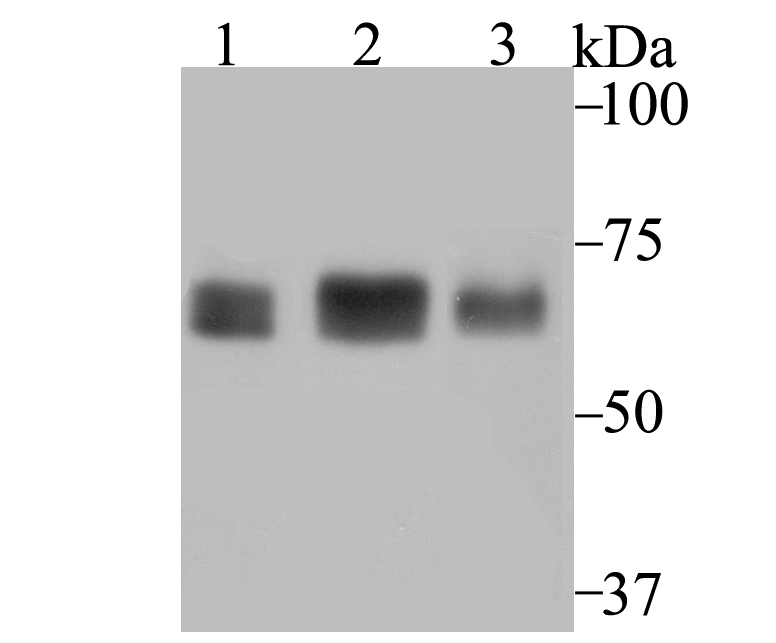
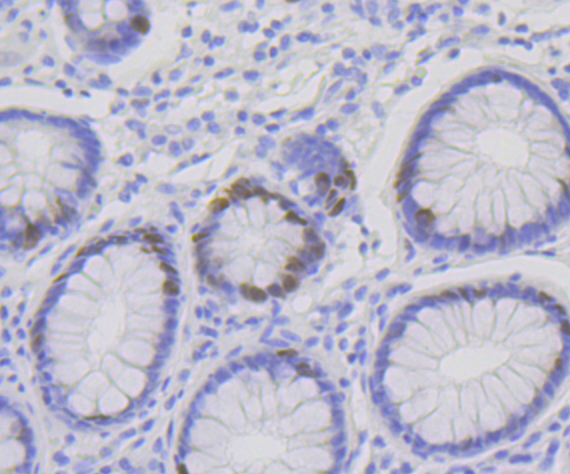
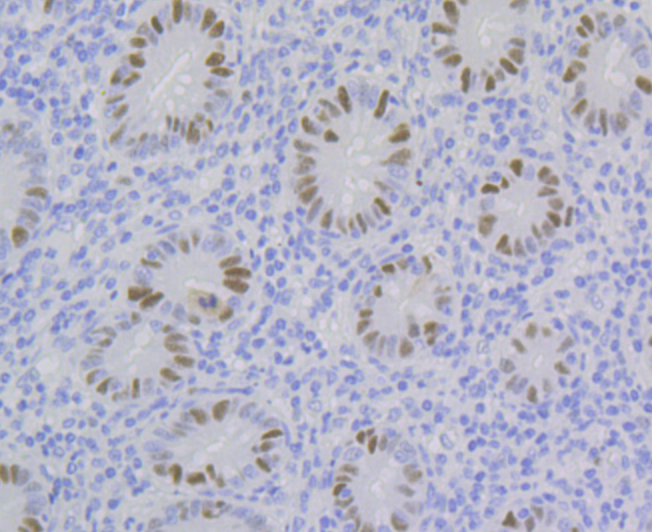
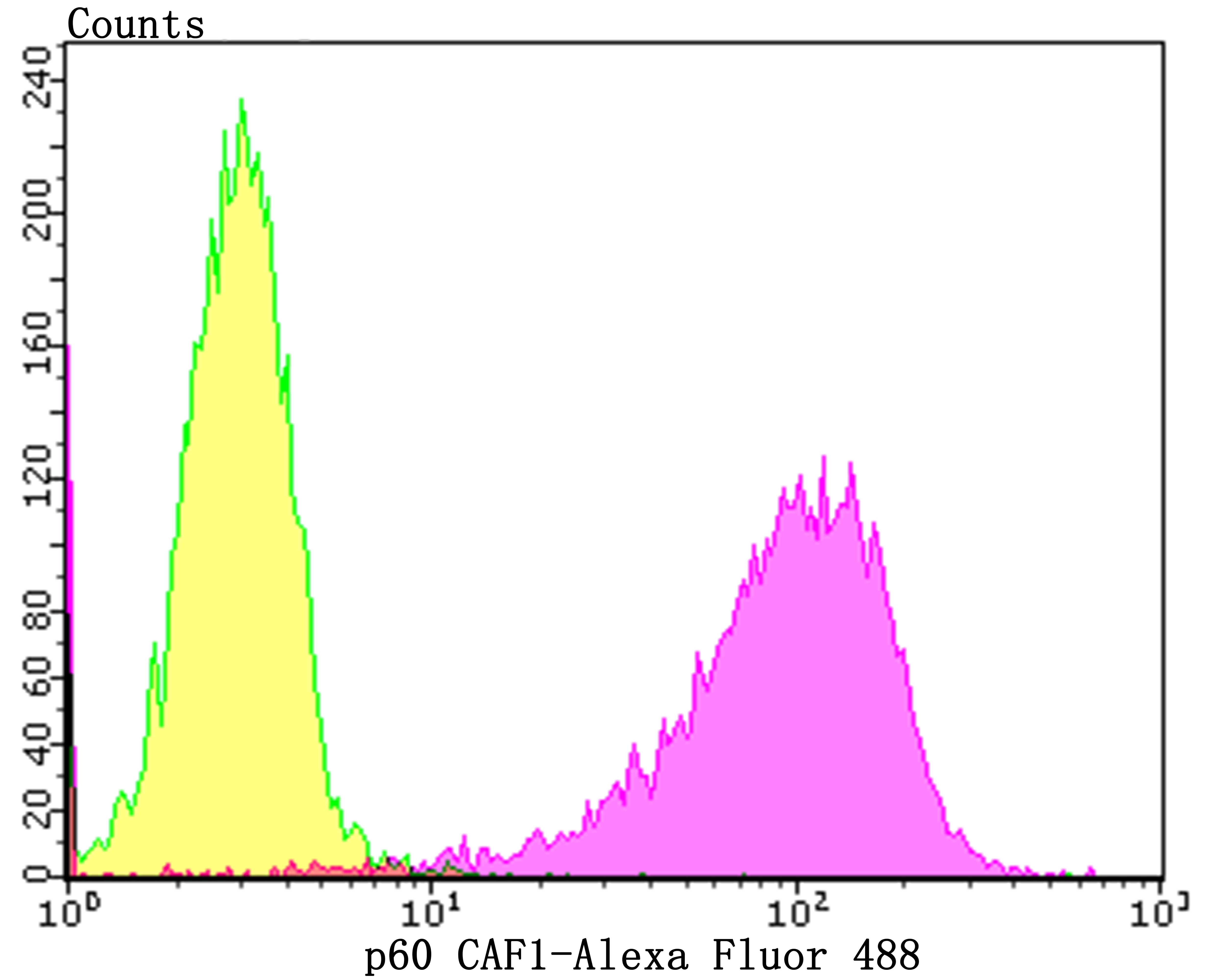
Chromatin assembly factor-1 (CAF-1) is a multisubunit protein complex that comprises three polypeptide subunits known as p150, p60, and p48. CAF-1 is a nucleosome assembly factor that deposits newly synthesized and acetylated histones H3/H4 into nascent chromatin during DNA replication. The p150 subunit of CAF-1 also supports the maintenance of heterochromatin, which requires the synthesis of both new histones and heterochromatin proteins and their orderly assembly during DNA replication. Heterochromatin is characterized as densely coiled chromatin that generally replicates late during S phase, has a low gene density, and contains large blocks of repetitive DNA that is relatively inaccessible to DNA-modifying reagents. In late S phase, p150 directly associates with heterochromatin associated proteins 1 (HP1α, HP1β and HP1γ). As cells prepare for mitosis, CAF-1 p150 and some HP1 progressively dissociate from heterochromatin, coinciding with the phosphorylation of histone H3. The HP1 proteins reassociate with chromatin at the end of mitosis, as histone H3 is dephosphorylated.