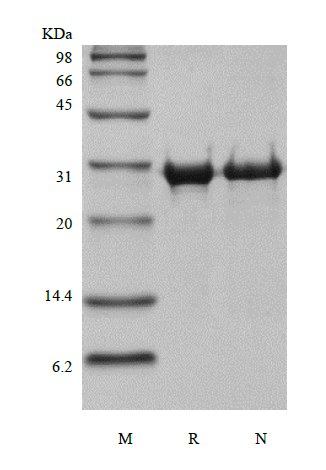
As the first member of membrane type (MT) MMPs, MMP-14, also known as MT1-MMP, plays an important role in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling by being able to degrade type I collagen, activate pro-MMP-2 and process cell adhesion molecules such as CD44 and integrin alpha V. MMP-14 is therefore a key enzyme in many physiological and pathological processes such as angiogenesis and tumor invasion. Structurally, MMP-14 consists of the following domains: a pro domain containing the furin cleavage site, a catalytic domain containing the zinc-binding site, a hinge region, a hemopexin-like domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplamasic tail. Recombinant Human MMP-14 consists of the pro and catalytic domains, which can be activated by treatment with furin as described in Activity Assay Protocol.