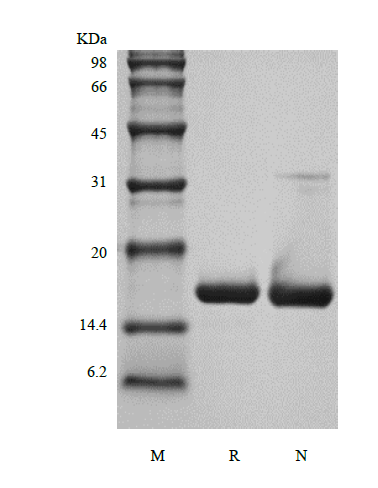
IL-1RA was initially called the IL-1 inhibitor which is encoded by the IL1RN gene and it is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. IL-1RA is secreted by various types of cells including immune cells, epithelial cells, and adipocytes. IL-RA has functions of inhibiting the activity of interleukin-1 by binding to receptor IL1R1 and preventing its association with the coreceptor IL1RAP for signaling. IL-1RA is also used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease in which IL-1 plays a key role. The murine IL-1RA is a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 152 amino acids and it has been shown to block the inflammatory responses induced by IL-1 both in vitro and in vivo. The protein shows 26 % amino acid homology to IL-1β and 19% homology to IL-1α. It also shares 90 % a.a. sequence identity with rat IL-1RA.