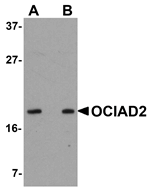
OCIAD2 was identified by its sequence similarity with OCIAD1, and together OCIAD1 and OCIAD2 form the OCIA domain family. OCIAD2 mRNA was found to be expressed at higher levels in invasive adenocarcinoma mixed subtype with bronchioloalveolar carcinoma component (BAC) of the lung. Loss of OCIAD2 expression was significantly correlated with lymphatic invasion, blood vessel invasion, and lymph node metastasis, indicating that OCIAD2 may play a role in cell adhesion and prevention of cell migration. While the function of OCIAD2 is still unknown, its expression in adenocarcinoma with BAC component is significantly associated with a favorable prognosis and may serve as a marker for selecting tumors that are treatable by limited surgery.