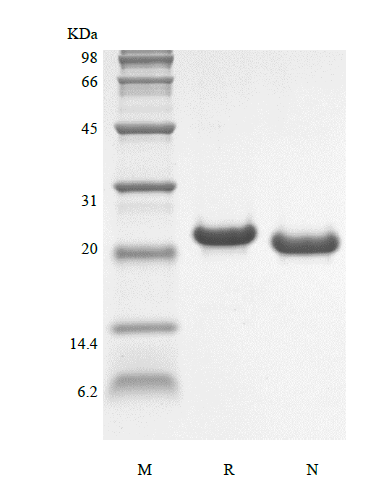
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) encoded by the IL-6 gene, acts as both a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine. It is secreted by T cells and macrophages to stimulate immune response. It plays an essential role in the final differentiation of B-cells into Ig-secreting cells involved in lymphocyte and monocyte differentiation. It also induces myeloma and plasmacytoma growth and induces nerve cells differentiation acts on B-cells, T-cells, hepatocytes, hematopoietic progenitor cells and cells of the CNS. The mouse IL-6 is a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 187 amino acids and it signals through a cell-surface type I cytokine receptor complex consisting of the ligand-binding IL-6Rα chain (CD126), and the signal- transducing component gp130 (also called CD130). The mouse IL-6 shares 40 % and 85 % a.a. sequence identity with human and rat IL-6 and it is equally active on human and rat cells.