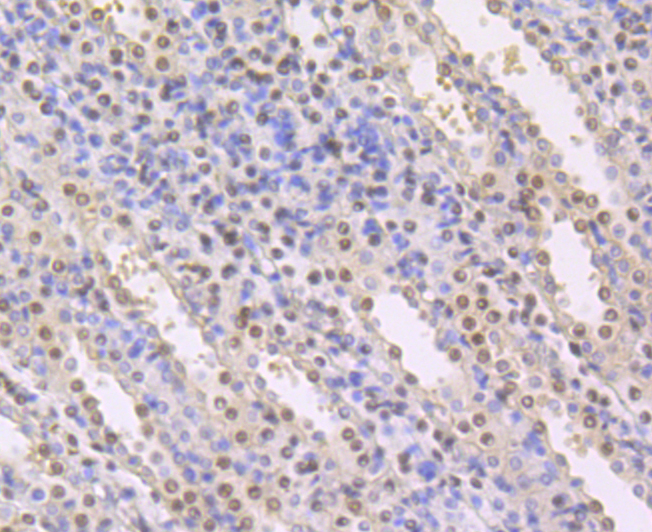
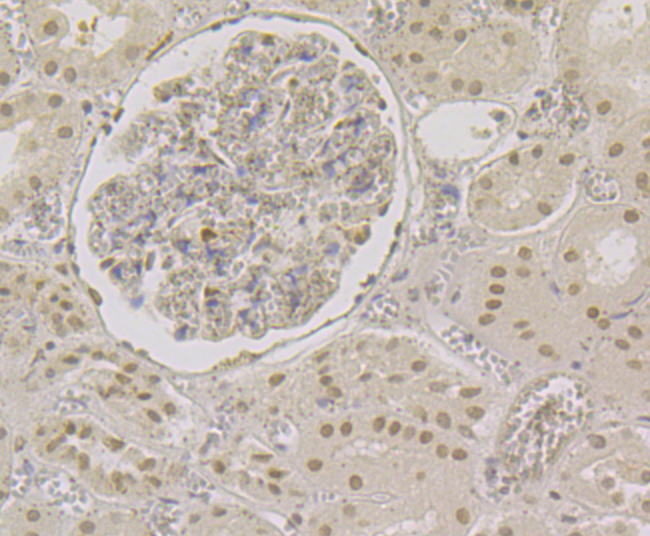
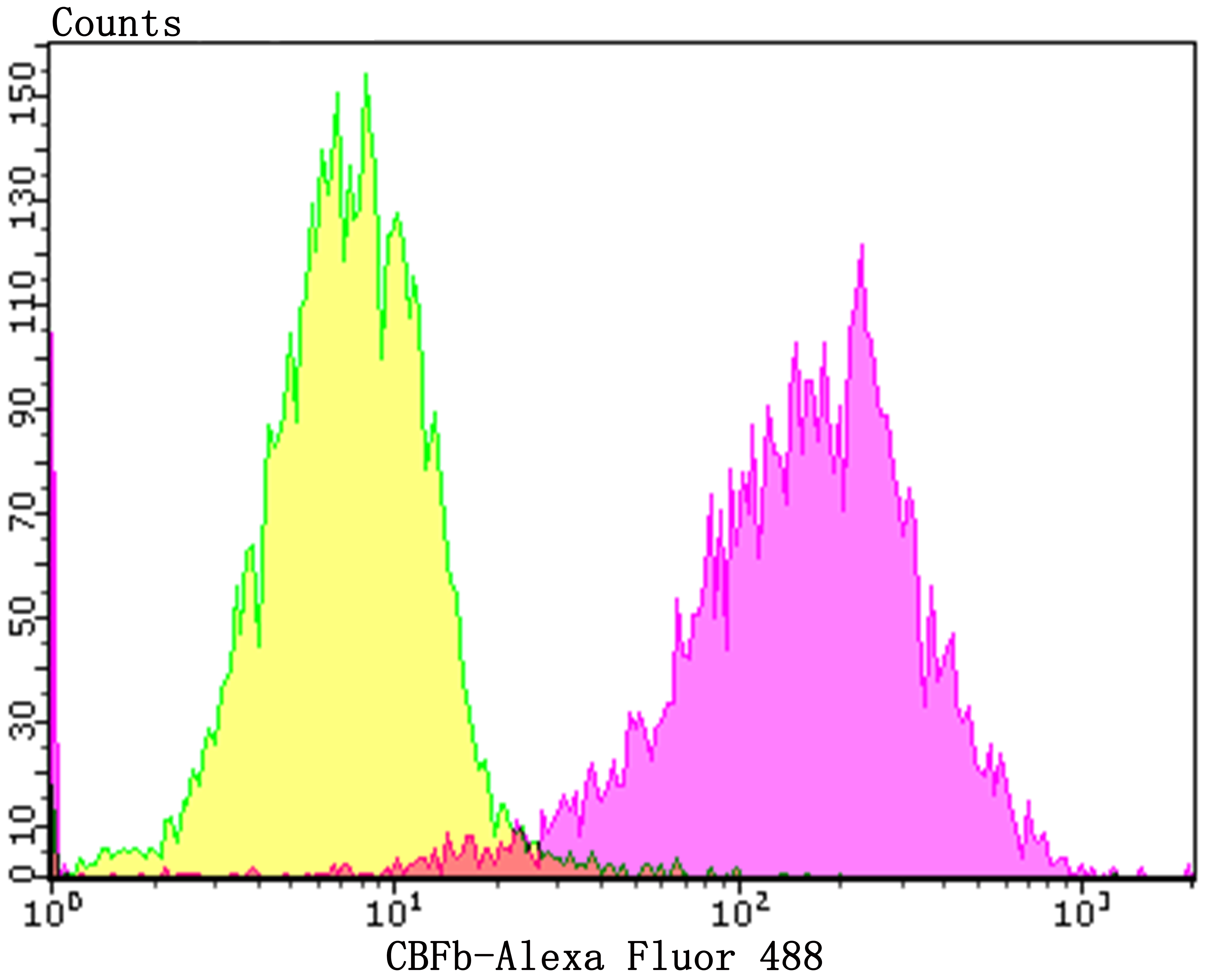
The transcription factor Polyomavirus enhancer binding protein 2 (PEBP2), also designated Osf2 (Osteoblast-specific transcription factor), CBFA1 (Core Binding Factor) and AML3 (Acute myeloid leukemia), is composed of two subunits, a and b, which are essential for the regulation of hematopoiesis and osteogenesis. The PEBP2a subunits, PEBP2aA, PEBP2aB and PEBP2aC, are encoded by three RUNX genes, all of which contain a 128-amino acid region homologous to the highly conserved Drosophila segmentation gene, Runt. This region is involved in DNA binding and heterodimerization with the regulatory b subunit, which facilitates DNA binding of the a subunit. Both subunits are required for in vivo function; the disruption of either gene results in a lack of definitive hematopoiesis followed by embryo death in utero due to hemorrhage in the central nervous system. The gene encoding PEBP2b is the target of chromosomal inversion 16 (p13;q22) with the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, producing a chimeric gene, PEBP2b/CBFB-SMMHC, that is associated with human acute myeloid leukemia.