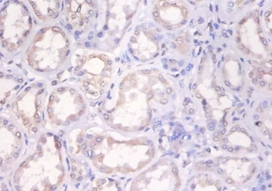
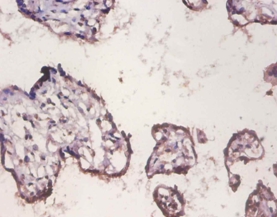
Variant histone H2A which replaces conventional H2A in a subset of nucleosomes. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Required for checkpoint-mediated arrest of cell cycle progression in response to low doses of ionizing radiation and for efficient repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) specifically when modified by C-terminal phosphorylation.
[1] "H2A.X. a histone isoprotein with a conserved C-terminal sequence, is encoded by a novel mRNA with both DNA replication type and polyA 3' processing signals."Mannironi C., Bonner W.M., Hatch C.L.Nucleic Acids Res. 17:9113-9126(1989) [2] "Cloning of