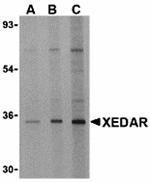
X-linked ectodysplasin-A2 receptor (XEDAR) is a recently isolated member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family that is highly expressed during embryonic development and binds to ectodysplatin-A2 (EDA-A2). Two predominantly expressed isoforms, XEDAR-s and XEDAR-L, differ by only a 21-amino region at the juxtamembrane region of the cytoplasmic domain. Neither isoform possesses a death domain and both have been shown to act mainly through TRAF3 and TRAF6 to activate the NF-κB and JNK pathways. Cells transfected with XEDAR and treated with EDA-A2 cause the assembly of a secondary complex containing FADD, caspase-8 and caspase-10, leading to the activation caspase-8 and caspase-3, and finally apoptosis. The EDA-A2-induced apoptosis is dependent on caspase-9 activation, as various pharmacological and genetic inhibitors of caspase-8 blocked apoptosis following EDA-A2 treatment.