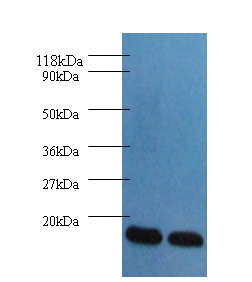
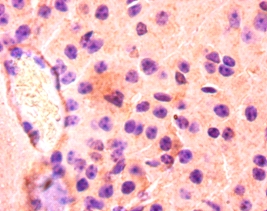
The intracellular fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) belongs to a multigene family. FABPs are divided into at least three distinct types, namely the hepatic-, intestinal- and cardiac-type. They form 14-15 kDa proteins and are thought to participate in the uptake, intracellular metabolism and/or transport of long-chain fatty acids. They may also be responsible in the modulation of cell growth and proliferation. Fatty acid-binding protein 3 gene contains four exons and its function is to arrest growth of mammary epithelial cells. FABP3 gene is a candidate tumor suppressor gene for human breast cancer.
[1] Manabe K, Kamihata H, Motohiro M, Senoo T, Yoshida S, Iwasaka T.Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein level as a predictive biomarker of contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Eur J Clin Invest. 2011 Oct 17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362. [2] Dinh