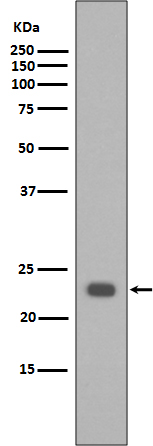
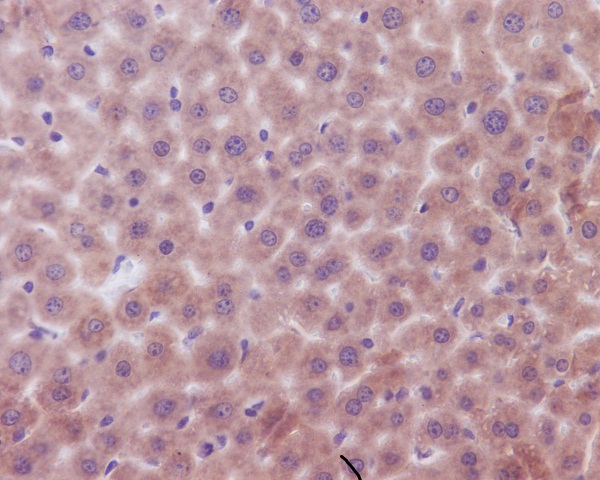
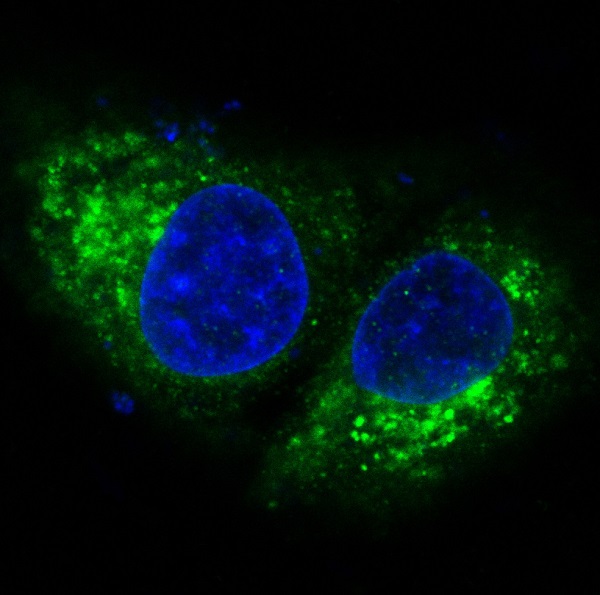
Bak is a proapoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. This protein is located on the outer membrane of mitochondria and is an essential component for transduction of apoptotic signals through the mitochondrial pathway. Upon apoptotic stimulation, an upstream stimulator like truncated BID (tBID) induces conformational changes in Bak to form oligomer channels in the mitochondrial membrane for cytochrome c release. The release of cytochrome c to the cytosol activates the caspase-9 pathway and eventually leads to cell death.