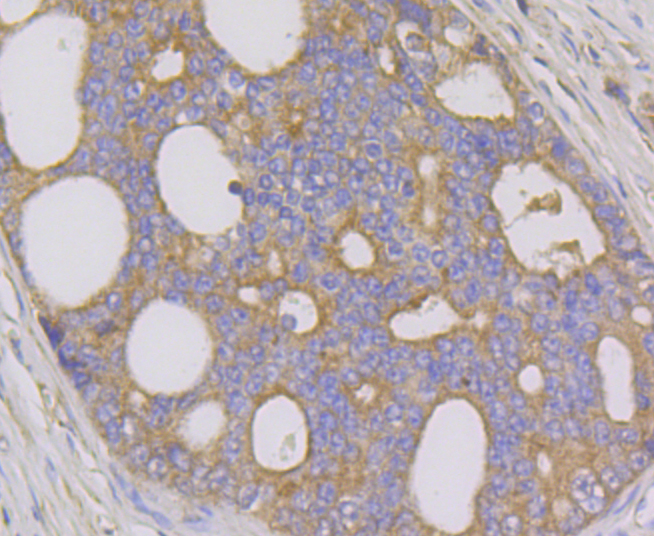
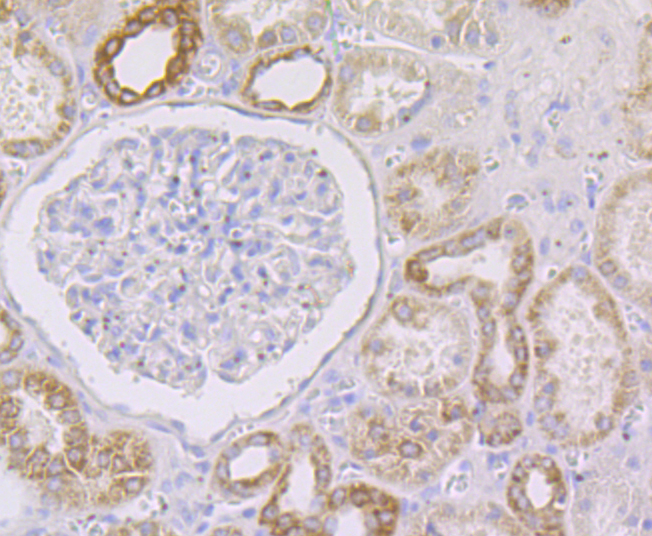
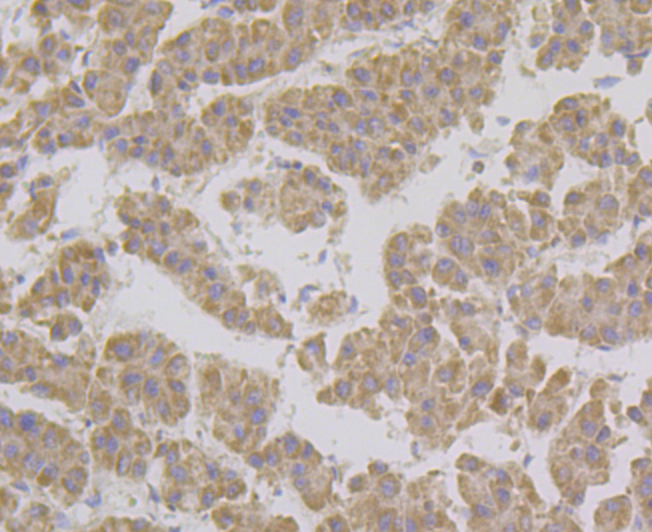
The GRIM family of proteins appear to be novel types of tumor suppressors. Grim19, which stands for gene associated with retinoic-interferon-induced mortality 19 protein, is also designated cell death-regulatory protein Grim-19 or NADH dehydrogenase ubiquinone 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 13. The Grim19 protein plays two roles within the cell. As a member of the interferon-beta and retinoic acid-induced pathway of cell death, Grim19 induces apoptosis. As part of the mitochondrial complex I, Grim19 is essential for its assembly and electron transfer activity. It transfers electrons to the respiratory chain from NADH and plays a role in the interferon/all-trans-retinoic acid (IFN/RA) cell death pathway. It localizes primarily to the mitochondrion, but may translocate to the nucleus upon IFN/RA treatment. Grim19 may also be useful as a biological marker or target for drug development.