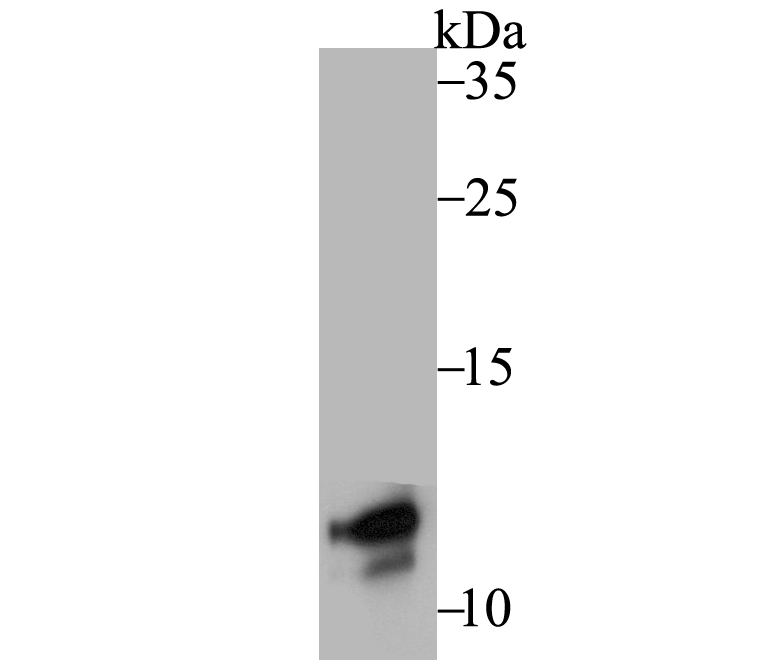
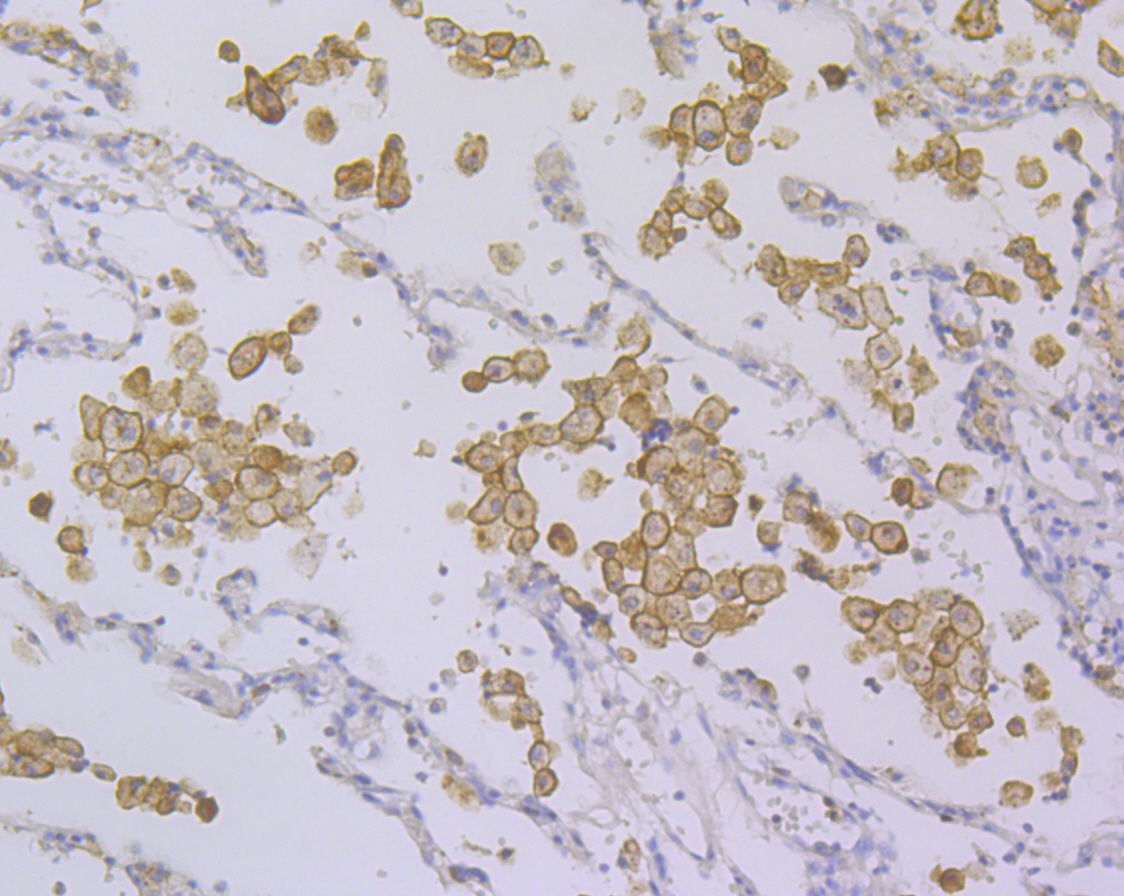
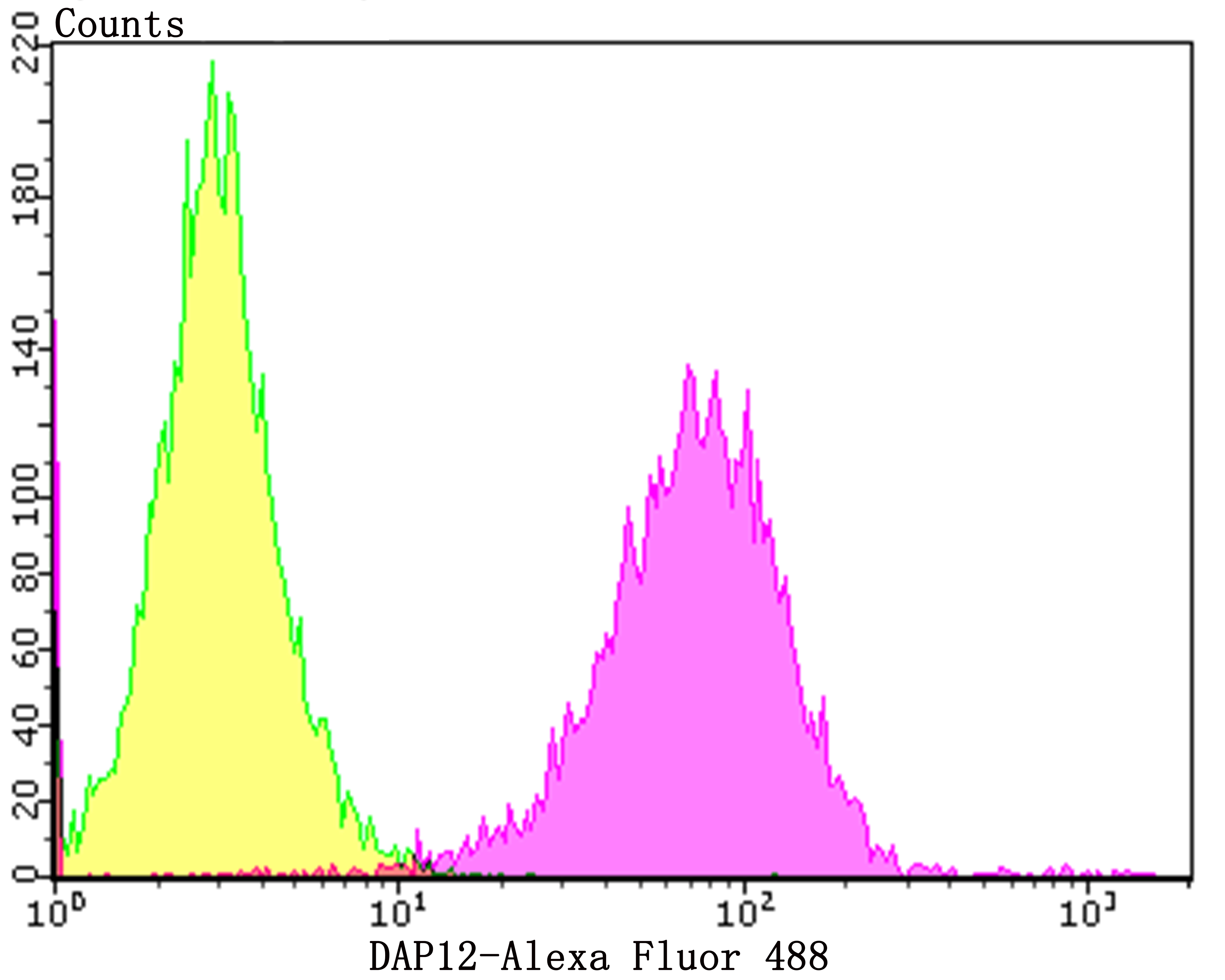
Natural killer (NK) cells are regulated by stimulatory and inhibitory signals from a variety of receptors. Three main receptor families are responsible for NK cells recognition of MHC I molecules, including Ly-49, CD94/NKG2 and KIR (killer-cell inhibitory receptor). DAP12 is a phosphoprotein that is involved in the activation of NK cells. This protein interacts with membrane glycoproteins of the KIR family, resulting in cellular activation. DAP12 also binds to CD94/NKG2C, an activating NK cell receptor belonging to the C-type lectin superfamily. Additional proteins that bind to DAP12 include Ly-49D and Ly-49H, which associate with DAP12 in the plasma membrane. Phosphorylated DAP12 binds to ZAP-70 and Syk, suggesting that the activation pathway may be similar to that of the T and B cell antigen receptors.