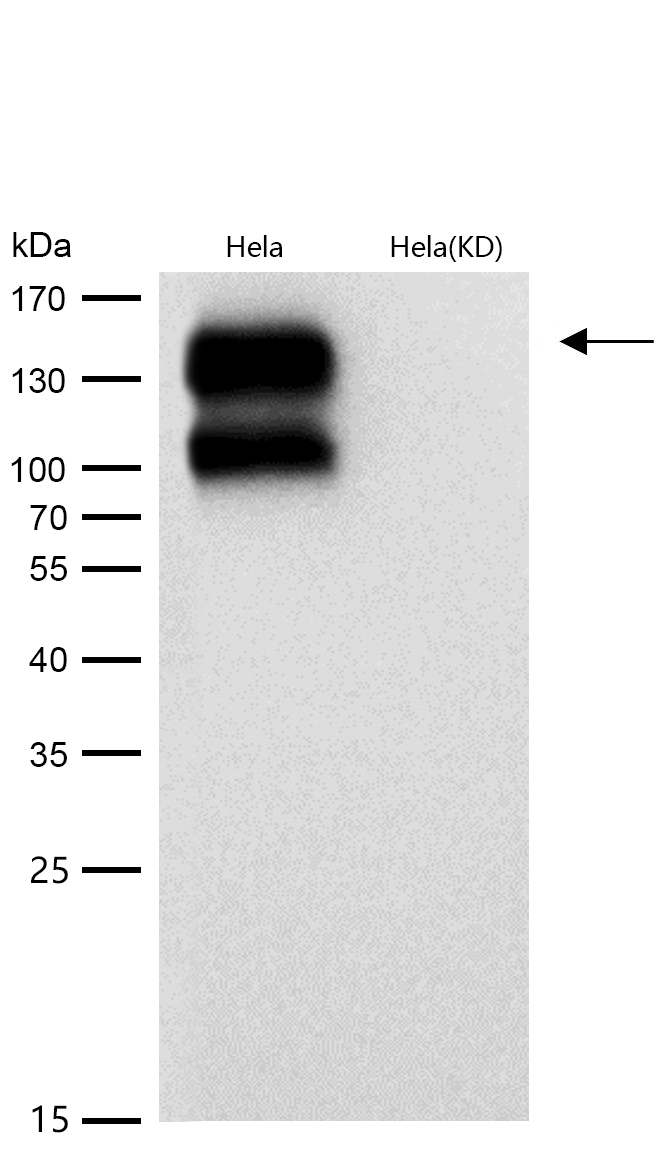
Integrins are heterodimeric proteins made up of alpha and beta subunits. At least 18 alpha and 8 beta subunits have been described in mammals. Integrin family members are membrane receptors involved in cell adhesion and recognition in a variety of processes including embryogenesis, hemostasis, tissue repair, immune response and metatastatic diffusion of tumor cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a beta subunit. Six alternatively spliced variants have been found for this gene which encode five proteins with alternate carboxy termini.