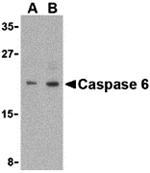
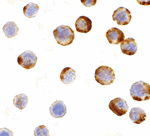
Caspases are a family of cysteine proteases that can be divided into the apoptotic and inflammatory caspase subfamilies. Unlike the apoptotic caspases, members of the inflammatory subfamily are generally not involved in cell death but are associated with the immune response to microbial pathogens. The apoptotic subfamily can be further divided into initiator caspases, which are activated in response to death signals, and executioner caspases, which are activated by the initiator caspases and are responsible for cleavage of cellular substrates that ultimately lead to cell death. Caspase-6 is an executioner caspase that was identified based on its homology with human caspases 2 and 3 as well as the C. elegans cell death protein CED-3. It possesses two isoforms, of which only the longer form possesses protease activity. Caspase-6 is highly expressed in adult brain and may play a role in several neuronal pathologies.