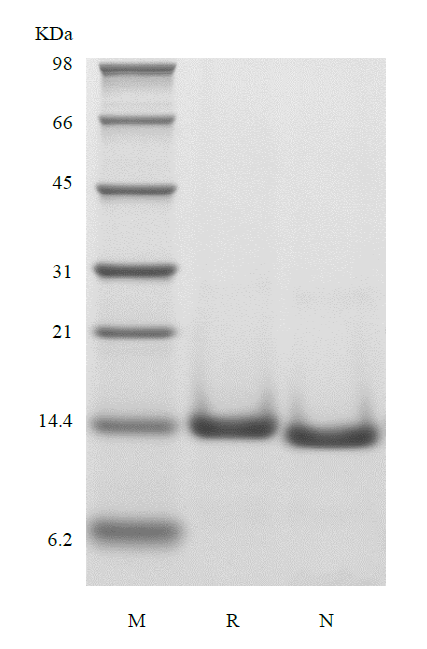
Cystatin C is a member of family 2 of the Cystatin superfamily. It is involved in processes such as tumor invasion and metastasis, inflammation and some neurological diseases. It inhibits many cysteine proteases such as papain and cathepsins B, H, K, L and S. It is ubiquitous in human tissues and body fluids. A point mutation in the gene coding for the 120 amino acid mature Cystatin C causes a hereditary form of amyloid angiopathy in which the protein variant (Leu68 to Gln) is deposited in the cerebral arteries, leading to fatal cerebral hemorrhage. Cystatin C may have additional clinical applications. For example, it is a good marker for glomerular filtration rate.