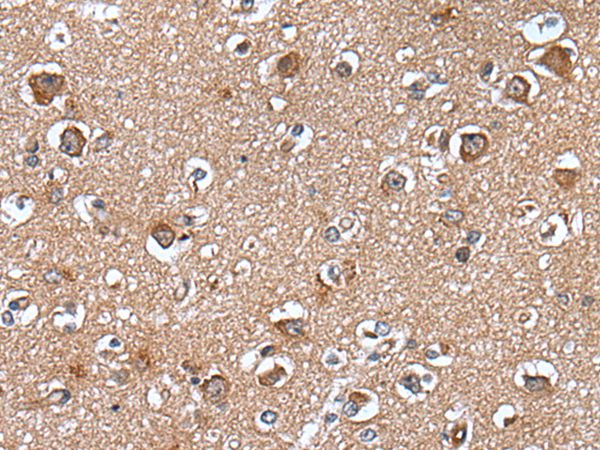
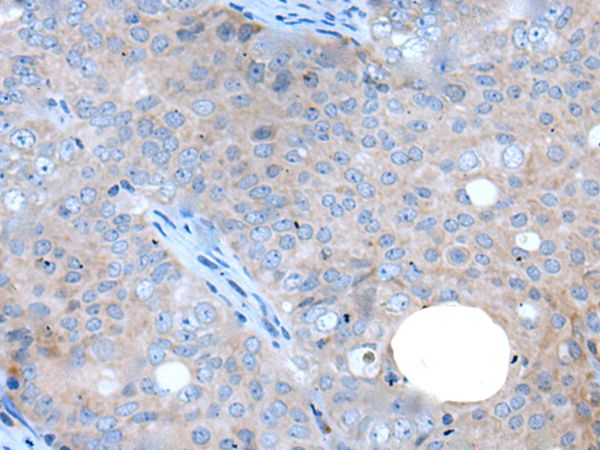
WAPL (wings apart-like), also known as WAPAL or FOE, is a 1,190 amino acid protein that contains one WAPL domain and is expressed as two alternatively spliced isoforms, one of which localizes to the nucleus. Expressed in an isoform-dependent manner in heart, skeletal muscle and uterine cervix tumor tissue, WAPL is involved in sister-chromatid adhesion and overall cell growth, specifically playing a role in the development and metastasis of cancerous tissue. The gene encoding WAPL maps to human chromosome 10, which houses over 1,200 genes and comprises nearly 4.5% of the human genome. Defects in some of the genes that map to chromosome 10 are associated with Charcot-Marie Tooth disease, Jackson-Weiss syndrome, Usher syndrome, nonsyndromatic deafness, Wolman¡¯s syndrome, Cowden syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 and porphyria.