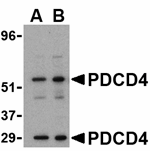
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, plays major roles in development and normal tissue turnover in addition to tumor formation. During this process, the expression patterns of numerous genes are radically altered. One such gene is the programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4), whose expression was found to be upregulated in all cell lines following the onset of apoptosis. PDCD4 encodes a tumor suppressor protein whose expression is lost in carcinomas of breast, colon, lung and prostate. It can bind to and inhibit the helicase activity of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A and inhibit the transactivation and transformation mediated by the transcription factor AP-1. The kinase Akt regulates PDCD4 by phosphorylation, decreasing the ability of PDCD4 to interfere with the transactivation of AP-1-responsive promoter by c-Jun. There are two known isoforms of PDCD4.