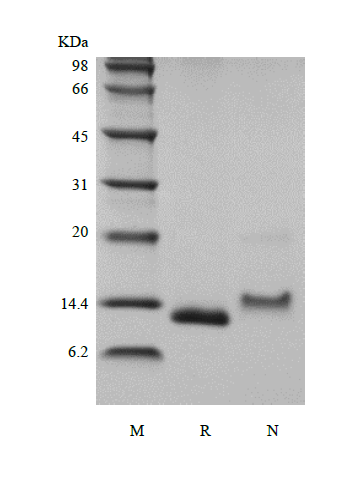
CCL2, also named monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and small inducible cytokine A2, is a small cytokine that belongs to the CC chemokine family. It is a monomeric polypeptide, with a molecular weight of approximately 13 kDa and it is anchored in the plasma membrane of endothelial cells by glycosaminoglycan side chains of proteoglycans. Research shows that CCR2 and CCR4 are two cell surface receptors that bind CCL2. CCL2 exhibits a chemotactic activity for monocytes and basophils. However, it does not attract neutrophils or eosinophils. CCL2 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases characterized by monocytic infiltrates, like psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis or atherosclerosis and it may be involved in the recruitment of monocytes into the arterial wall during the disease process of atherosclerosis. Mature human CCL2 shares 78-79 % a.a. identity with canine, porcine and equine CCL2, while mouse and rat express a form of CCL2 that is extended by 49 a.a. and shares only ~56 % a.a. identity within the common region.