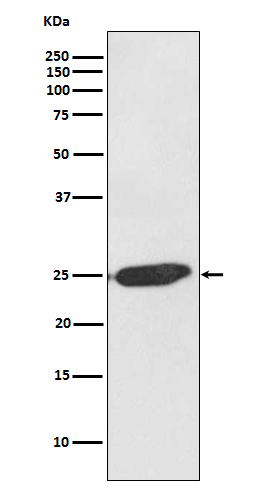
SNAP25 forms a core complex with the SNARE proteins syntaxin and synaptobrevin to mediate synaptic vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane during Ca2+-dependent exocytosis. This complex is responsible for exocytosis of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Neurotransmitter release is inhibited by proteolysis of SNAP25 by botulinum toxins A and E. SNAP25 plays a secondary role as a Q-SNARE involved in endosome fusion; the protein is associated with genetic susceptibility to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).