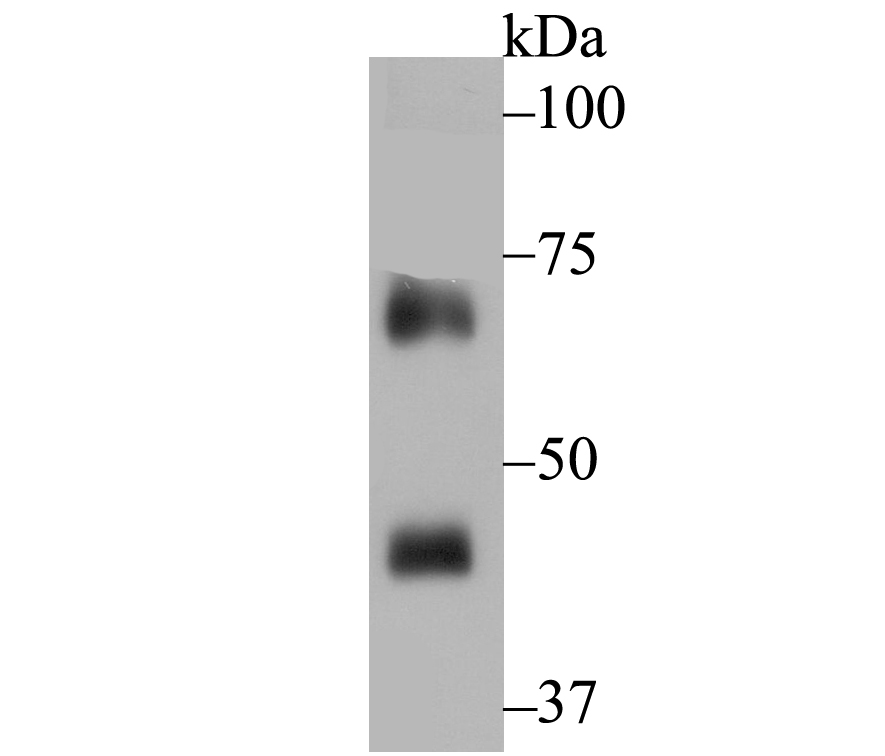
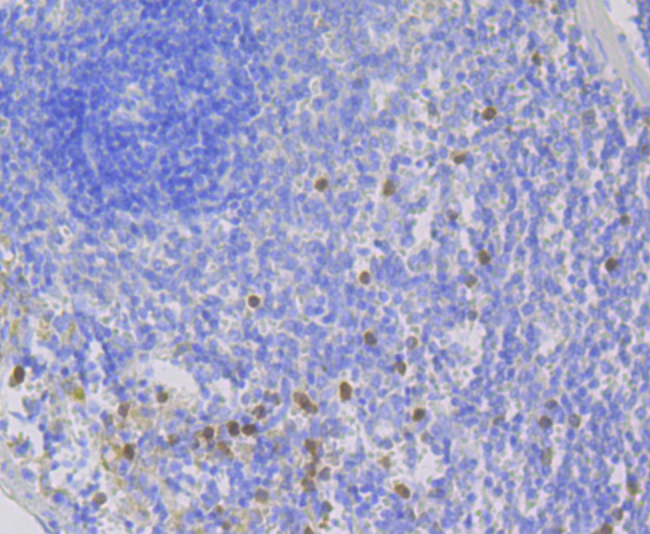
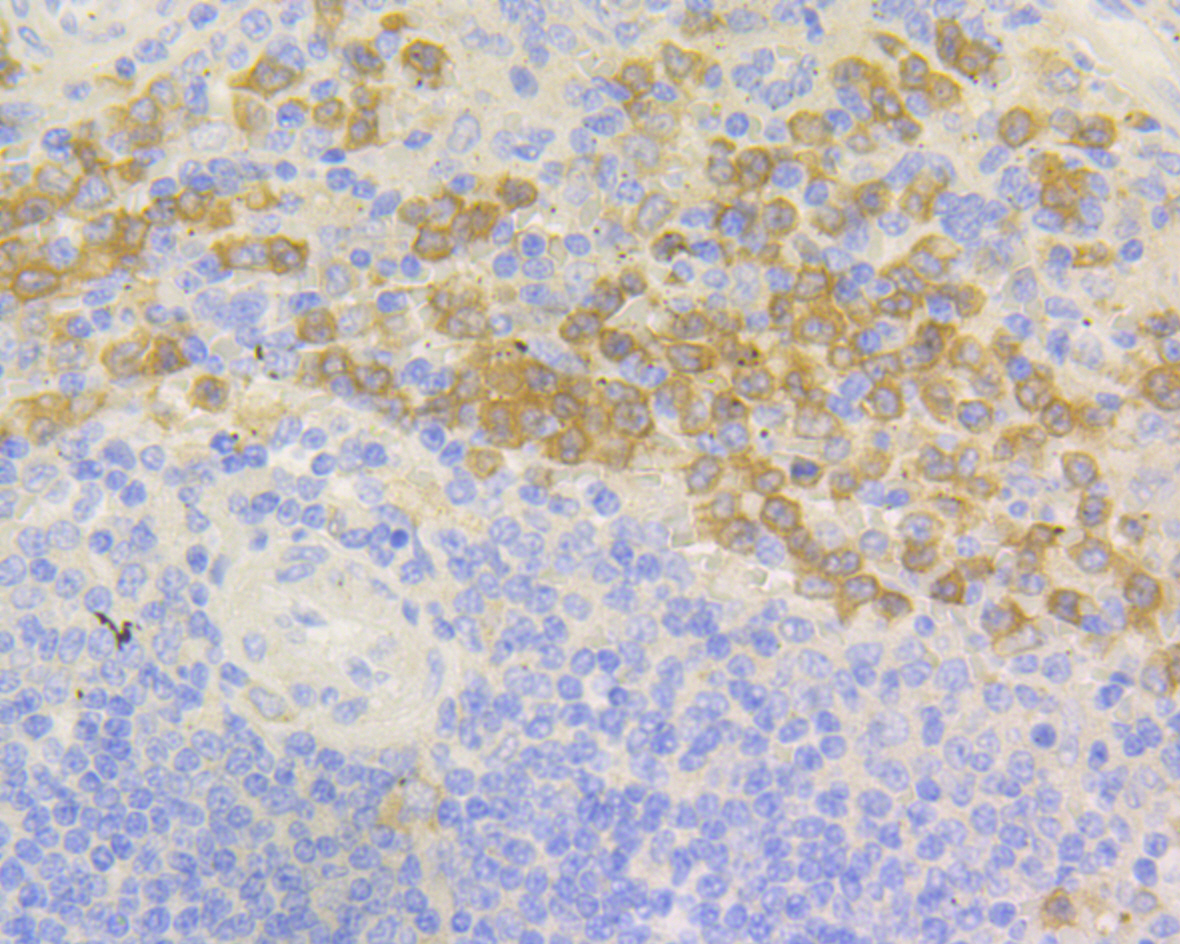
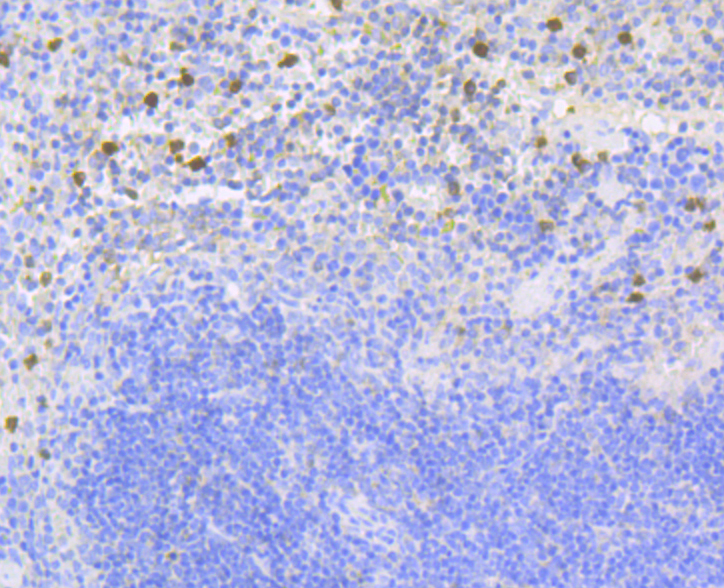
The heredity disease chronic granulomatous disease (CGF) has been linked to mutations in p47phox and p67phox. The cytosolic proteins p47phox and p67phox, also designated neutrophil cytosol factor 1(NCF1) and NCF2, respectively, are required for activation of the superoxide-producing NADPH oxidase in neutrophils and other phagocytic cells. During activation of the NADPH oxidase, p47phox and p67phox migrate to the plasma membrane where they associate with cytochrome b558 and the small G protein Rac to form the functional enzyme complex. Both p47phox and p67phox contain two Src homology 3 (SH3) domains. The C-terminal SH3 domain of p67phox has been shown to interact with the proline rich domain of p47phox, suggesting that p47phox may faciliate the transport of p67phox to the membrane.