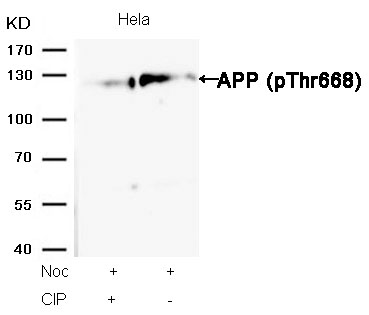
APP encodes a cell surface receptor and transmembrane precursor protein that is cleaved by secretases to form a number of peptides. Some of these peptides are secreted and can bind to the acetyltransferase complex APBB1/TIP60 to promote transcriptional activation, while others form the protein basis of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease. Mutations in this gene have been implicated in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease and cerebroarterial amyloidosis (cerebral amyloid angiopathy). Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene.
Hung, A.Y. and Selkoe, D.J. (1994) EMBO J. 13, 534-542.
Suzuki, T. et al. (1994) EMBO J. 13, 1114-1122
Ando, K. et al. (1999) J. Neurosci. 19, 4421-4427.
Iijima, K.I. et al. (2000) J. Neurochem. 75, 1085-1091