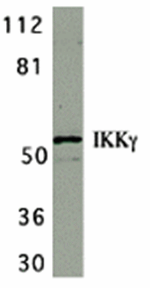
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a ubiquitous transcription factor and an essential mediator of gene expression during activation of immune and inflammatory responses. NF-κB mediates the expression of a great variety of genes in response to extracellular stimuli. NF-κB is associated with IκB proteins in the cell cytoplasm, which inhibit NF-κB activity. The IκB kinase (IKKα and IKKβ) phosphorylates IkB and mediates NF-κB activation. A novel molecule in the IKK complex was recently identified and termed IKKγ/NEMO/FIP3/IKKAP1. IKKγ interacts with IKKβ and is required for the activation of IKK complex and NF-κB by LPS, PMA, TNF, and IL-1 stimulation. FIP3 was also shown to bind to RIP and NIK and to mediate TNF-induced NF-κB activation.