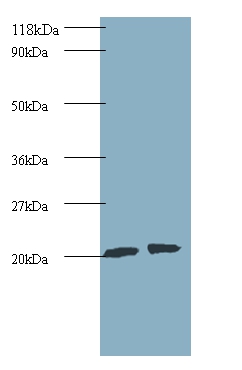
The ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) family comprises a group of structurally and functionally conserved 21 kDa proteins, which are members of the Ras superfamily of regulatory GTP-binding proteins. Arf is involved in intracellular protein traffic to and within the Golgi complex. Arf has a number of disparate activities including maintenance of organelle integrity, assembly of coat proteins, as a co-factor for cholera toxin and as an activator of phospholipase D. The Arf family is divided functionally into the Arf and the Arf-like (Arl) proteins. Arfs share more than 60% sequence identity, appear to be ubiquitous in eukaryotes, and are highly conserved evolutionarily.
[1]"Selective amplification of additional members of the ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) family: cloning of additional human and Drosophila ARF-like genes."Clark J., Moore L., Krasinskas A., Way J., Battey J.F., Tamkun J.W., Kahn R.A.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.