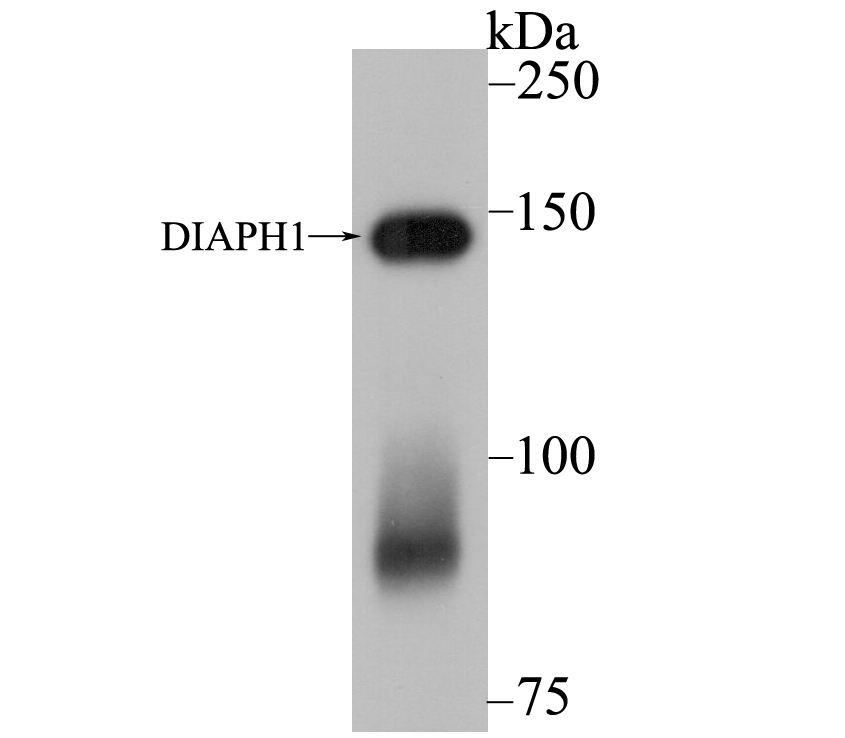
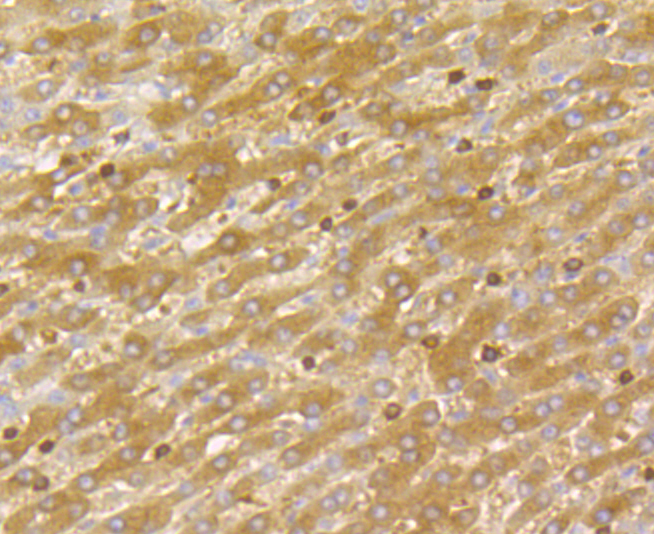
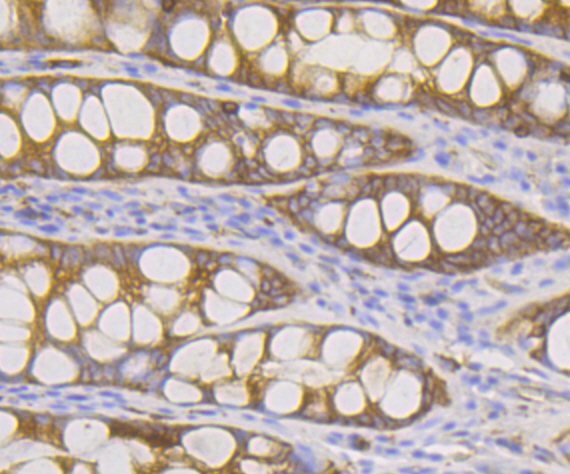
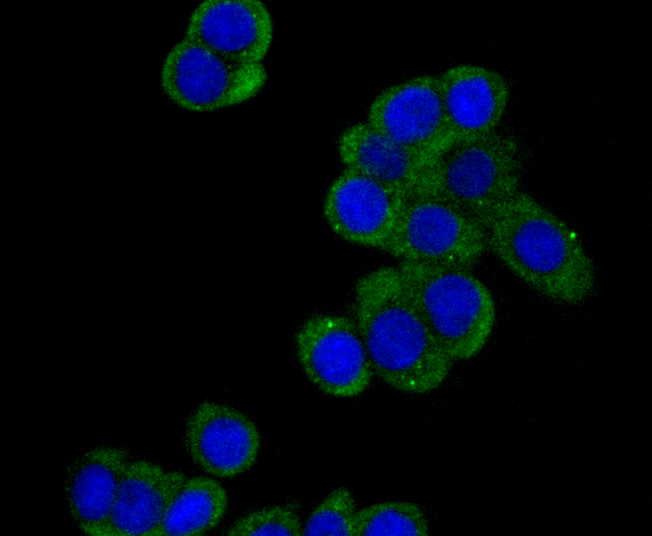
Dia 1, also known as DIAPH1 (diaphanous homolog 1) or DRF1, a mammalian homolog of the Drosophila diaphanous gene, belongs to a family of formin homology (FH) proteins which are characterized by having tandemly aligned FH1 (formin homology 1) and FH2 (formin homology 2) domains in their carboxy terminal regions. Dia 1 contains a DAD (diaphanous autoregulatory) domain, which is involved in the elongation of actin filaments, and a GBD/FH3 (Rho GTPase-binding/formin homology 3) domain, which interacts with the DAD domain via autoinhibitory interactions to regulate the activation of Dia 1. Dia 1 is required for the assembly of F-actin structures, and regulates the polymerization and depolymerization of actin filaments. Localizing to the cell membrane, Dia 1 is expressed in a wide range of tissues, including brain, heart, lung and kidney. Defects to the gene encoding Dia 1 have been linked to deafness autosomal dominant type 1 (DFNA1), a disorder characterized by sensorineural hearing loss..