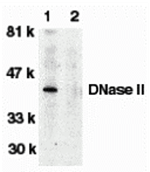
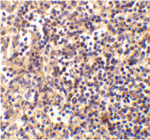
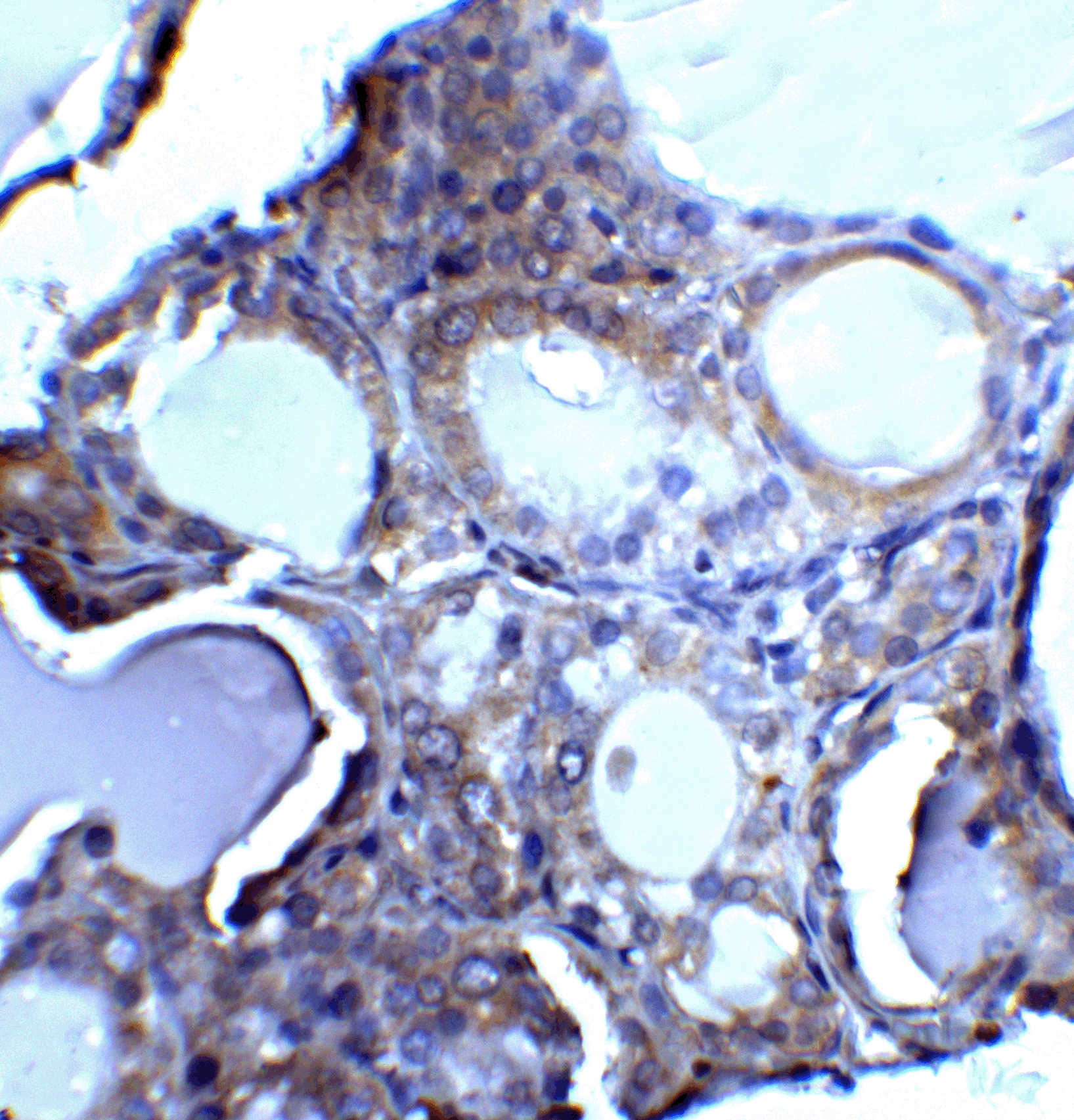
Apoptosis is characterized by several morphological nuclear changes including chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation. These changes are triggered by the activation of members of caspase family, caspase activated DNase, and several novel proteins including AIF and Acinus. DNase II causes both chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation. The genes encoding human, porcine, and murine DNase II have been cloned. The DNase II gene encodes a 40 kDa proenzyme. The mature enzyme consists of two non-identical subunits, the 32 kDa (alpha) and 12 kDa (beta) chains, generated by proteolytic processing. Overexpression of DNase II induces chromatin condensation. DNase II is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues.